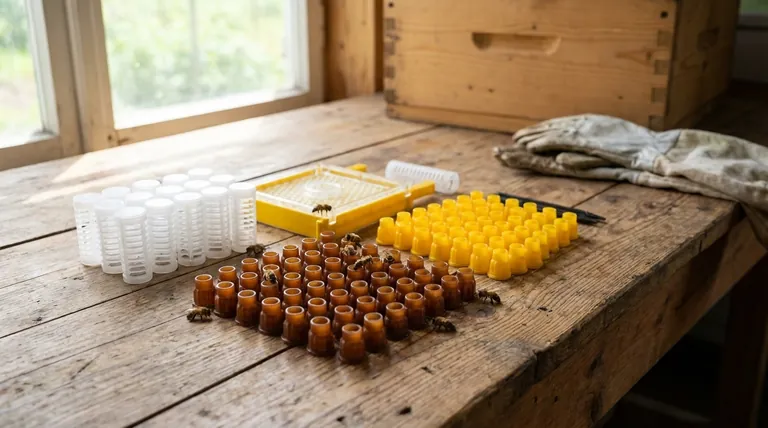
A specific set of core genetic pathways were found to differ between QE-queens and other queen types. These include the mTOR, MAPK, Wnt, Notch, Hedgehog, FoxO, and Hippo signalling pathways, all of which are deeply involved in regulating the fundamental biological processes that define a queen.
The key takeaway is not just the names of these pathways, but what they represent collectively: they are the master controls for growth, development, reproduction, and longevity that are uniquely tuned to create and sustain the honeybee queen phenotype.
The Genetic Blueprint of a Queen
Understanding these genetic differences provides a window into how a single genome can produce such dramatically different outcomes as a short-lived worker or a long-lived, highly reproductive queen. These pathways don't operate in isolation; they form an interconnected network that directs the bee's biological destiny.
Pathways for Growth and Metabolism
These pathways respond to nutritional cues and control the queen's larger size and immense reproductive capacity.
The mTOR Pathway
The mTOR (mechanistic Target of Rapamycin) pathway is a central regulator of cell growth and metabolism. It acts as a nutrient sensor; when activated by ample food (like royal jelly), it promotes protein synthesis and cell proliferation, driving the rapid growth required to become a queen.
The FoxO Pathway
The FoxO (Forkhead box O) pathway is often seen as a counterbalance to mTOR. It plays a critical role in stress resistance, metabolism, and longevity. Differences in this pathway are linked to the queen's significantly longer lifespan compared to worker bees.
Pathways for Development and Differentiation
These are ancient, highly conserved pathways that determine the fate of cells during an organism's development. They are crucial for establishing the queen's unique anatomy during the larval stage.
The Wnt Pathway
The Wnt signalling pathway is fundamental for body plan development. In bees, it is essential for processes like ovary development, which is dramatically larger and more active in queens.
The Notch and Hedgehog Pathways
Both Notch and Hedgehog are critical for cell-to-cell communication that dictates cell fate. Variations in these pathways help ensure that larval cells differentiate into queen-specific tissues and organs rather than those of a worker.
Pathways for Stress and Longevity
These pathways manage cellular homeostasis and response to stress, directly contributing to the queen's robust health and long life.
The MAPK Pathway
The MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) pathway is a chain of proteins that communicates signals from the cell surface to the DNA in the nucleus. It is involved in managing cellular responses to stress, and its distinct regulation in queens contributes to their enhanced longevity.
The Hippo Pathway
The Hippo pathway is a key regulator of organ size, controlling both cell proliferation and programmed cell death. Its differential activity is vital for developing and maintaining the queen's large, specialized reproductive organs.
Understanding the Interconnected System
It is a common mistake to view each of these pathways as an independent switch. The reality is that they are deeply intertwined, and a change in one has cascading effects on the others.
The Growth vs. Longevity Trade-off
The mTOR and FoxO pathways provide a classic example of this interconnectedness. High mTOR activity is necessary for the rapid growth and high reproductive output of a queen, but it is often associated with a shorter lifespan in other organisms.
In queens, this system appears uniquely balanced. The molecular machinery, including FoxO and other pathways, has been tuned to manage the stresses of high metabolic output, allowing for both massive reproduction and exceptional longevity—a biological feat that is still being explored.
What These Pathways Reveal About Queen Biology
Analyzing these genetic differences allows researchers to pinpoint the core mechanisms behind the honeybee caste system.
- If your primary focus is caste differentiation: The key takeaway is that developmental pathways like Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog are the master architects that build a queen during the larval stage.
- If your primary focus is reproduction: The key takeaway is that the nutrient-sensing mTOR pathway is the engine driving the queen's unparalleled reproductive output.
- If your primary focus is longevity: The key takeaway is that pathways like FoxO and MAPK provide the cellular resilience that allows a queen to live years, not weeks.
Ultimately, these genetic pathways are the software that runs on the hardware of the bee genome, executing the precise program that makes a queen a queen.
Summary Table:
| Pathway | Primary Function in Queen Biology |
|---|---|
| mTOR | Drives rapid growth & high reproductive output (nutrient sensor) |
| FoxO | Promotes stress resistance & exceptional longevity |
| Wnt, Notch, Hedgehog | Directs queen-specific development & anatomy (e.g., ovary size) |
| MAPK, Hippo | Manages cellular stress & regulates organ size |
Equip Your Apiary with Knowledge-Driven Solutions
Understanding the complex genetics behind queen vitality is the first step. The next is ensuring your beekeeping operation has the robust supplies and equipment to support healthy, productive colonies.
HONESTBEE specializes in providing commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-quality, wholesale-focused supplies. From hive components to protective gear, our products are designed to help you manage thriving colonies, just as these genetic pathways manage a queen's biology.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how HONESTBEE can be a reliable partner in your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Jenter Queen Rearing Kit Complete Set for Bee Breeding
- No Grafting Queen Rearing Kit: System for Royal Jelly Production and Queen Rearing
- Nicot Queen Rearing Kit for Beekeeping and Grafting in Nicot System
- Retractable Chinese Queen Rearing Grafting Tools Equipment
- Plastic Chinese Queen Grafting Tool for Bee Queen Rearing
People Also Ask
- What is essential for successful queen rearing in beekeeping? Master Genetics & Boost Your Apiary's Health
- How does regular queen replacement enhance honey production? Master High-Yield Beekeeping with Professional Equipment
- Why is a high-precision BOD Incubator utilized during the queen bee emergence stage? Ensure Superior Queen Quality
- How do high-precision temperature-controlled incubation units assist in the breeding of queen bees? Master Bee Genetics
- Why is strict biological safety management required for imported queen bees? Protect Your Ecosystem and Crop Yields
- Why is it necessary to provide a composite nutrient mixture to queen rearing starter colonies? Boost Larval Acceptance
- How is the original colony configured after the cell starter has been set up on Day 0? Master Your Queen Rearing Hive
- Why is the application of natural beeswax necessary before deploying plastic queen rearing equipment? Expert Tips



















