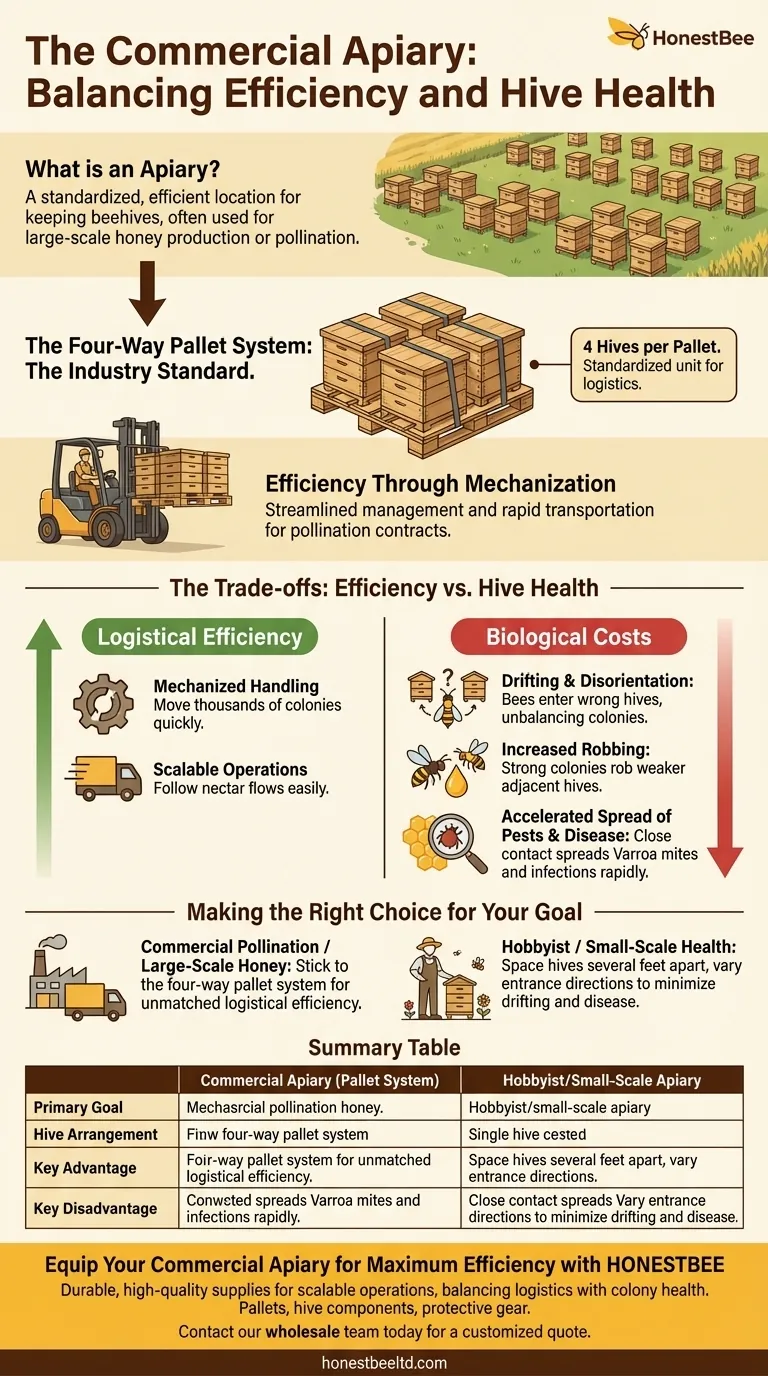
At its core, an apiary is simply any location where beehives are kept. In commercial beekeeping, however, an apiary is a highly standardized and efficient operation. Hives are typically arranged in groups of four on a single wooden pallet, a system designed to streamline management and transportation.
The standard arrangement in commercial apiaries—four hives grouped on a pallet—is a masterclass in logistical efficiency. However, this optimization for transport and labor introduces significant trade-offs for colony health, particularly concerning disease spread and bee disorientation.

The Logic of Commercial Apiary Design
The layout of a commercial apiary is driven by economics and logistics, not by the ideal preferences of honey bees. This distinction is key to understanding why they are set up the way they are.
What Defines a Commercial Apiary?
While any collection of hives is an apiary, a commercial operation is defined by its scale. These apiaries often contain 32 or more hives and are managed for large-scale honey production or, more commonly, for pollination services.
The Four-Way Pallet System
The fundamental unit of a modern commercial apiary is the four-way pallet. Four individual bee colonies are strapped onto a specially designed wooden pallet.
This grouping is not arbitrary. It creates a single, standardized block that is the basis for all further logistics. The entire apiary is an array of these four-hive units.
Efficiency Through Mechanization
The pallet system exists to serve one machine: the specialized forklift. This equipment allows a single operator to lift and move four hives at once.
This level of mechanization is what makes modern commercial beekeeping possible. It allows beekeepers to rapidly move thousands of colonies to follow nectar flows or fulfill pollination contracts for crops like almonds, apples, and blueberries.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Efficiency vs. Hive Health
While logistically brilliant, placing hives in such close proximity creates challenges for the bees. The efficiency gained by the beekeeper comes at a biological cost to the colonies.
The Problem of "Drifting"
Foraging bees can become disoriented when returning to a dense block of identical-looking hives. Drifting occurs when a bee accidentally enters the wrong hive.
This unbalances the apiary. Weaker colonies lose foragers and resources to stronger, adjacent colonies, causing the weak to get weaker and the strong to get stronger. Beekeepers may try to mitigate this by having the hive entrances on a single pallet face in different directions.
Increased Risk of Robbing
Close quarters make it easier for bees from strong colonies to rob honey from weaker, nearby hives. A weak colony can be quickly overwhelmed and destroyed by robber bees from a hive just inches away.
Accelerated Spread of Pests and Disease
This is the most significant downside. Pests like the Varroa mite, and the diseases they transmit, can spread rapidly between colonies that are in direct contact.
An infected hive on a pallet can easily infest its three neighbors, creating a "hotspot" that compromises the health of the entire unit. A more distanced placement, while less efficient, provides a crucial buffer against this rapid transmission.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal apiary layout depends entirely on your objectives, balancing logistical needs against ideal bee biology.
- If your primary focus is commercial pollination or large-scale honey production: The four-way pallet system is the industry standard for a reason; its logistical efficiency is unmatched for managing hives at scale.
- If your primary focus is hobby beekeeping or maximizing the health of a few colonies: Avoid the dense pallet model. Give each hive several feet of space and use varied entrance orientations to minimize drifting and disease transfer.
- If you are a landowner hosting hives for pollination: Understand that commercial beekeepers using palletized systems are prioritizing mobility and will require forklift access to the apiary site.
Ultimately, understanding the apiary layout is understanding the fundamental compromise between the needs of the beekeeper and the natural biology of the bees.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Commercial Apiary (Pallet System) | Hobbyist/Small-Scale Apiary |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Large-scale honey production, pollination services | Colony health, honey for personal use |
| Hive Arrangement | Groups of 4 hives on a single pallet | Hives spaced several feet apart |
| Key Advantage | High efficiency for transport and management (mechanized) | Reduced disease spread and less bee disorientation |
| Key Disadvantage | Increased risk of disease/pest transmission and bee drifting | Logistically challenging for large numbers of hives |
Equip Your Commercial Apiary for Maximum Efficiency with HONESTBEE
As a commercial beekeeper or distributor, your success hinges on the reliability and efficiency of your equipment. The four-hive pallet system is the backbone of a scalable operation, and using the right supplies is critical for managing its unique challenges.
HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment—including pallets, hive components, and protective gear—designed specifically for the demands of commercial apiaries and wholesale distributors. We help you build resilient operations that balance logistical needs with colony health.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your apiary equipment needs and receive a customized quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Versatile Ratchet Hive Strap with S-Hooks for Secure Fastening
- Heavy Duty Ratchet Hive Strap
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of a stainless steel hive tool? Essential Equipment for Professional Beekeeping
- How should beekeepers handle bees when using a hive tool? Master Calm, Deliberate Techniques
- What are the specific applications of a beekeeping chisel? Master Hive Maintenance with Precision Tools
- Why is it important to compare the progress of different hives? A Beekeeper's Key Diagnostic Tool
- Which technical challenges in hive maintenance are addressed by using a professional stainless steel hive tool?



















