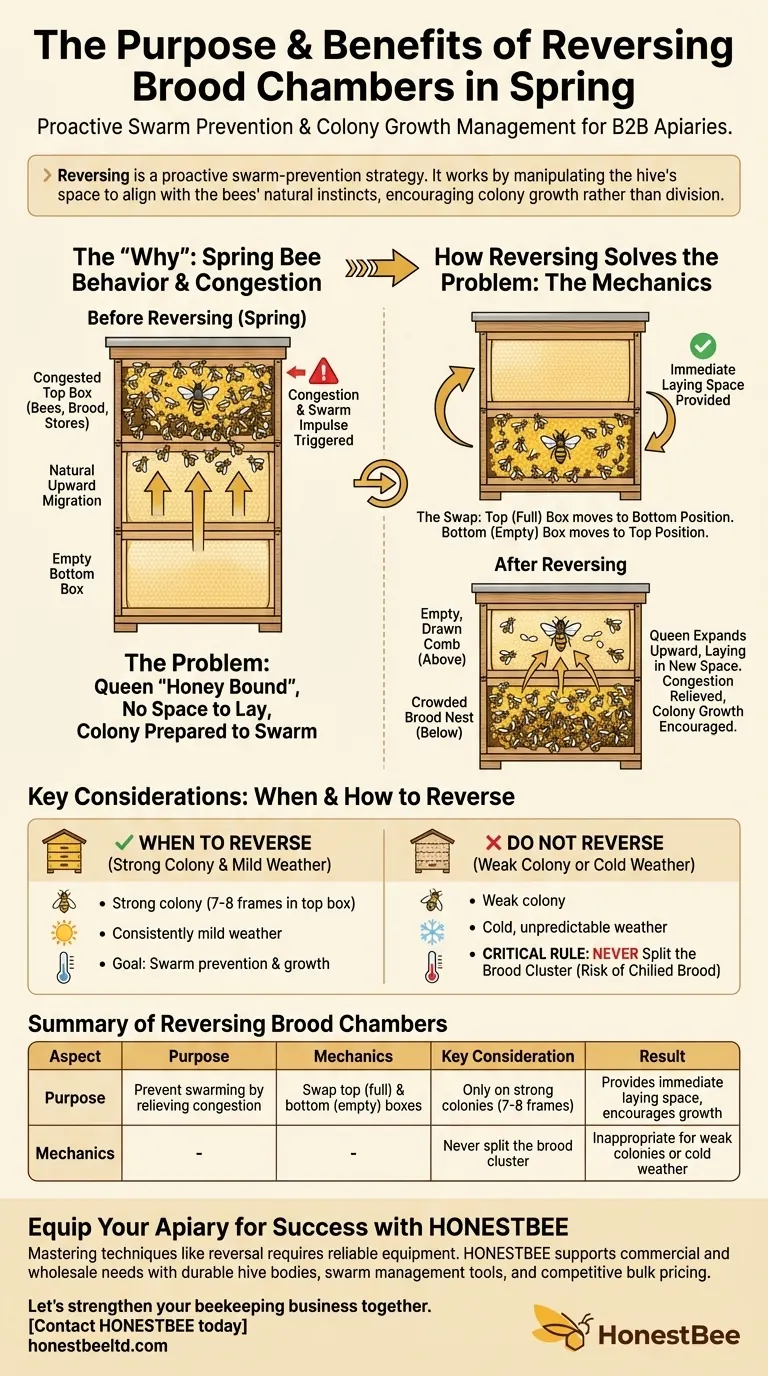
The primary purpose of reversing brood chambers is to manage a honeybee colony's natural upward expansion in the spring. This technique creates vital space for the queen to lay eggs, which reduces congestion in the brood nest and helps prevent the colony from deciding to swarm.
Reversing is a proactive swarm-prevention strategy. It works by manipulating the hive's space to align with the bees' natural instincts, encouraging colony growth rather than division.

The "Why" Behind Reversing: Spring Bee Behavior
To understand why reversing works, you must first understand how a honeybee colony behaves as winter turns to spring.
The Natural Upward Migration
Throughout the winter, the bee cluster consumes its honey stores, slowly moving upward through the hive. By spring, the colony and the queen are naturally concentrated in the top brood chamber, which is now full of bees, brood, and remaining food stores.
The Congestion Problem
The queen needs empty cells to lay her eggs and expand the colony's population for the upcoming nectar flow. If the top box is congested with honey, pollen, and existing brood, she may become "honey bound," with nowhere to lay. The bottom box, which the bees have vacated, often has ample empty comb.
The Swarm Impulse
Congestion is the primary trigger for swarming. When the queen has no room to lay and the hive is packed with bees, the colony's instinct is to divide by raising a new queen and having the old queen leave with half the bees.
How Reversing Solves the Problem
Reversing is a simple mechanical swap that directly addresses the congestion that leads to swarming.
The Mechanics of the Swap
The beekeeper simply swaps the position of the two brood chambers. The top box, which is full of bees and brood, is moved to the bottom position. The bottom box, which is mostly empty, is moved to the top position.
Providing Immediate Laying Space
This action places the crowded brood nest directly below a box of empty, drawn-out comb. Since bees naturally want to expand upward, the queen will readily move into the new top box to continue laying, immediately relieving the congestion.
Encouraging a Stronger Colony
By giving the colony a clear path for expansion, reversing encourages the bees to build a larger, more populous workforce. This results in a stronger colony that is better prepared to gather a surplus of nectar once the main flow begins.
Key Considerations and When Not to Reverse
Reversing is a powerful tool, but applying it at the wrong time or to the wrong colony can be detrimental.
The Critical Rule: Don't Split the Brood
The single most important rule is to never split the cluster of brood. If you place a box of empty comb between two frames of brood in cool spring weather, the bees may not be able to keep both areas warm. This can lead to chilled and dead larvae.
When Reversing is Appropriate
You should only reverse a hive when the colony is strong. The bees should occupy at least seven or eight frames in the top box, and the weather should be consistently mild enough for them to easily expand and keep the entire brood nest warm.
The Difference from a Queen Excluder
While reversing can help contain the queen's laying activity, its primary purpose is different from that of a queen excluder. Reversing manages brood nest space to prevent swarming. A queen excluder is a physical barrier placed above the brood chambers specifically to keep the queen from laying eggs in the honey supers.
Applying This to Your Hive Management
Your decision to reverse should be based on a direct inspection of your colony's strength and condition.
- If your primary focus is swarm prevention in a strong hive: Reversing is one of the most effective actions you can take once the top brood box becomes crowded in early spring.
- If your colony is weak or the weather is still cold and unpredictable: Do not reverse. You risk harming the brood and setting back the colony's development.
- If your goal is simply to produce clean honey: Use a queen excluder above your well-managed brood boxes when you add your honey supers.
Proactively managing your hive's space is the key to guiding its natural instincts toward growth and productivity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Purpose of Reversing | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prevent swarming by relieving congestion in the brood nest. | Only perform on strong colonies occupying 7-8 frames in the top box. |
| Mechanics | Swap the top (full) and bottom (empty) brood boxes. | Never split the brood cluster; ensure consistent, mild weather. |
| Result | Provides immediate laying space for the queen, encouraging upward expansion. | Inappropriate for weak colonies or during cold, unpredictable weather. |
Equip Your Apiary for Success with HONESTBEE
Mastering techniques like brood chamber reversal is key to maintaining healthy, productive colonies. As a commercial beekeeper or equipment distributor, having reliable, high-quality supplies is just as critical to your operation's success.
HONESTBEE supports your commercial and wholesale needs by providing:
- Durable Brood Chambers & Hive Bodies: Built to withstand seasonal manipulations and promote optimal colony growth.
- Essential Swarm Management Tools: From frames to foundations, get the equipment you need to implement best practices.
- Wholesale-Focused Operations: Competitive pricing and bulk quantities tailored for commercial apiaries and distributors.
Let's strengthen your beekeeping business together.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale supply requirements and how our products can contribute to your hive management success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Australian Langstroth Beehive Boxes for Beekeeping Wholesales
- Langstroth Honey Bee Box Hive Boxes for Different Depths
- Langstroth Bee Hives Bee Keeping Box for Beginners Beekeeping
- Portable Bee Mating Hive Boxes Mini Mating Nucs 8 Frames for Queen Rearing
- Professional Insulated Plastic Bee Hives
People Also Ask
- What are the sizes of supers available in a standard hive? A Guide to Deep, Medium, and Shallow Boxes
- What are beehive boxes, and what are they used for? The Essential Guide to Hive Components
- What are the three types of beehives? Find the Perfect Hive for Your Beekeeping Philosophy
- How does the frame capacity of a Langstroth box affect hive management? Optimize for Weight and Efficiency
- What options exist for the number of frames in a Langstroth hive box? Choosing the Right Hive Width for Efficiency



















