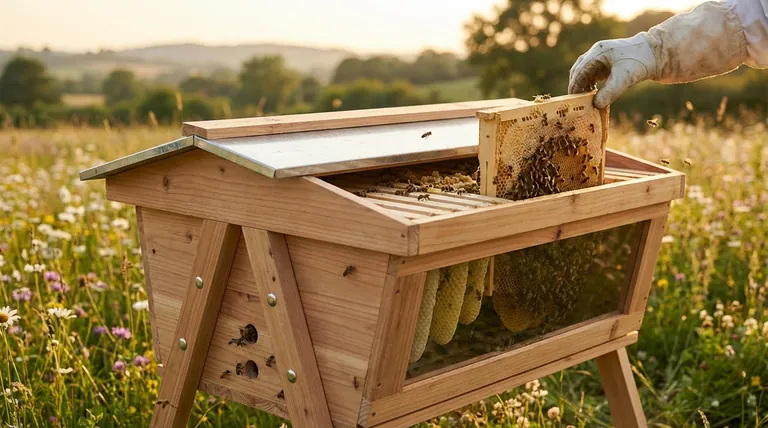
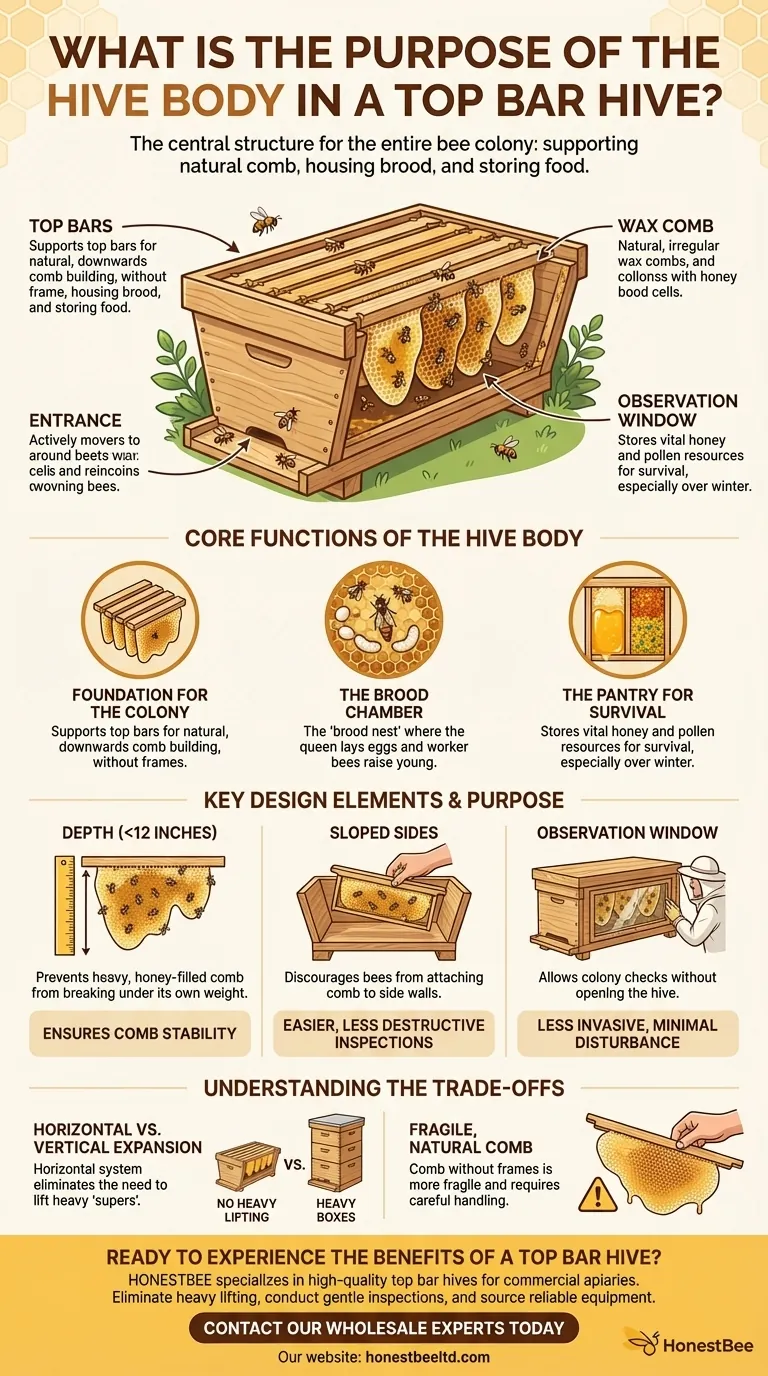
At its core, the hive body of a top bar hive is the central structure that houses the entire bee colony. It serves as the primary enclosure, supports the top bars from which bees build their comb, and functions as the brood chamber where the queen lays her eggs.
The purpose of the hive body goes beyond simple containment. Its specific design, from its depth to its sloped sides, is engineered to facilitate natural bee behavior while making hive management simpler and less physically demanding for the beekeeper.

The Core Functions of the Hive Body
The hive body is the heart of the top bar hive, serving several critical roles simultaneously. It is the colony's nursery, pantry, and fortress all in one.
A Foundation for the Colony
The most fundamental purpose of the hive body is to provide a structure that supports the top bars. Bees hang from these bars and construct their comb naturally downwards, without the use of pre-made frames or foundations.
The Brood Chamber
This structure is the living quarters for the colony, often called the brood nest or brood box. It is where the queen bee lays her eggs and where worker bees raise the young bees (the brood).
The Pantry for Survival
The hive body also acts as the primary storage area for the colony's food. The bees store pollen and honey in the comb, which are vital resources for their survival, especially through the winter.
Key Design Elements and Their Purpose
The specific dimensions and features of a top bar hive body are not arbitrary. Each element is designed with the bees' natural tendencies and the beekeeper's ease of management in mind.
The Importance of Depth
The depth of the hive body is typically 12 inches or less. This is a critical design feature to prevent the comb, when heavy with honey, from breaking off the top bar under its own weight.
The Logic of Sloped Sides
Most top bar hives feature sloped sides. This simple design element discourages bees from attaching their comb to the side walls of the hive, making it much easier for the beekeeper to lift and inspect a single comb without breaking it.
The Role of the Observation Window
Many designs include a full-length observation window. This allows the beekeeper to check on the colony’s size, health, and progress without opening the hive, leading to less invasive inspections and less disturbance for the bees.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The design of the top bar hive body offers distinct advantages, but it's important to understand the associated trade-offs compared to other hive styles like the common Langstroth hive.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Expansion
The top bar hive is a horizontal system. Unlike a Langstroth hive, you do not add more boxes (or "supers") vertically. The main benefit is that it completely eliminates the need for heavy lifting.
Fragile, Natural Comb
Because bees build their own comb without the support of frames, the comb is more fragile. The hive body's design helps protect it, but the beekeeper must handle each bar with deliberate care during inspections.
Potential for Side Attachment
While the sloped sides greatly reduce the issue, bees may still occasionally attach comb to the hive body walls. This requires careful management to separate the comb without damaging it during an inspection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the purpose of the hive body helps you determine if a top bar hive aligns with your beekeeping philosophy.
- If your primary focus is minimal heavy lifting: The single, horizontal hive body is ideal, as management and honey harvesting never require lifting boxes that can weigh 50 pounds or more.
- If your primary focus is less-invasive management: The ability to inspect one bar at a time, combined with an observation window, makes the top bar hive body perfectly suited for gentle beekeeping.
- If your primary focus is natural beekeeping: The hive body is designed to allow bees to build their own comb according to their natural instincts, a core principle of this approach.
Ultimately, the top bar hive body is designed as a complete, self-contained environment that respects the natural biology of the honeybee.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation for Colony | Supports top bars for natural comb building | Encourages natural bee behavior |
| Brood Chamber | Houses the queen and raises young bees | Centralized nursery for the colony |
| Food Pantry | Stores honey and pollen for survival | Essential resource for overwintering |
| Design Feature | Purpose | Key Benefit |
| Shallow Depth (<12") | Prevents heavy comb from breaking | Ensures comb stability |
| Sloped Sides | Discourages comb attachment to walls | Easier, less destructive inspections |
| Observation Window | Allows hive checks without opening | Minimal disturbance to the bees |
Ready to experience the benefits of a top bar hive for yourself?
At HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying high-quality, durable top bar hives and beekeeping equipment designed for commercial apiaries and distributors. Our hives are built to support natural beekeeping practices while maximizing efficiency and minimizing physical strain.
We help you:
- Eliminate heavy lifting with our expertly crafted horizontal hive systems.
- Conduct gentle, efficient inspections with hive bodies featuring optimal sloped sides and depth.
- Source reliable equipment for a sustainable and productive beekeeping operation.
Let's discuss your apiary's needs. Contact our wholesale experts today to get a quote and learn more about our product range!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Top Bar Beehive for Beekeeping Wholesales Kenya Top Bar Hive
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a top bar hive? Simpler, Bee-Centric Beekeeping for All
- What are the most popular types of hives besides the Langstroth? Top Bar & Horizontal Hives Explained
- What is a horizontal top bar hive? Discover Natural and Ergonomic Beekeeping Benefits
- How does the top bar hive help control varroa mites? A Natural Approach to Mite Management
- What are the specific environmental challenges of using a horizontal Top Bar hive in cold climates? Survival Strategies



















