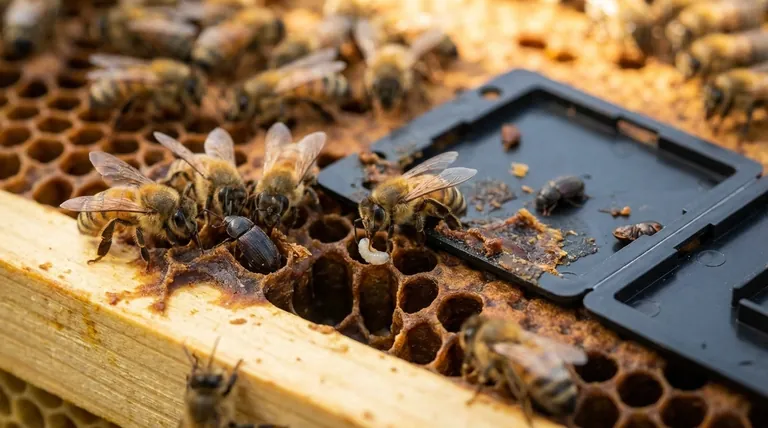
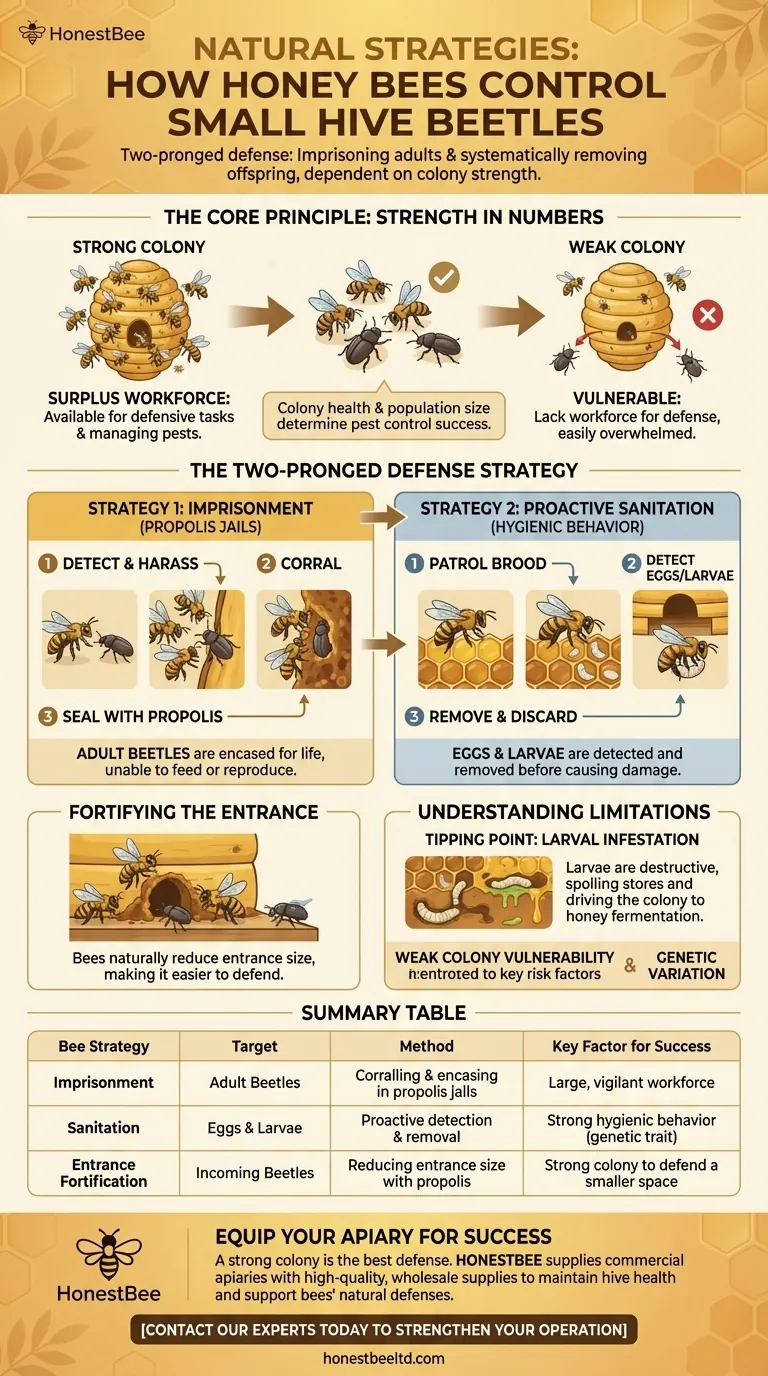
At their core, honey bees rely on two primary natural strategies to manage small hive beetles: physically imprisoning the adult beetles and systematically removing their offspring. A large, vigilant workforce corrals adult beetles into "jails" constructed from propolis, while other bees patrol the hive to locate and discard beetle eggs and larvae before they can cause damage.
A honey bee colony's defense against small hive beetles is not about direct confrontation, but about containment and sanitation. The success of these natural strategies is almost entirely dependent on the strength and population size of the colony itself.

The Core Principle: Strength in Numbers
A hive's ability to control pests is a direct reflection of its health and population. For small hive beetles, this principle is the most critical factor determining whether the bees or the beetles will win.
Why a Strong Colony is the Best Defense
A populous colony has a surplus of bees not dedicated to foraging or brood care. This available workforce can be allocated to defensive tasks, such as guarding the entrance, patrolling the comb, and dealing with invaders. A strong colony simply outnumbers the beetles, managing them before they can establish a reproductive foothold.
The Beetle's Advantage
Adult small hive beetles are difficult for bees to kill. Their hard, smooth shell makes them resistant to stings, and their small size allows them to scurry into crevices to hide. Because direct combat is ineffective, bees have evolved behavioral strategies focused on containment rather than extermination.
The Bees' Two-Pronged Defense Strategy
Facing an intruder they cannot easily kill, honey bees have developed a sophisticated, two-part system to neutralize the threat posed by small hive beetles.
Strategy 1: Imprisonment and Containment
The most well-known bee defense is the creation of "propolis jails." When guard bees encounter an adult beetle, they will harass and corral it into a corner or crevice within the hive. Other bees then encase the beetle behind a wall of propolis, a sticky resin collected from plants. These beetles are effectively imprisoned for life, unable to feed or lay eggs.
Strategy 2: Proactive Sanitation (Hygienic Behavior)
While some adults are jailed, the real danger comes from beetle larvae. Bees with strong hygienic traits constantly patrol the brood nest and honey stores. They use their sense of smell to detect and remove beetle eggs and newly hatched larvae, disposing of them outside the hive. This proactive cleaning prevents a larval infestation from ever taking hold.
Fortifying the Entrance
Bees naturally reduce the size of their hive entrance using propolis. A smaller, more defensible entrance limits the number of beetles that can enter the hive undetected and makes it easier for guard bees to manage incoming traffic.
Understanding the Limitations
While effective, these natural defenses can be overwhelmed. A beekeeper must understand the tipping point where the beetle population outpaces the bees' ability to control them.
The Tipping Point: Larval Infestation
If a beetle manages to lay eggs that go undetected, the resulting larvae are catastrophically destructive. They tunnel through comb, consuming pollen, honey, and bee brood. As they feed, they leave behind a slime that causes the remaining honey to ferment and foul, creating an odor that can drive the entire bee colony to abscond.
The Weak Colony's Vulnerability
A small, stressed, or queenless colony lacks the necessary workforce to perform these defensive behaviors effectively. There are not enough bees to patrol the comb, build propolis jails, or guard the entrance. In these hives, even a small number of beetles can quickly lead to a full-blown, hive-destroying infestation.
Genetic Variation
Not all honey bee colonies are created equal. The instinct and efficiency of hygienic behavior is a genetic trait that varies significantly between different bee stocks. Some colonies are naturally more aggressive and meticulous in removing pests, while others are more passive.
Supporting Your Bees' Natural Defenses
As a beekeeper, your role is not to replace the bees' defenses, but to create an environment where their natural strategies can succeed.
- If your primary focus is proactive prevention: Maintain a strong, populous colony with a productive queen, as this provides the workforce needed to manage pests.
- If you are managing a weaker or new colony: Reduce the hive's internal space and entrance size to match the population, making their defensive job more manageable.
- If you are selecting new bees: Choose bee stocks known for strong hygienic behavior, as this provides a genetic advantage against beetles and other pests.
By understanding and reinforcing their innate behaviors, you empower your bees to successfully defend their own home.
Summary Table:
| Bee Strategy | Target | Method | Key Factor for Success |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imprisonment | Adult Beetles | Corralling and encasing in propolis jails | Large, vigilant workforce |
| Sanitation | Beetle Eggs & Larvae | Proactive detection and removal from the hive | Strong hygienic behavior (genetic trait) |
| Entrance Fortification | Incoming Beetles | Reducing entrance size with propolis | Strong colony to defend a smaller space |
Equip your apiary with the right tools for success. A strong colony is the best defense against small hive beetles. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, wholesale-focused supplies needed to maintain hive health and support your bees' natural pest management strategies. Contact our experts today to discuss your needs and strengthen your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
- Reusable Clear Small Hive Beetle Traps for Beehives Beetle Trapping Tools
- Durable Galvanized Steel Frame Grip
- Professional Bamboo Queen Isolation Cage
- Professional Insulated Winter Hive Wrap for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Why are grid bottom boards with sticky inserts better for hive parasite levels? Precision and Data Integrity Explained
- What is the primary purpose of removing mouse guards from beehives during the spring? Optimize Your Hive's Spring Growth
- What is the function of the wooden wire mesh trap in monitoring Oriental hornet populations? Expert Insights
- How does the regular cleaning of beehives contribute to pest prevention? Elevate Apiary Hygiene & Colony Health
- Why are high-frequency disease detection kits essential? Protect Your Apiary with Advanced Biosecurity
- What is the function of plastic jars containing soapy water and old honeycomb fragments within a wax moth trap structure?
- What protective functions do hanging wires and ropes serve? Safeguard Your Beehives from Pests and Predators
- How can I keep ants out of my honey? A Simple, Permanent Solution



















