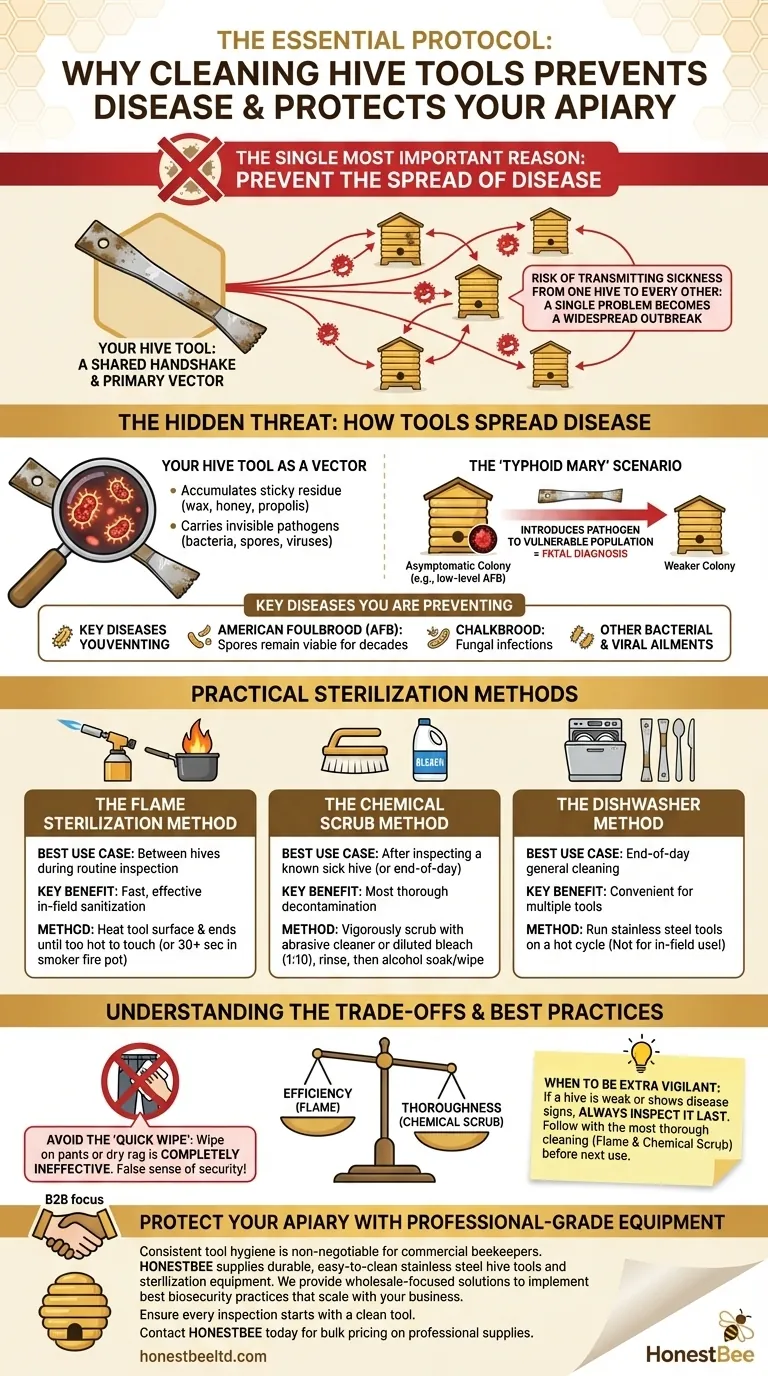
The single most important reason to clean your hive tool between inspecting different hives is to prevent the spread of disease. Your hive tool is the primary vehicle for transferring microscopic pathogens—like bacterial spores, viruses, and fungal agents—from one colony to another. Just as a surgeon sterilizes instruments between patients, a beekeeper must sanitize their tools to protect the health of each individual hive.
Think of your apiary as a neighborhood and your hive tool as a shared handshake. Without proper hygiene, you risk transmitting a sickness from one house to every other house you visit, potentially causing a widespread outbreak from a single, isolated problem.

The Hidden Threat: How Your Tools Spread Disease
A hive tool that appears clean to the naked eye can be covered in invisible pathogens. Understanding how this happens is the first step toward effective apiary biosecurity.
Your Hive Tool as a Vector
As you pry frames, scrape burr comb, and remove propolis, your hive tool accumulates a sticky residue of wax, honey, and propolis. These substances are perfect carriers for bacteria and spores.
A pathogen present in one hive—even a strong hive that shows no outward signs of sickness—can easily adhere to your tool.
The "Typhoid Mary" Scenario
The greatest risk comes from asymptomatic colonies. A hive may be infected with a low level of a pathogen like American Foulbrood (AFB) spores but have a strong enough population to keep it in check.
When you use your uncleaned tool from this seemingly healthy hive in a weaker or smaller colony, you introduce the pathogen to a population that cannot fight it off. You have unknowingly turned one hive's manageable problem into another's fatal diagnosis.
Key Diseases You Are Preventing
Proper sterilization directly mitigates the risk of spreading devastating honey bee diseases.
The most critical of these is American Foulbrood (AFB), a bacterial disease whose spores are incredibly resilient and can remain viable on equipment for decades. You are also preventing the spread of fungal infections like Chalkbrood and other bacterial or viral ailments.
Practical Sterilization Methods
Effective cleaning doesn't have to be complicated. The key is choosing a method and applying it consistently between every hive.
The Chemical Scrub Method
This is a highly thorough process ideal for end-of-day cleaning or after inspecting a known sick hive.
Scrub the tool vigorously with a stainless-steel scrubber and an abrasive cleaner or a diluted bleach solution (1 part bleach to 10 parts water). Rinse thoroughly with water and then soak or wipe down with isopropyl alcohol for final sanitization.
The Flame Sterilization Method
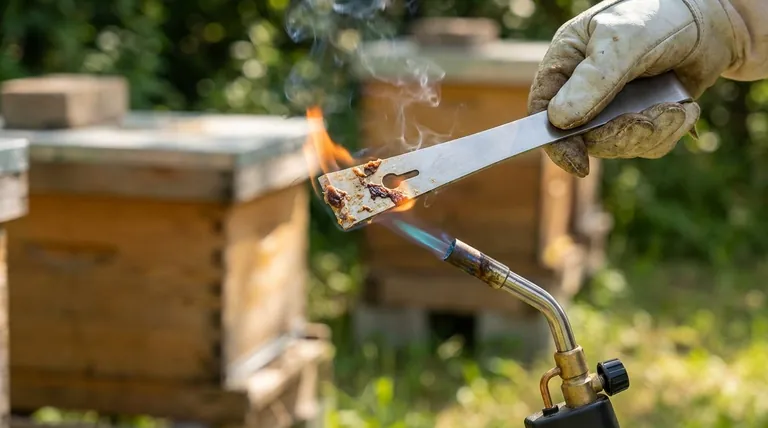
This is the fastest and most practical method for use in the field between hives.
Use a simple propane blow torch to heat the entire surface of the tool until it is too hot to touch, paying special attention to the ends. Alternatively, you can place the tool directly into the hot fire pot of your smoker for at least 30 seconds while pumping the bellows to ensure high heat.
The Dishwasher Method
For an easy end-of-day solution, you can run your stainless steel hive tools through a dishwasher on a hot cycle. This is effective for general cleaning but is not a substitute for in-field sanitization between hives.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method involves balancing speed, convenience, and the level of risk you are facing.
Efficiency vs. Thoroughness
Flame sterilization is the clear winner for efficiency in the apiary. It is fast, effective against most pathogens, and allows you to move from one hive to the next with minimal downtime.
The chemical scrub is more thorough but is too time-consuming to be practical between every hive during a busy inspection day. Reserve it for when you have a known disease concern or for your final cleanup.
The Risk of a "Quick Wipe"
Simply wiping your tool on your pants or with a dry rag is completely ineffective. This action provides a false sense of security while doing virtually nothing to remove or kill microscopic spores and bacteria.
When to Be Extra Vigilant
If you identify a hive that is weak, struggling, or showing clear signs of disease, always inspect it last. This minimizes the chance of cross-contamination.
After inspecting a suspicious hive, your tool should undergo the most thorough cleaning possible—ideally both flame and a chemical scrub—before it is used again on any colony.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
Your approach to tool hygiene should adapt to your specific situation. Consistent practice is the goal.
- If your primary focus is routine yard inspections: Flame sterilization with a propane torch between each hive is the most effective and practical protocol.
- If you are dealing with a known sick hive: Inspect that hive last, and then thoroughly decontaminate your tool using a chemical scrub and soak before its next use.
- If you manage multiple bee yards: Consider carrying two or three hive tools, using a clean one for each yard and sterilizing them all at the end of the day to prevent cross-yard contamination.
This simple act of hygiene is one of the most powerful and responsible actions you can take to ensure the long-term health and survival of your bees.
Summary Table:
| Cleaning Method | Best Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Sterilization | Between hives during routine inspection | Fast, effective in-field sanitization |
| Chemical Scrub | After inspecting a known sick hive | Most thorough decontamination |
| Dishwasher | End-of-day general cleaning | Convenient for multiple tools |
Protect Your Apiary with Professional-Grade Equipment
As a commercial beekeeper or distributor, your apiary's health is your livelihood. Consistent tool hygiene is non-negotiable for disease prevention. HONESTBEE supplies durable, easy-to-clean stainless steel hive tools and sterilization equipment designed for the rigorous demands of commercial operations.
We help you implement best practices in biosecurity with wholesale-focused solutions that scale with your business. Ensure every hive inspection starts with a clean tool.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss bulk pricing on professional beekeeping supplies and build a healthier, more productive apiary.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Premium Italian Style Hive Tool with Hardwood Handle
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a professional stainless steel hive tool in IFB? Optimize Your Colony Strength Assessment
- What is the significance of professional hive-making tools? Scale Your Stingless Bee Farm with Precision Equipment
- How does the hive splitting process contribute to colony management? Master Your Apiary Recovery Strategies
- What are the specific applications of a beekeeping chisel? Master Hive Maintenance with Precision Tools
- How should beekeepers handle bees when using a hive tool? Master Calm, Deliberate Techniques



















