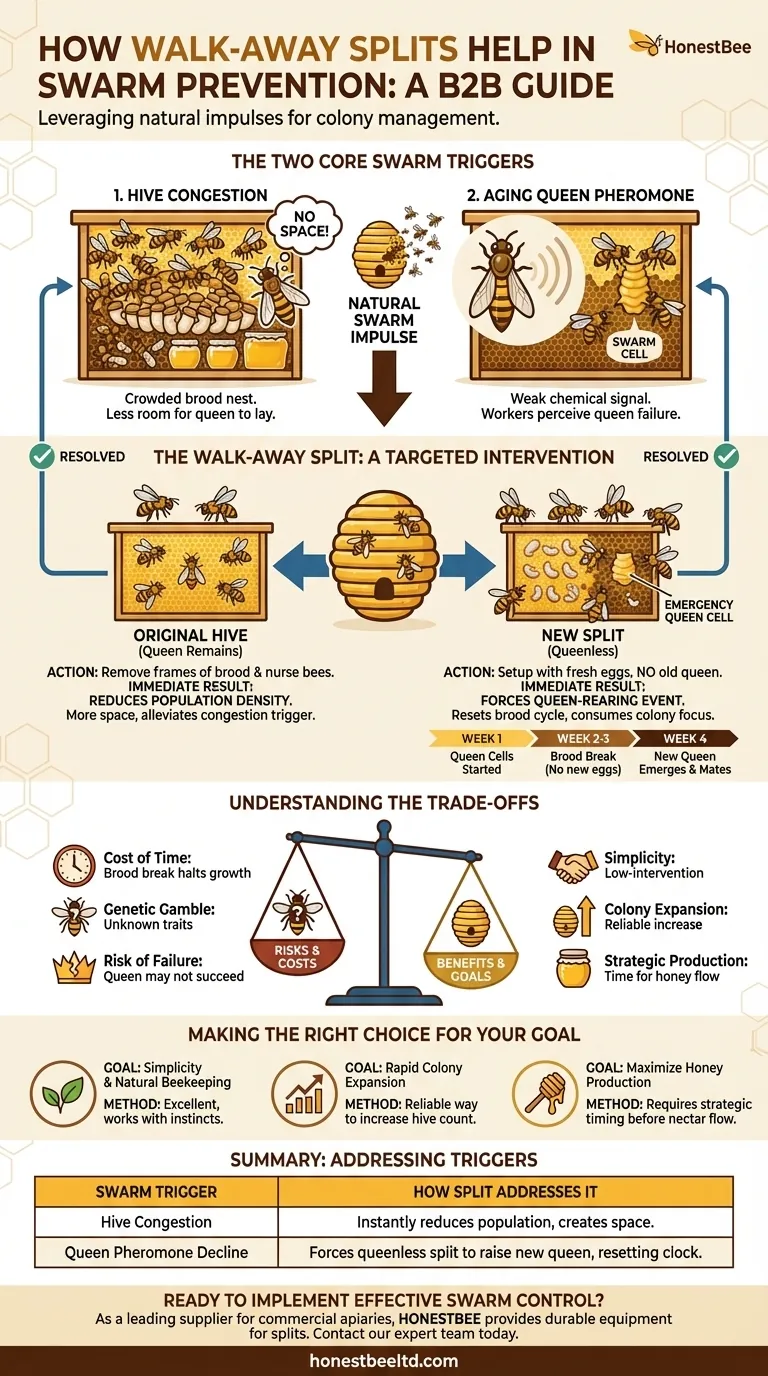
At its core, a walk-away split prevents swarming by proactively dividing a colony's population and resources. This manipulation directly counters the two main triggers for swarming: hive congestion and the colony's impulse to raise a new queen. By splitting the hive, you create more space in the original location and force the queenless half to focus its energy on raising a new monarch, effectively resetting its reproductive clock.
A walk-away split is more than just a preventative measure; it is a management technique that leverages the honey bee's natural swarm impulse. Instead of trying to suppress this instinct, you redirect it to create a new, viable colony under your control.
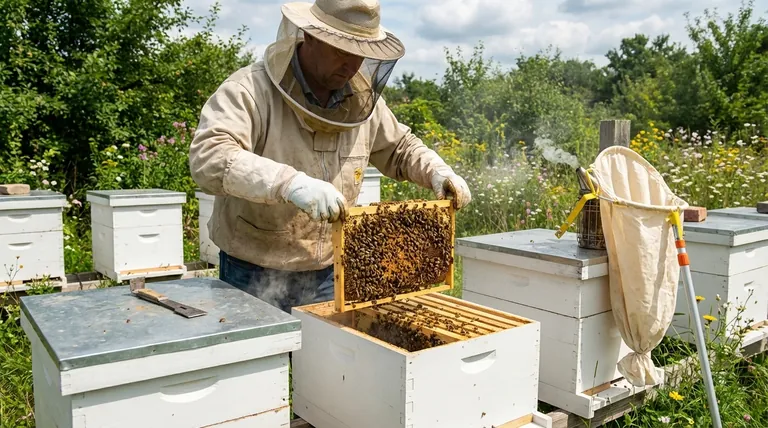

The Two Core Triggers of Swarming
To understand why a split works, you must first understand why a colony decides to swarm. It is not a sign of distress but a natural, successful method of reproduction for the superorganism.
Trigger 1: Hive Congestion
A healthy, growing colony rapidly fills its available space. When the brood nest becomes crowded with bees, brood, and resources, there is physically less room for the queen to lay eggs.
This congestion is the primary environmental signal that the colony has become powerful enough to divide. The bees recognize that the current home is at capacity.
Trigger 2: An Aging Queen Pheromone Profile
The queen bee produces a chemical signature known as queen mandibular pheromone (QMP). This pheromone spreads throughout the hive, signaling her presence and suppressing the workers' instinct to raise a new queen.
As a queen ages, her pheromone output can decline. Furthermore, in a very large and congested colony, her pheromones are not distributed as effectively. When worker bees perceive a drop in this signal, they interpret it as a sign that the queen is failing or that the colony is too large, and they begin constructing swarm cells to raise her replacement.
How a Walk-Away Split Directly Addresses These Triggers
A walk-away split is a targeted intervention that short-circuits both of the primary swarm triggers. The process involves moving several frames from the strong hive into a new hive box.
It Immediately Reduces Population Density
By removing frames of brood and their attendant nurse bees, you instantly create a significant amount of new space in the original hive.
This action directly alleviates the congestion trigger. With more room to work, the remaining bees are less likely to feel the pressure to leave, and the queen has more open cells in which to lay.
It Forces a Queen-Rearing Event
The new hive, or "split," is set up with frames containing fresh eggs, larvae, capped brood, honey, and pollen, but crucially, without the old queen.
Because this new colony is now queenless, its survival depends on raising a new one. The workers will select several of the youngest larvae (from the eggs you provided) and begin feeding them royal jelly to create emergency queen cells. This queen-rearing process consumes the colony's focus for weeks, completely diverting it from any swarming intentions.
It Resets the Brood Cycle
The entire queen-rearing process—from egg to a mated, laying queen—takes approximately one month. During this period, the new split experiences a brood break, where no new eggs are being laid.
This pause in brood production further reduces population pressure and also serves as a natural break in the life cycle of pests like the Varroa mite, which require brood to reproduce. The original hive, now with a smaller population, also has its swarm impulse significantly reduced.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the walk-away split is not a perfect solution for every situation. You must understand the compromises involved.
The Cost of Time
The month-long brood break in the new split means a temporary halt in population growth. If you perform the split just before a major nectar flow, you may be sacrificing a portion of your potential honey harvest from that new colony.
The Genetic Gamble
In a walk-away split, you allow the bees to choose which egg becomes the next queen. While this often produces a queen well-suited to your local environment, you have no control over the specific genetics, temperament, or productivity of the new monarch. This is a key difference from introducing a commercially raised queen with known traits.
The Risk of Failure
Queen-rearing is not guaranteed. The new queen may not emerge successfully, could be lost during her mating flight, or could return as a poor layer. You must monitor the split after about four weeks to confirm you have a healthy, laying queen, and be prepared to intervene if it has failed.
Distinguishing Swarming from Absconding
It is critical to know that a split addresses swarming, which is natural reproduction. It does not solve absconding, where the entire colony abandons the hive due to extreme stress, such as a severe pest infestation (Varroa mites, hive beetles), disease, or lack of food.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to perform a walk-away split depends entirely on your objectives as a beekeeper.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and natural beekeeping: The walk-away split is an excellent, low-intervention method that works with the bees' instincts.
- If your primary focus is rapid colony expansion: This is one of the most reliable ways to increase your hive count using your own bee stock.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: Be strategic. Split your hives well before the main nectar flow to allow both colonies to build up strength in time.
Ultimately, understanding and anticipating your colony's biological imperatives is the true key to successful swarm management.
Summary Table:
| Swarm Trigger | How a Walk-Away Split Addresses It |
|---|---|
| Hive Congestion | Instantly reduces bee population and creates more space in the original hive. |
| Queen Pheromone Decline | Forces the queenless split to raise a new queen, resetting the colony's reproductive clock. |
Ready to implement effective swarm control and grow your apiary?
As a leading supplier for commercial apiaries and distributors, HONESTBEE provides the durable equipment and supplies you need to perform splits and other hive manipulations with confidence. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable gear required for successful, large-scale beekeeping.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific needs and how we can support your operation's growth and productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Professional Telescopic Pole Bee Swarm Catcher
- Plastic Beetle Blaster Trap Beekeeping Tools and Supplies
- Professional Multi-Component Bucket Wasp Trap
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
- Commercial Grade Vertical Electric Bee Sweeper for Bee Removal
People Also Ask
- Do honey bees leave their hives? Understanding the Critical Role of Swarming
- Where is the best place to put a bee trap? Intercept Scout Bees for Maximum Swarm Capture
- How frequently should pollen be harvested from the traps? Ensure Optimal Hive Health & Superior Quality
- How do beekeepers catch bees? Master Swarm Capture for Apiary Success
- How do commercial beekeepers prevent swarming? Master Proactive Hive Management



















