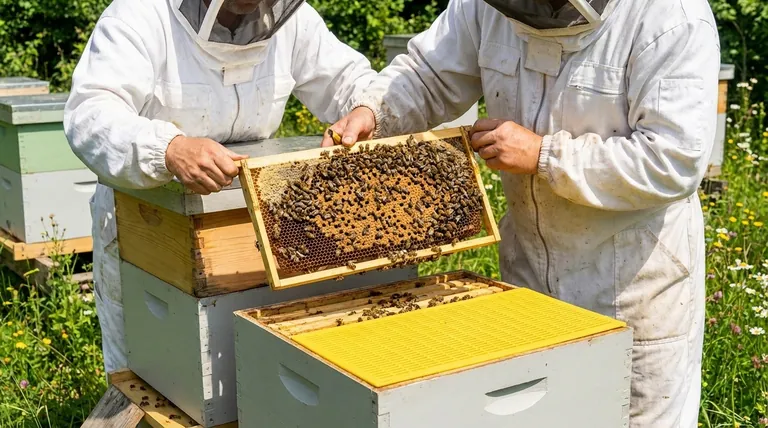
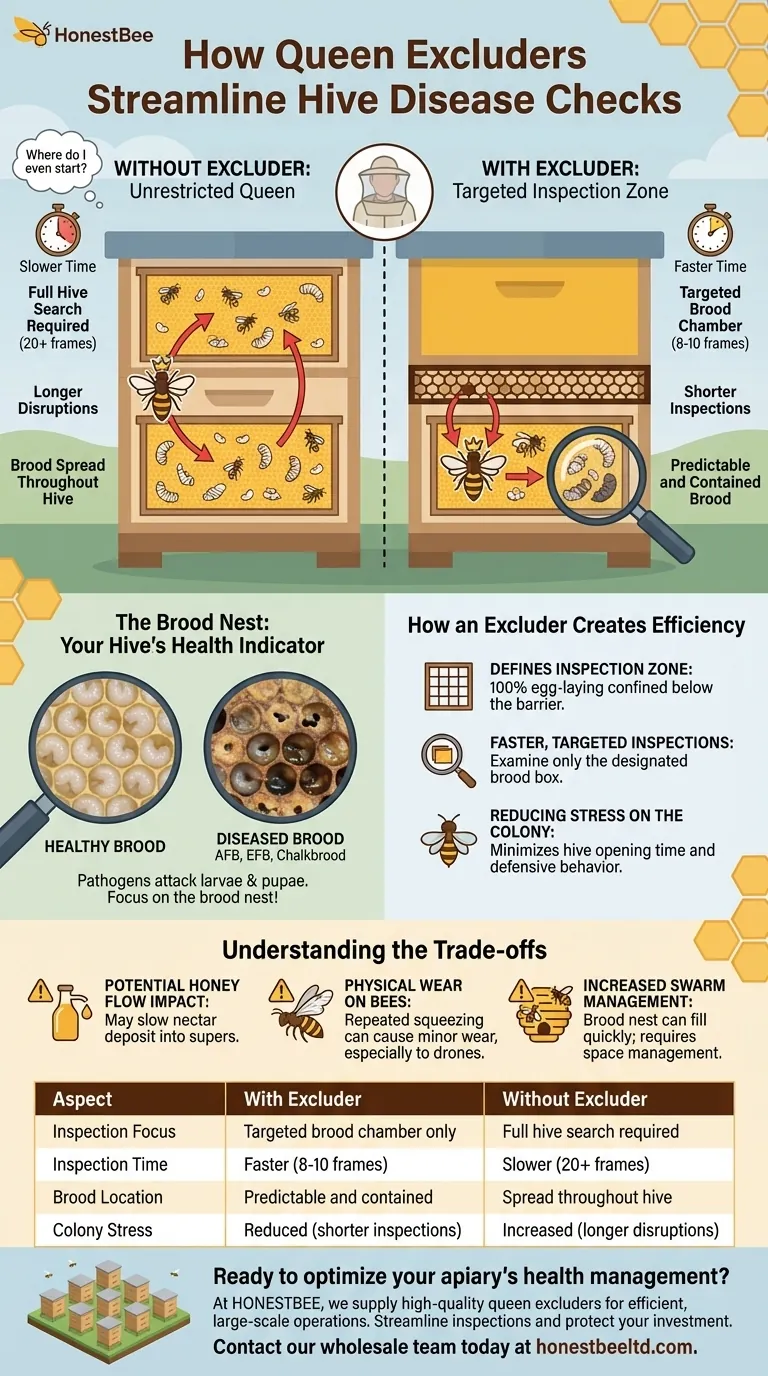
In short, queen excluders streamline disease checks by creating a predictable and contained brood area. By physically preventing the queen from moving into the upper honey supers, an excluder ensures that all egg-laying—and therefore all developing brood—is confined to the lower hive bodies. This allows you to know exactly where to look for signs of trouble.
By forcing the queen to lay eggs only in the lower hive boxes, an excluder allows a beekeeper to inspect for brood diseases with maximum efficiency. This strategy transforms a colony-wide search into a targeted inspection of only the frames that matter for disease diagnosis.

The Brood Nest: Your Hive's Health Indicator
To understand the value of an excluder, you must first understand why the brood nest is the focal point of any serious health inspection.
Why Brood is the Central Concern
The most devastating honey bee diseases, such as American Foulbrood (AFB), European Foulbrood (EFB), and Chalkbrood, are pathogens that attack bee larvae and pupae.
Symptoms like discolored larvae, sunken cappings, or unpleasant odors manifest directly within the brood cells. Therefore, a thorough health check is primarily an inspection of the brood nest.
The Challenge of an Unrestricted Queen
Without an excluder, a prolific queen may lay eggs wherever she finds open cells. This can include frames in the upper boxes, which are ideally meant for honey storage.
This forces the beekeeper to search through potentially every box in the hive to find all the patches of brood, significantly increasing the time and disruption of an inspection.
How an Excluder Creates Efficiency
A queen excluder is a simple grid that is sized to allow worker bees to pass through but is too small for the larger queen (and drones). Placing it between the brood boxes and the honey supers creates a clear division of labor within the hive.
Defining the Inspection Zone
The excluder establishes the lower boxes as the dedicated brood chamber. You know with certainty that 100% of the queen's egg-laying activity is happening below this barrier.
Faster, Targeted Inspections
This consolidation of brood means you no longer need to hunt for it. You can perform a complete disease check by only lifting and examining the frames within the designated brood box(es).
This turns a potentially 20-frame inspection into a more manageable 8 or 10-frame task, saving immense time and labor, especially across multiple hives.
Reducing Stress on the Colony
Shorter, more focused inspections are less disruptive. You minimize the time the hive is open, reducing temperature fluctuations and defensive behavior from the bees. This leads to a calmer colony and a more pleasant beekeeping experience.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While excellent for inspection efficiency, queen excluders are not without drawbacks. Their use requires a conscious trade-off.
Potential Impact on Honey Flow
The excluder can act as a bottleneck. Some beekeepers argue that workers are reluctant to pass through it, which can slow the rate at which they deposit nectar in the honey supers above. This is often called a "honey barrier."
Physical Wear on Bees
Forcing thousands of bees to repeatedly squeeze through the grid can cause minor wear and tear on their wings over time. This is particularly an issue for larger drones, who can get stuck or damaged.
Increased Swarm Management
By confining the queen, the brood nest can fill with eggs, pollen, and honey more quickly. If the queen runs out of space to lay, the colony may feel congested and initiate swarm preparations. Using an excluder requires you to be more vigilant about providing adequate space in the brood chamber.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a queen excluder depends entirely on your management philosophy and primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is simplified health checks and operational efficiency: An excluder is an invaluable tool for creating a predictable inspection routine, especially for newer beekeepers or those managing many hives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production with minimal barriers: You may choose to operate without an excluder, but you must accept the trade-off of conducting more time-consuming, full-colony inspections.
Ultimately, using an excluder is a strategic choice that balances the need for hive control against the natural dynamics of the colony.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | With Excluder | Without Excluder |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection Focus | Targeted brood chamber only | Full hive search required |
| Inspection Time | Faster (8-10 frames) | Slower (20+ frames) |
| Brood Location | Predictable and contained | Spread throughout hive |
| Colony Stress | Reduced (shorter inspections) | Increased (longer disruptions) |
Ready to optimize your apiary's health management?
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality tools needed for efficient, large-scale operations. Our queen excluders are designed for durability and precision, helping you conduct faster, more targeted disease checks across your entire operation.
Let us help you streamline your inspections and protect your investment.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your needs and discover how HONESTBEE can support your commercial beekeeping success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- Premium Wood Framed Metal Wire Queen Bee Excluder
- Beehive Entrance Discs Plastic Bee Entrance Disc for Bee Hives
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What are the typical designs and materials of a queen excluder? Choose the Best Gear for Your Apiary Efficiency
- What is the significance of using queen excluders in research? Enhance Data Integrity and Hive Control
- What are the disadvantages of using metal queen excluders? Key Insights for Apiary Management
- What is the significance of using queen excluders in tropical bee management? Boost Honey Purity & Colony Stability
- What is the core function of a Queen Excluder in royal jelly production? Boost Yields with Behavioral Management



















