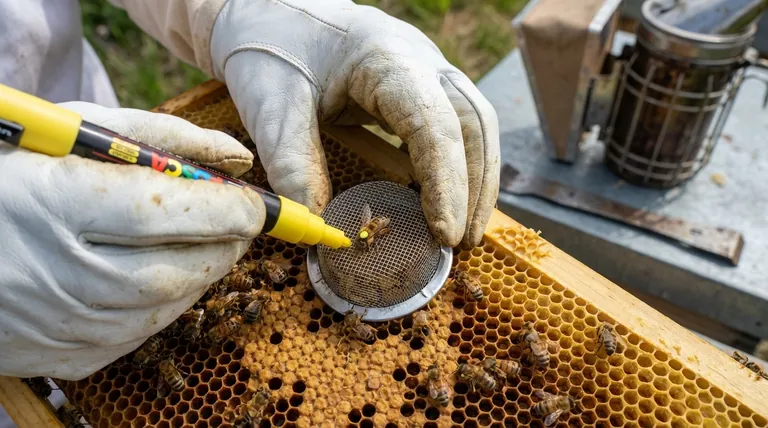
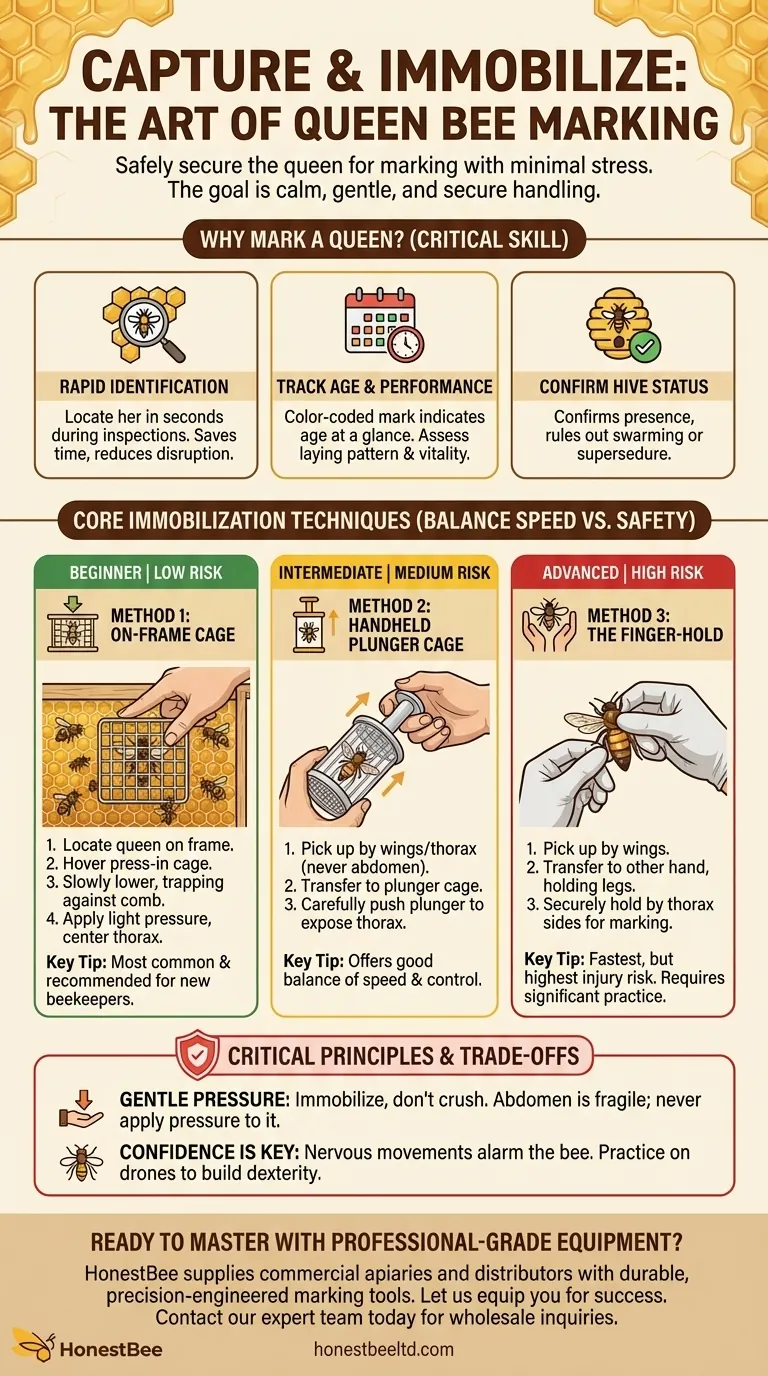
To safely immobilize a queen bee for marking, you must gently secure her either on the comb with a press-in marking cage or off the comb by hand. The most common tool-assisted method involves hovering a cage over the bee, pressing down lightly to trap her against the comb, and centering her thorax between the cage's threads for marking.
The core challenge is not just immobilizing the queen, but doing so with minimal stress to protect the single most important member of the colony. The right method depends entirely on your confidence and skill level, but the goal is always calm, gentle, and secure handling.

Why Marking a Queen is a Critical Skill
Before learning the "how," it is essential to understand the "why." Marking your queen is a foundational practice in modern beekeeping that provides immediate, actionable intelligence about your hive.
For Rapid Identification
A marked queen can be located in seconds during a hive inspection, saving you significant time and reducing the disruption to the colony. An unmarked queen can be nearly impossible to find among tens of thousands of other bees.
To Track Her Age and Performance
A color-coded mark allows you to know the queen's age at a glance. This helps you assess her laying pattern and overall vitality, enabling you to proactively decide when she may need to be replaced before her production declines.
To Confirm Hive Status
Seeing your marked queen confirms she is still present and that the colony has not swarmed or quietly replaced her (a process called supersedure). If a new, unmarked queen appears, you know a major event has occurred in the hive.
Core Immobilization Techniques
There are three primary methods for immobilizing a queen, ranging from low to high difficulty. Your choice should be based on your experience and comfort level.
Method 1: The On-Frame Cage (Lowest Risk)
This is the most common and recommended method for new beekeepers.
- Locate the queen on a frame of comb.
- Gently hover a press-in marking cage over her.
- Slowly lower the cage, trapping her against the surface of the comb.
- Apply just enough light pressure to immobilize her without causing injury. Ensure her thorax (the middle section of her body) is visible through the grid for easy marking.
Method 2: The Handheld Plunger Cage (Intermediate Skill)
This method involves briefly handling the queen to move her into a dedicated marking device.
- First, gently pick the queen up by her wings or thorax, never by her abdomen. Use your thumb and forefinger with a calm, deliberate motion.
- Transfer her into a one-handed queen marking cage, which often features a soft plunger.
- Carefully push the plunger up until the queen is gently pressed against the top grid, with her thorax exposed for marking.
Method 3: The Finger-Hold (Advanced Skill)
This technique is used by experienced beekeepers for its speed and efficiency, but it carries the highest risk of injury if done incorrectly.
- Gently pick the queen up by her wings.
- Carefully transfer her to your other hand, holding her legs with your fingers.
- Finally, gently but securely hold her by the sides of her thorax between your thumb and index finger, leaving the top of her thorax clear for the mark.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing a method involves balancing speed against safety. Your primary responsibility is the well-being of the queen.
Risk of Injury and Stress
Any handling can stress the queen. Anxious or clumsy movements can result in a damaged leg or, in the worst case, a fatally injured queen. The on-frame cage method minimizes direct handling and is therefore the safest for beginners.
The Importance of Gentle Pressure
The goal is to immobilize, not crush. The queen's thorax is robust, but her abdomen is fragile and contains her reproductive organs. Never apply pressure to the abdomen. With any cage, apply only enough force to stop her from moving.
Confidence is Key
A beekeeper who is nervous will be jerky and hesitant, which is more likely to alarm or harm the bee. It is better to use a slower, safer method with confidence than to attempt a difficult one with anxiety. Practice on drones (male bees) to build your dexterity and confidence.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of method should align directly with your current skill level to ensure the safety of your queen.
- If your primary focus is safety and you are new to beekeeping: Use the on-frame press-in marking cage, as it requires the least amount of direct handling.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and you have some experience: The handheld plunger cage offers a good balance of speed and control once you are comfortable picking up the queen.
- If your primary focus is speed and you are a confident expert: The finger-hold technique is the fastest method, but it should only be attempted after significant practice.
Mastering this skill transforms you from a bee-haver into a true beekeeper, empowering you with precise control over your hive management.
Summary Table:
| Method | Skill Level | Risk Level | Key Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Frame Cage | Beginner | Low | Press-in marking cage |
| Handheld Plunger Cage | Intermediate | Medium | One-handed marking cage |
| Finger-Hold | Advanced | High | None (Hands only) |
Ready to Master Queen Marking with Professional-Grade Equipment?
Confident, gentle handling starts with the right tools. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with durable, precision-engineered queen marking cages and handling tools designed for minimal stress and maximum efficiency.
Let us equip you for success. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable, high-quality supplies your business depends on.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your apiary's equipment needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Queen Bee Marking Pen POSCA Queen Marking Pens for Beekeeping Bee Markers
- Queen Bee Marking Pen UNI Medium Point for Queen and Bee Marking
- Queen Bee Marking Tube Cage Bottle Catcher Holder with Clear Plastic Plunger Marker
- Jenter Queen Rearing Kit Complete Set for Bee Breeding
- Hexagonal Direct Comb Introduction Queen Bee Cage
People Also Ask
- Why is specialized marking paint used for identifying the thorax of honeybees? Enhance Age-Related Bioassay Precision
- What should be done if a marked queen flies away? A Beekeeper's Guide to Calm Recovery
- Why is abdominal marking considered an important component for improving the long-term visibility of queen bees?
- What are the main advantages of queen marking? Instantly Identify & Track Your Queen Bee
- What are the three fundamental steps in the process of marking a queen bee? Master Safe and Precise Hive Management
- What is the primary function of specialized Marking Pens in beekeeping? Essential Tools for Honey Bee Tracking
- What precautions should be taken during queen marking? Ensure Colony Acceptance and Queen Safety
- How can a beekeeper determine the year a queen hatched? Master the International Color Code



















