At its core, a bee smoker is a specialized tool that generates cool, dense smoke to calm honey bees, making hive inspections safer and less stressful for both the beekeeper and the colony. It works by burning a slow-smoldering fuel inside a metal canister and using attached bellows to gently puff the smoke into and around the hive.
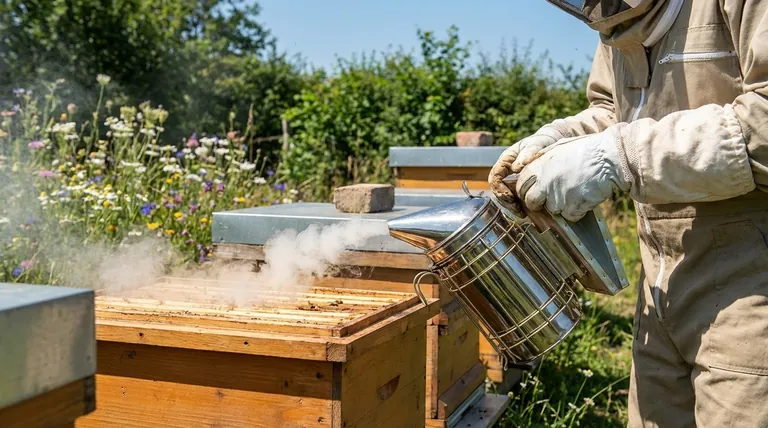
The true function of a bee smoker is not to sedate bees, but to interrupt their primary method of communication. By masking the alarm pheromones that signal danger, the smoke prevents a colony-wide defensive response, allowing a beekeeper to work peacefully.

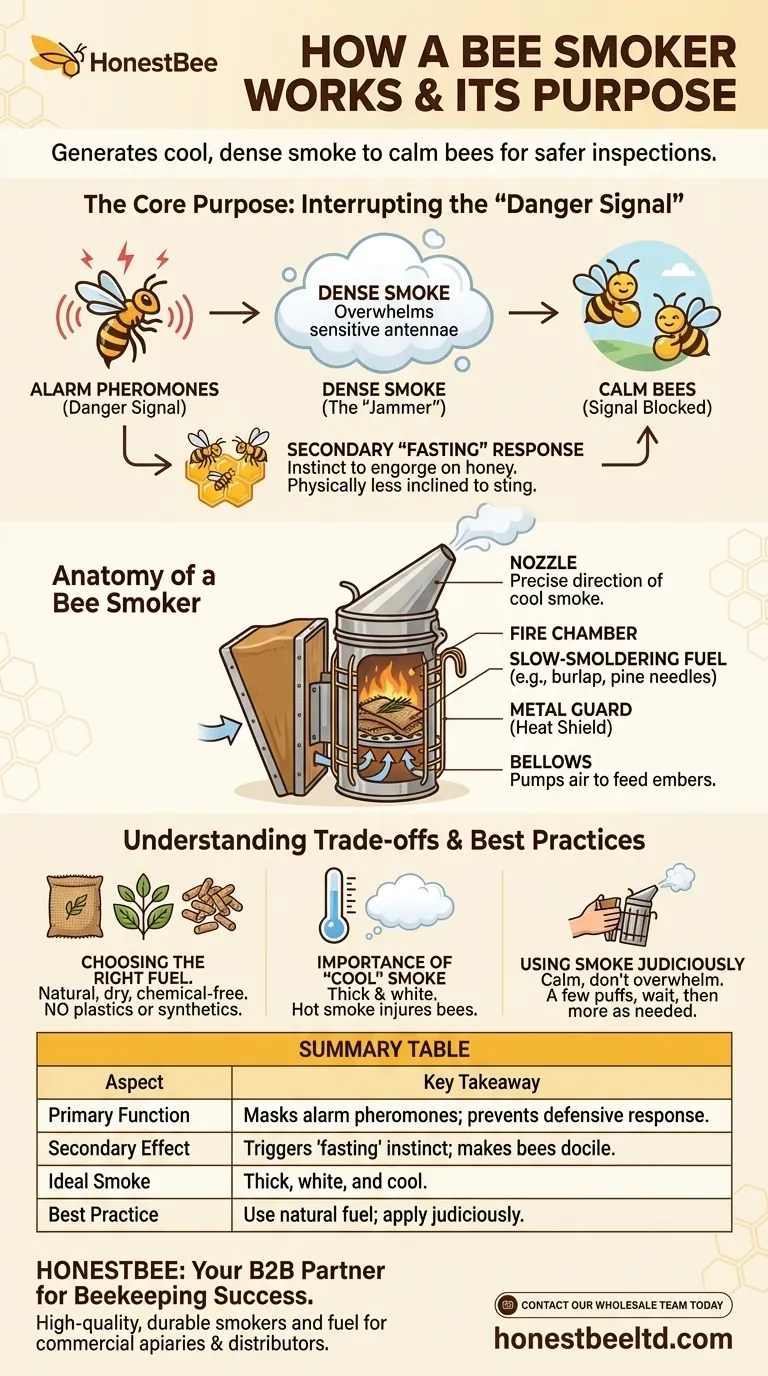
The Core Purpose: Interrupting the "Danger Signal"
When bees perceive a threat, their first line of defense is chemical. A bee smoker effectively neutralizes this defense system.
How Bees Communicate Danger
Honey bees release alarm pheromones when they feel threatened or are injured. This chemical signal instantly alerts other bees in the vicinity, triggering aggressive and defensive behaviors like stinging.
Once one bee stings, the pheromone concentration increases, creating a chain reaction that can quickly lead to a full-blown defensive attack from the entire colony.
How Smoke Masks the Signal
The smoke produced by a bee smoker works by overwhelming the bees' sensitive antennae, which they use to detect these pheromones.
The dense smoke particles essentially "jam" the signal, preventing the alarm message from spreading throughout the hive. The bees are no longer able to effectively coordinate a defensive response.
The Secondary "Fasting" Response
Smoke also triggers a secondary, instinctual response. Bees associate smoke with a potential forest fire, a major threat to their hive.
Their instinct is to prepare to abandon the hive. They do this by consuming as much honey as possible, engorging their stomachs. This makes them physically more docile and less inclined to sting, as a bee with a full stomach has difficulty flexing its abdomen to do so.
Anatomy of a Bee Smoker
A bee smoker is a simple yet effective device, typically consisting of three main parts.
The Fire Chamber
This is the stainless steel cylinder where the fuel is burned. It usually includes an inner grate or "burning plate" to keep the fuel elevated for better airflow. A metal guard or heat shield surrounds the chamber to protect the beekeeper from burns.
The Bellows
The bellows are the pump mechanism, traditionally made of wood and leather. Squeezing the bellows forces air into the bottom of the fire chamber, feeding the embers and pushing smoke out of the top.
The Nozzle
A conical lid with a spout, the nozzle allows the beekeeper to precisely direct the cool smoke towards the hive entrance or over the frames inside the hive.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Using a smoker is a skill. The goal is to calm the bees, not to overwhelm them.
Choosing the Right Fuel
The fuel must be natural, dry, and free of chemicals. Good options include untreated burlap, pine needles, dried leaves, wood pellets, or commercially available smoker fuel. Never use plastics, treated wood, or synthetic materials that can release toxic fumes.
The Importance of "Cool" Smoke
The objective is to produce thick, white, and cool smoke. Hot smoke or embers can injure or kill the bees. A properly lit and managed smoker will smolder gently rather than burn aggressively.
Using Smoke Judiciously
Too much smoke can be counterproductive. It can stress the bees, cause them to consume excessive amounts of honey, and potentially taint the flavor of the honey if used heavily during a harvest.
A common practice is to apply a few gentle puffs at the hive entrance before opening it, wait 30-60 seconds, and then apply a few more puffs under the lid once it is cracked open.
How to Apply This to Your Beekeeping
Your approach to using a smoker should match your specific task.
- If your primary focus is a quick inspection: A few puffs at the entrance and under the lid are usually sufficient to keep the colony calm for a brief check.
- If your primary focus is a longer task like a harvest: You will need to apply smoke more periodically, perhaps every few minutes, to keep the alarm pheromones suppressed as you work through the hive.
- If your primary focus is minimizing bee stress: Use the absolute minimum amount of cool smoke necessary to get the job done, observing the bees' behavior and applying more only when you see signs of agitation.
Ultimately, the bee smoker is a tool that enables a respectful partnership between the beekeeper and the bees.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Masks alarm pheromones to prevent colony-wide defensive response. |
| Secondary Effect | Triggers a 'fasting' instinct, making bees docile. |
| Ideal Smoke | Thick, white, and cool to avoid harming bees. |
| Best Practice | Use natural, chemical-free fuels and apply smoke judiciously. |
Ready to work with your bees more safely and efficiently?
A reliable bee smoker is fundamental to effective hive management. At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-quality, durable smokers and fuel designed for professional use.
Let us equip you with the tools you need for a successful season. Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- European Stainless Steel Bee Smoker for Honey Bee Hive
- Premium Traditional Copper Bee Smoker with Bellows
- Professional Bee Smoker with Elongated Spout and Durable Bellows for Beekeeping
- Heavy-Duty Bee Smoker with Durable Plastic Bellows for Beekeeping
- Heavy Duty Manual Bee Smoker Blower for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Do bees hate the smell of smoke? The Truth About Beekeeping's Most Vital Tool
- What do you smoke bees with? The Key to Calm, Safe Hive Inspections
- How can beekeepers reduce the likelihood of getting stung? Master Gentle Handling & Protective Gear
- Can you use smoke to get rid of bees? The Truth About Bee Behavior and Control
- How should smoke be applied to a beehive during inspection? Master the Gentle Art of Calming Bees



















