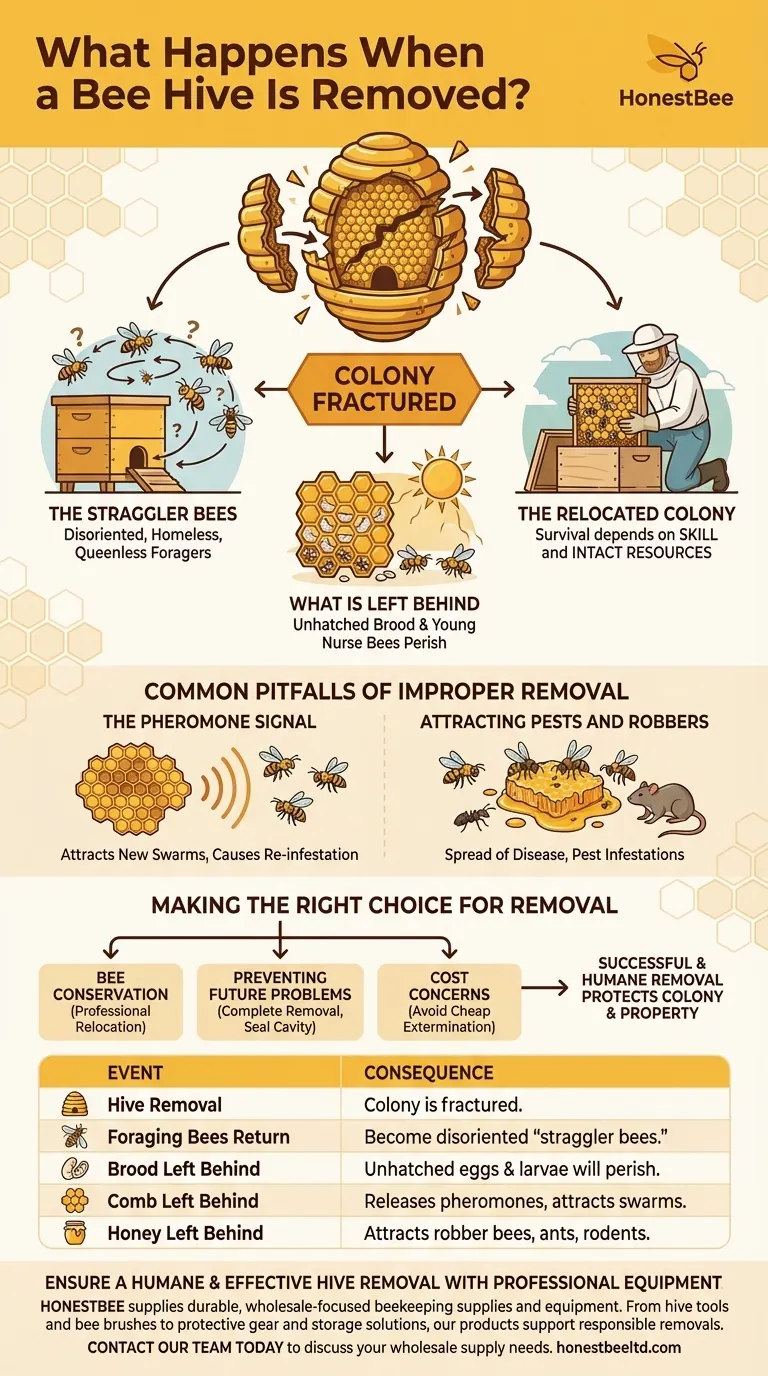
In short, removing a bee hive fractures the colony. The bees that are away from the hive during the removal become disoriented "straggler bees" upon their return. The main colony, including the queen, is typically relocated, but any young, flightless bees or unhatched brood left behind will perish without the care of the adult workers.
The core issue with hive removal is colony separation. The success of the relocated bees depends on the quality of the removal, while the foraging bees left behind face a dire situation without their home, queen, and social structure.

The Immediate Aftermath of Removal
When a hive is physically taken from a location, it sets off a chain reaction for every member of that colony, whether they were present or not.
The Fate of the Straggler Bees
The most immediate and visible consequence involves the foraging bees. These are the workers who were out collecting pollen and nectar when their home was removed.
They return to the exact spot where their hive entrance used to be, guided by precise spatial memory. Upon finding it gone, they become visibly confused, flying in circles and attempting to land where their home once stood. These straggler bees are now homeless and queenless.
What Is Left Behind
A professional removal aims to take the entire colony, but this isn't always possible. In many cases, parts of the colony are left behind.
This often includes unhatched brood—the eggs and larvae—as well as young nurse bees that are not yet old enough to fly. Without the warmth, protection, and feeding provided by the adult workforce, this next generation of bees will not survive. Stores of pollen and honey may also be left.
The Challenge for the Relocated Colony
The main group of bees, successfully removed with their queen, faces the challenge of re-establishing their colony in a new location.
Their survival depends heavily on the skill of the person who performed the removal. If enough of the brood comb and food stores are kept intact and moved with them, their chances of thriving are high.
Common Pitfalls of Improper Removal
Simply taking away the bees and the bulk of the hive is not a complete solution. The remnants can cause significant problems down the line.
The Pheromone Signal
Honey and wax comb are saturated with powerful pheromones that act as a strong "home" signal for bees.
If any comb is left behind in a wall or ceiling cavity, these scents will attract scout bees from other swarms in the future. This makes re-infestation of the same spot highly likely.
Attracting Pests and Robbers
Exposed honey left behind will attract opportunistic bees from other nearby hives, a behavior known as "robbing." This can lead to the spread of disease between colonies.
Furthermore, the abandoned honey and wax can attract other pests like ants, cockroaches, or rodents, creating an entirely new infestation problem.
Making the Right Choice for Removal
Understanding the consequences of hive removal is key to handling the situation responsibly and effectively.
- If your primary focus is bee conservation: You must contact a professional beekeeper or a live bee removal service that specializes in relocating, not exterminating, the entire colony.
- If your primary focus is preventing a future problem: Ensure that the removal includes taking all of the wax comb and honey, and that the cavity is sealed to prevent another swarm from being attracted to the residual scent.
- If you are concerned about cost: Remember that a cheap extermination often leads to more expensive problems later, such as pest infestations or structural damage from melting honey.
Ultimately, a successful and humane bee hive removal protects the colony's future while permanently solving the immediate problem.
Summary Table:
| Event | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Hive Removal | Colony is fractured. |
| Foraging Bees Return | Become disoriented "straggler bees" without a home or queen. |
| Brood Left Behind | Unhatched eggs and larvae will perish without adult care. |
| Comb Left Behind | Releases pheromones that attract new swarms, causing re-infestation. |
| Honey Left Behind | Attracts robber bees and other pests like ants and rodents. |
Ensure a Humane and Effective Hive Removal with Professional Equipment
A successful hive removal protects both the colony and your property. For commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, having the right tools is essential for conducting or facilitating humane removals that prevent future problems.
HONESTBEE supplies the durable, wholesale-focused beekeeping supplies and equipment you need. From hive tools and bee brushes to protective gear and storage solutions, our products support beekeepers in performing responsible removals that safeguard the colony's future.
Let us equip your operation for success. Contact our team today to discuss your wholesale supply needs and ensure you have the right tools for the job.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Professional Multi-Function Stainless Steel Hive Tool
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Professional Insulated Plastic Bee Hives
People Also Ask
- What is the hive tool used for? The Essential Multi-Tool for Every Beekeeper
- What are the basic tools for beekeeping? Essential Starter Kit for Safe & Successful Hive Management
- Why use professional beekeeping tools for beehive inspections? Crucial Support for Pollinator Protection Policies
- What is the operational mechanism of a beehive smoker? Master Bee Calm and Safety During Harvesting
- How should beekeepers handle bees when using a hive tool? Master Calm, Deliberate Techniques



















