At its core, bee venom is a complex defensive biotoxin. It is a colorless, acidic liquid that honeybees deploy through their stinger when they perceive a threat to themselves or their colony. While traditionally associated with a painful sting, modern methods have been developed to collect this substance for use in therapeutic and cosmetic applications without killing the bee.
Bee venom is not a simple fluid but a potent mixture of proteins and peptides. Understanding its composition and the modern, non-lethal collection process is crucial to evaluating its use and ethical implications.
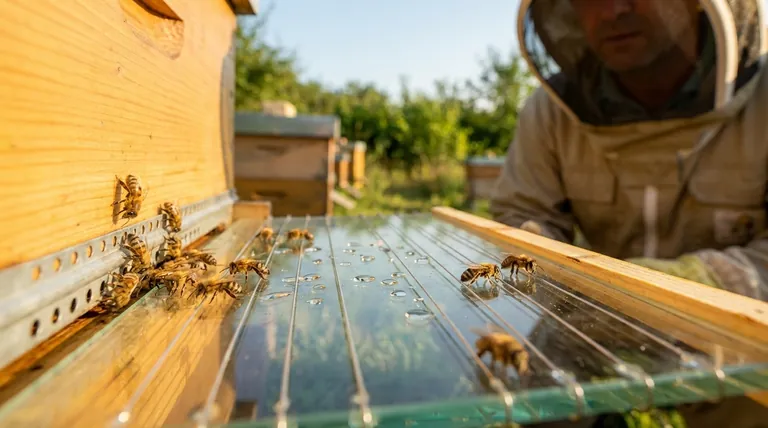

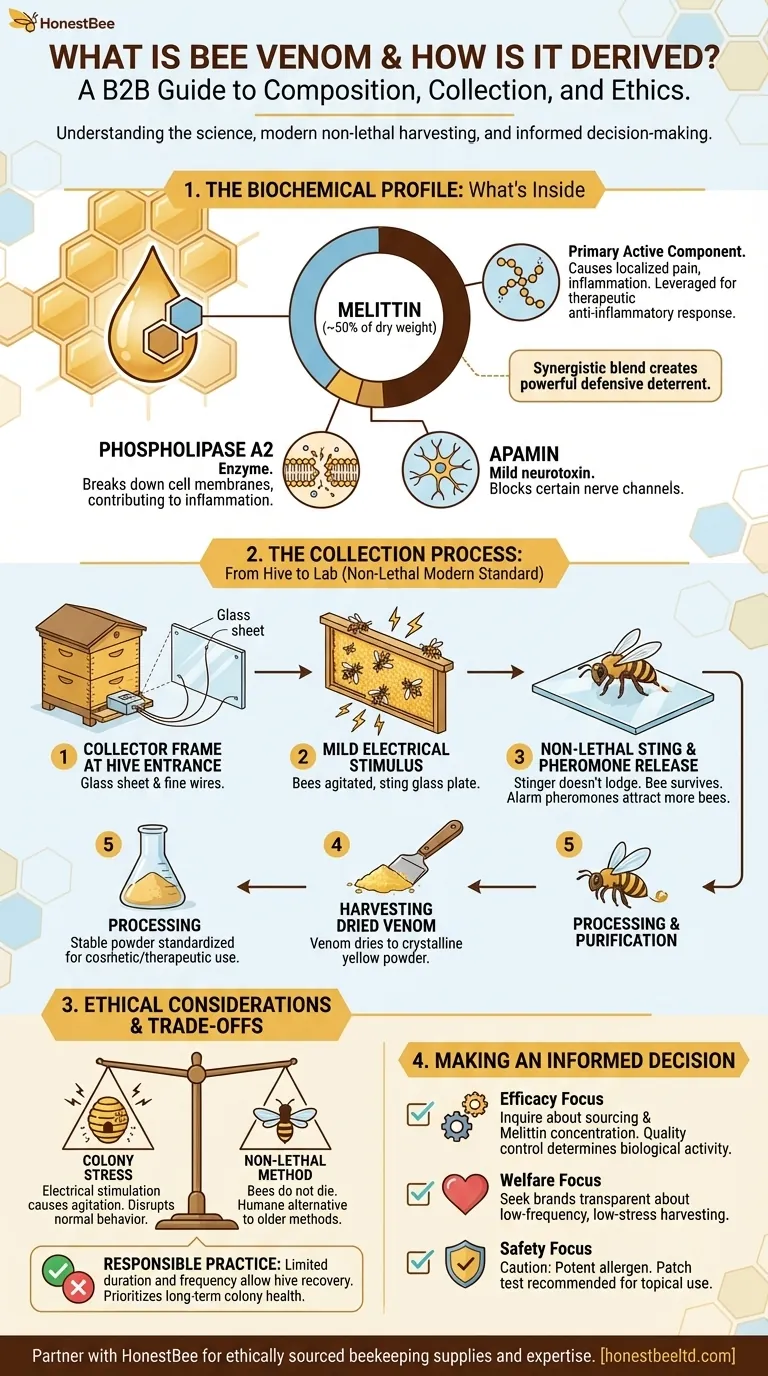
The Biochemical Profile: What's Inside Bee Venom
The effects of bee venom are not caused by a single chemical but by a sophisticated blend of active components, each with a specific function.
The Primary Active Component: Melittin
Melittin is the most abundant compound in bee venom, making up about 50% of its dry weight. It is a powerful peptide primarily responsible for the localized pain, inflammation, and itching associated with a bee sting.
In a therapeutic context, it is this inflammatory response that is often leveraged, as it can trigger the body's own anti-inflammatory and healing mechanisms.
Key Enzymes and Peptides
Beyond melittin, the venom contains other critical substances. Phospholipase A2 is an enzyme that breaks down cell membranes, contributing to inflammation and pain. Apamin is a mild neurotoxin that can block certain nerve channels.
Together, these components work synergistically to create a powerful deterrent to predators.
The Collection Process: From Hive to Lab
The method for deriving bee venom is a critical factor in its quality, sustainability, and ethical standing. The process has evolved significantly to prioritize the well-being of the bees.
The Modern Standard: The Collector Frame
The vast majority of commercially available bee venom is harvested using a device called a collector frame. This is a glass sheet fitted with a grid of wires that conduct a very mild electrical current.
This frame is placed at the entrance of the beehive. As bees pass over it, they receive a light electrical stimulus.
A Non-Lethal Process
The stimulus agitates the bees, causing them to sting the surface of the glass plate. Because the stinger cannot get lodged in the smooth glass, the bee retracts it and survives the process—unlike when stinging skin.
Small droplets of venom are deposited on the glass. The bees also release alarm pheromones, which signal other bees to sting the plate, increasing the yield.
Harvesting and Processing
Once the collection is complete, the frame is removed. The venom dries on the glass into a crystalline substance.
This dried venom is then carefully scraped off the plate, resulting in a fine, yellowish powder. This powder is stable and can be purified and standardized for use in various products, from skincare creams to injectable solutions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Ethical Questions
While the modern collection method is designed to be non-lethal, it is not without impact. Objectivity requires us to consider the potential stress placed on the honeybee colony.
Colony Stress
The electrical stimulation and release of alarm pheromones can cause significant agitation within the hive. This stress can disrupt the colony's normal behavior for a period.
Responsible beekeepers mitigate this by using the collector for limited durations and not collecting too frequently, allowing the hive ample time to recover.
The Question of Harm
While bees do not die during the collection process, the experience is inherently stressful. The ethical debate centers on whether this induced stress for commercial gain is justifiable.
Proponents argue that it is a far more humane alternative to older methods and that responsible practices ensure the long-term health and survival of the colony, which is paramount to the beekeeper.
Making an Informed Decision
When evaluating a product or therapy involving bee venom, understanding its origin is as important as understanding its function.
- If your primary focus is efficacy: Inquire about the sourcing and concentration of the venom. The presence of key components like melittin, confirmed through proper quality control, is what determines the biological activity.
- If your primary focus is animal welfare: Seek out brands that are transparent about their collection methods, emphasizing low-frequency, low-stress harvesting that prioritizes long-term colony health.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Always remember that bee venom is a potent substance and a known allergen. Its use should be approached with caution, and a patch test is highly recommended for any topical application.
By understanding both the science of the substance and the ethics of its collection, you can make a truly informed choice.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Component | Melittin (approx. 50% of dry weight) |
| Other Key Compounds | Phospholipase A2, Apamin |
| Modern Collection Method | Non-lethal electrical stimulation via collector frame |
| Final Product Form | Dried, crystalline yellow powder |
| Primary Ethical Consideration | Stress on the bee colony from the collection process |
Ensure Your Bee Venom is Ethically and Effectively Sourced
Navigating the complexities of bee venom sourcing requires a partner with expertise and integrity. At HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors. Our deep understanding of hive health ensures that the products you use or sell are backed by responsible practices.
We help you:
- Source equipment that supports sustainable and humane apiculture.
- Access reliable information for making informed decisions about api-sourced products.
- Build a supply chain that prioritizes both efficacy and bee welfare.
Ready to enhance your operations with a trusted supplier? Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Retractable Chinese Queen Rearing Grafting Tools Equipment
- Wooden Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Bee Frame Grooving Machine | Precision Slotting for Bee Frame Making
- No Grafting Queen Rearing Kit: System for Royal Jelly Production and Queen Rearing
- Electric Flatting and Embossing Machine with Tray for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using grafting tools in queen rearing? Mastering Precision Transfer for High-Quality Breeding
- How many days after egg-laying do queens emerge? Master the 16-Day Queen Rearing Cycle
- What is the ideal age and appearance of larvae for grafting to produce the best queens? Master the 4-20 Hour Window
- How does the precision of grafting tools affect the efficiency of honeybee queen breeding? Maximize Your Larval Survival
- What impact does the design of professional grafting tools have on queen bees? Maximize Longevity & Fecundity



















