At its core, oxalic acid is a multi-functional tool for plants. While it is widely known as a defense mechanism, its roles extend deep into the plant's internal regulation and survival systems. It acts primarily as a deterrent against herbivores by making plant tissues sour and physically irritating to consume.
Oxalic acid is far more than a simple defense chemical; it is a plant's internal regulator, allowing it to manage toxic mineral levels, defend against multiple threats, and maintain internal balance in a challenging environment.

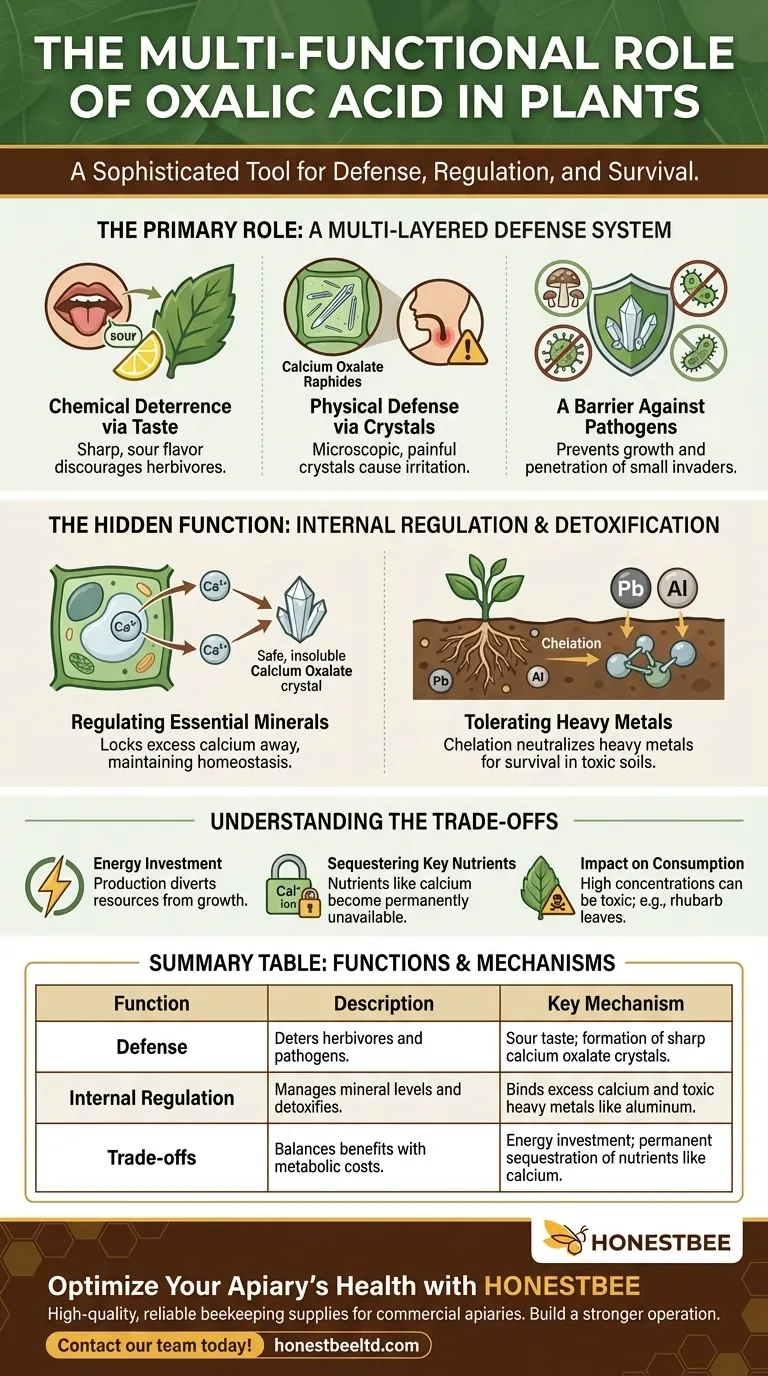
The Primary Role: A Multi-Layered Defense System
Plants cannot run from threats, so they have evolved sophisticated chemical and physical defenses. Oxalic acid is a key component of this stationary arsenal, operating on multiple levels.
Chemical Deterrence via Taste
The most direct defensive function is taste. Oxalic acid imparts a sharp, sour flavor to leaves and stems.
This unpalatable taste serves as an immediate signal to herbivores, discouraging them from consuming the plant and encouraging them to seek a more agreeable food source.
Physical Defense via Crystals
Many plants take this defense a step further by combining oxalic acid with calcium to form needle-sharp crystals called calcium oxalate.
These microscopic crystals, known as raphides, cause painful irritation to the mouth, throat, and digestive tract of any animal that attempts to eat the plant tissue. This provides a powerful physical deterrent that is far more effective than taste alone.
A Barrier Against Pathogens
The same calcium oxalate crystals that deter large animals can also act as a physical barrier against smaller invaders. These hard, sharp structures can help prevent the growth and penetration of certain fungal and bacterial pathogens.
The Hidden Function: Internal Regulation and Detoxification
Beyond its role as a weapon, oxalic acid is critical for maintaining the plant's internal health. It acts as a master regulator for minerals and toxins.
Regulating Essential Minerals
Calcium is vital for plant function, but high concentrations of free calcium ions in the cell's cytoplasm can be toxic and disrupt signaling pathways.
Plants use oxalic acid to bind with this excess calcium. The resulting calcium oxalate is insoluble, effectively locking the calcium away in a stable, harmless form and allowing the plant to maintain precise mineral homeostasis.
Tolerating Heavy Metals
For plants growing in contaminated environments, oxalic acid is a lifeline. It can bind to toxic heavy metals like aluminum, lead, or cadmium.
This process, known as chelation, neutralizes the heavy metals and prevents them from interfering with the plant's metabolic machinery, enabling survival in otherwise toxic soils.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The production and use of oxalic acid are not without costs. Plants must balance the benefits of this compound against its metabolic and nutritional implications.
The Energy Investment
Producing any specialized chemical compound requires an investment of energy and resources. A plant must divert assets that could have been used for growth or reproduction into making oxalic acid.
Sequestering Key Nutrients
While sequestering excess calcium is beneficial, it is also a one-way process. Once calcium is locked into an insoluble calcium oxalate crystal, it is no longer available to the plant for future nutritional needs.
Impact on Consumption
The very effectiveness of oxalic acid as a defense mechanism is why some plants high in the compound (like rhubarb leaves) are toxic. For humans, high consumption of soluble oxalates can contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
How This Shapes Our View of Plants
Understanding the diverse roles of oxalic acid provides a deeper insight into the complexity of plant life and its interaction with the environment.
- If your primary focus is botany or agriculture: Recognize that a plant's chemical profile is a sophisticated balance between defense, growth, and internal nutrient management.
- If your primary focus is ecology: View oxalic acid as a key mediator in plant-herbivore interactions and a critical adaptation for a plant's success in specific soil conditions.
- If your primary focus is nutrition: Understand that a plant's natural defense chemicals are the reason certain foods must be consumed in moderation or prepared in specific ways.
Ultimately, oxalic acid demonstrates that even the simplest-looking plant is a master of complex biochemistry, constantly managing a silent battle for survival.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Defense | Deters herbivores and pathogens. | Sour taste; formation of sharp calcium oxalate crystals. |
| Internal Regulation | Manages mineral levels and detoxifies. | Binds excess calcium and toxic heavy metals like aluminum. |
| Trade-offs | Balances benefits with metabolic costs. | Energy investment; permanent sequestration of nutrients like calcium. |
Optimize Your Apiary's Health with HONESTBEE
Just as plants rely on sophisticated systems like oxalic acid for defense and balance, your commercial apiary depends on high-quality, reliable equipment for success. HONESTBEE supplies durable beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors through our wholesale-focused operations.
Let us help you build a stronger, more productive operation. Contact our team today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover the HONESTBEE difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 12V Bee Mite Removal Evaporator Oxalic Acid Vaporizer for Bee Fumigation Treatment 180W Atomization
- Oxalic Acid Vaporizer 12V for Bee Varroa Mite Treatment
- Heavy Duty 12V Oxalic Acid Evaporator Vaporizer for Bee Varroa Mite Treatment Beekeeping Fumigator Atomizer
- Durable 12V Oxalic Acid Vaporizer for Varroa Mite Treatment Beehive Beekeeping Tool
- Wooden Bee Hive Frames for Beekeeping and Wholesale
People Also Ask
- What are the operational benefits of using oxalic acid vaporizers? Optimize Honey Bee Parasite Treatment Efficiency
- What are the purity requirements for oxalic acid? Protect Your Bees with Pharmaceutical-Grade Standards
- What are the procedural steps for performing oxalic acid vaporization? A Step-by-Step Guide for Mite Control
- What is the role of using a sugar water solution for oxalic acid? Enhance Mite Control with Better Adhesion
- How is the dribble method of oxalic acid application performed? Master Precise Varroa Mite Control



















