For effective use of a queen excluder, the most critical steps are to ensure it is installed correctly with a tight fit, to regularly monitor it for blockages that could impede worker bees, and to confirm the queen remains confined to the brood chamber below. Proper installation and maintenance are essential to gain its benefits without hindering your hive's productivity.
A queen excluder is a tool of control, designed to separate the queen's brood nest from your honey supers. While it simplifies honey harvesting and ensures purity, this control comes with trade-offs that require careful management and observation.

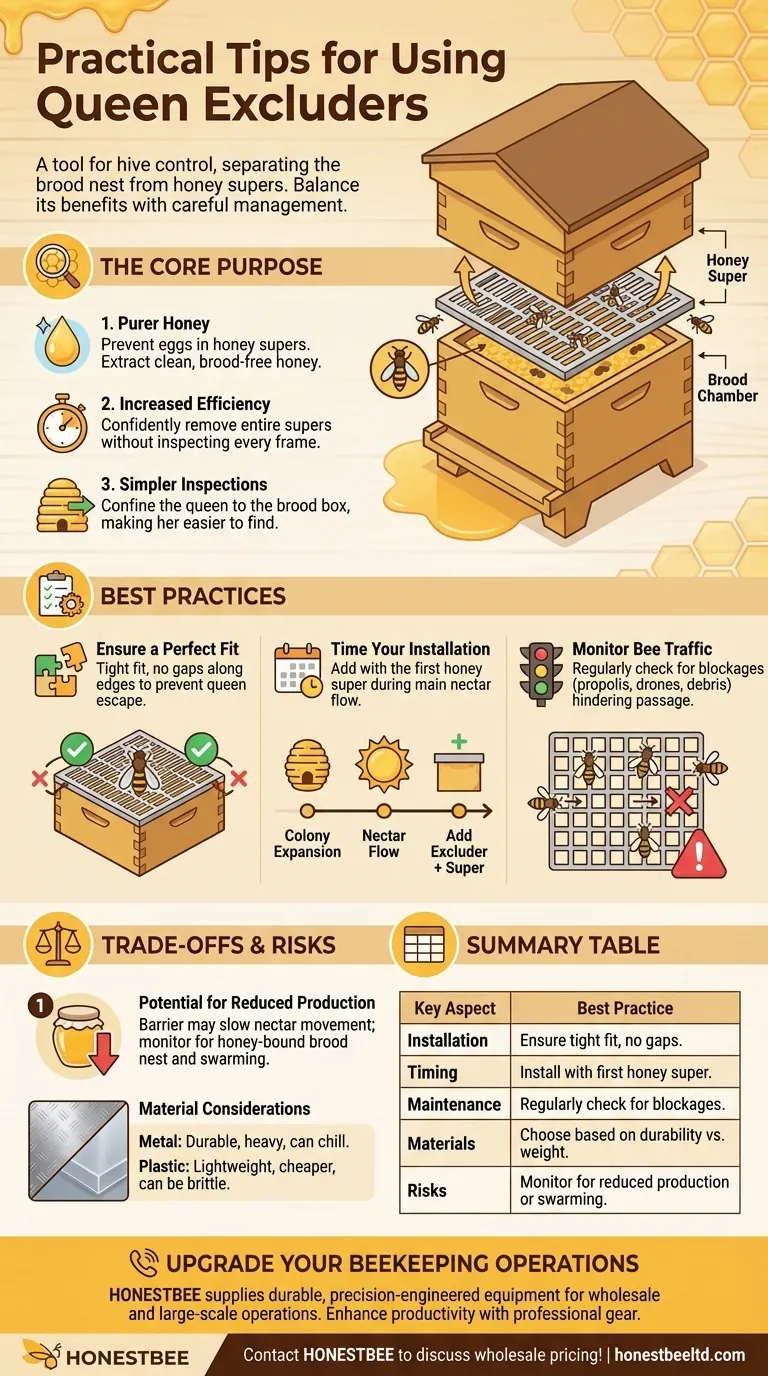
The Core Purpose of a Queen Excluder
Understanding why you are using an excluder is the first step toward using it correctly. It is fundamentally a tool for hive organization that serves several key purposes.
Producing Purer Honey
The primary goal is to prevent the queen from laying eggs in the honey supers.
Honey extracted from frames that have never contained brood is considered the purest and cleanest. It avoids the inclusion of shed cocoons, debris, or pollen that is often stored near developing bees.
Increasing Management Efficiency
For beekeepers, especially those with many hives, time is a critical factor.
An excluder allows you to remove entire honey supers for extraction with confidence, knowing you will not accidentally remove the queen or frames of brood. This eliminates the need to inspect every single frame during harvest.
Simplifying Hive Inspections
By placing an excluder, you confine the queen to a known area of the hive—the brood box.
This makes finding the queen significantly easier when you need to perform health checks, manage swarm potential, or requeen the colony.
Best Practices for Installation and Use
Proper technique transforms the excluder from a potential barrier into an effective management tool. Its success depends entirely on how it is implemented.
Ensure a Perfect Fit
The excluder must fit tightly across the top of the brood box, leaving no gaps along the edges.
Even a small space can allow a determined queen to squeeze through, defeating the entire purpose of the device.
Time Your Installation
There is no specific calendar date for adding an excluder.
It should be installed at the same time you add your first honey super, creating a clear boundary for the queen as the colony expands for the main nectar flow.
Monitor Bee Traffic
After installation, observe your bees. The worker bees must be able to pass through the grid without excessive difficulty.
Regularly check that the excluder has not become blocked by propolis, drone bees, or debris, as this can create a traffic jam and slow down honey production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Using a queen excluder is not without its potential downsides. An objective beekeeper understands these risks and manages against them.
Potential for Reduced Honey Production
The excluder is a physical barrier, and some bees may be hesitant to cross it.
This can slow the movement of nectar into the supers. If the brood nest becomes "honey-bound" (filled with nectar), it can limit the queen's laying space and potentially trigger swarming.
Material Considerations
Excluders are typically made of metal or plastic, and the choice has practical implications.
Metal excluders are more durable but can be heavy and may chill bees in colder climates. Plastic excluders are lighter and cheaper but can be more brittle over time.
Advanced Uses Beyond Honey Production
The excluder is a versatile tool for more than just honey supers.
It can be used to separate queens in a two-queen system or as a diagnostic tool. By placing it between two brood boxes, you can wait a few days and then check for eggs to determine which box contains the queen.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, whether and how you use a queen excluder should be dictated by your specific beekeeping philosophy and objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximum honey purity and harvest efficiency: Use an excluder, but remain vigilant in monitoring bee traffic and the condition of the brood nest.
- If your primary focus is minimal hive interference: You can choose to operate without an excluder, but be prepared to manage brood mixed in with your honey frames.
- If you need to find the queen or manage a specific hive issue: The excluder is an invaluable tool for temporarily isolating the queen and simplifying complex hive manipulations.
Treat the queen excluder as a strategic instrument that, when understood and applied thoughtfully, enhances your control over the hive.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Installation | Ensure a tight fit with no gaps to prevent queen escape. |
| Timing | Install when adding the first honey super during nectar flow. |
| Maintenance | Regularly check for blockages (propolis, drones) to maintain bee traffic. |
| Materials | Choose metal for durability or plastic for lightweight use. |
| Risks | Monitor for reduced honey production or swarming triggers. |
Upgrade Your Beekeeping Operations with Professional Equipment
For commercial apiaries and distributors, efficient tools like queen excluders are essential for scaling honey production and maintaining hive health. HONESTBEE supplies durable, precision-engineered beekeeping supplies and equipment tailored for wholesale and large-scale operations.
Let us help you enhance your productivity with reliable gear designed for professional beekeepers. Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your equipment needs and wholesale pricing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- Wooden Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- Premium Wood Framed Metal Wire Queen Bee Excluder
- Plastic Queen Bee Excluder for Bee Hive Wholesale
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of using metal queen excluders? Key Insights for Apiary Management
- What is the core function of a Queen Excluder in royal jelly production? Boost Yields with Behavioral Management
- What is the primary function of a Queen Excluder in honey purity? The Key to Commercial Grade Harvests
- What are the typical designs and materials of a queen excluder? Choose the Best Gear for Your Apiary Efficiency
- What function does a queen excluder serve? Boost Honey Purity and Breeding Accuracy



















