To maximize honey yields, a beekeeper must adopt a holistic approach focused on three core areas: building exceptionally strong and healthy colonies, ensuring access to abundant floral resources, and executing a timely, efficient harvest. It is not one single action but the cumulative effect of excellent year-round management that results in a significant honey surplus.
The central principle of maximizing honey yield is that a surplus is a byproduct of a thriving, unstressed colony. Your primary role is not to force production, but to remove obstacles and provide the resources your bees need to flourish naturally.

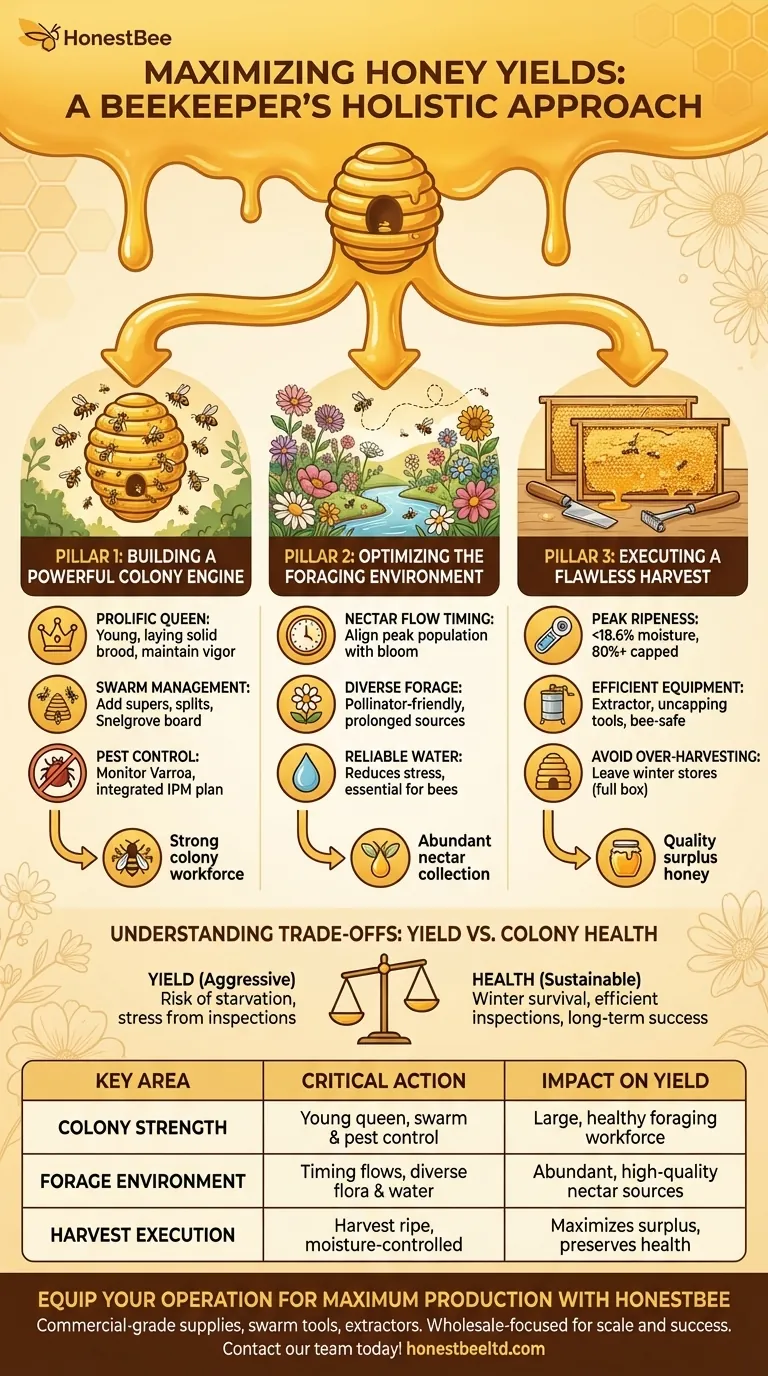
Pillar 1: Building a Powerful Colony Engine
The number of foraging bees is the single most significant factor in honey production. A large, healthy workforce is the engine of your honey-making operation.
The Critical Role of the Queen
A young, prolific queen is the foundation of a populous hive. She should be laying a solid, consistent brood pattern, ensuring a constant supply of new workers to replace the older foraging bees.
Consider replacing your queen every one to two years to maintain peak genetic vigor and egg-laying capacity.
Proactive Swarm Management
Swarming is a natural instinct, but it cuts your hive's workforce in half. Preventing swarms is essential for maximizing honey production.
Provide ample space by adding new boxes (supers) ahead of the colony's needs. Performing hive splits or using a Snelgrove board can also redirect the swarm impulse while retaining the bees.
Relentless Pest and Disease Control
Pests and diseases, particularly the Varroa mite, drain the colony's resources and weaken its overall health. A sick hive will consume honey stores rather than build them.
Regularly monitor for Varroa mites and treat them based on established economic thresholds. A consistent, integrated pest management (IPM) plan is not optional for serious honey production.
Pillar 2: Optimizing the Foraging Environment
Honey is simply concentrated plant nectar. Without access to a rich and diverse food source, even the strongest colony cannot produce a surplus.
Understanding the Nectar Flow
The nectar flow is the period when flowers are producing abundant nectar. Your entire management strategy should revolve around ensuring your colony reaches peak population just as the main flow begins.
Research the primary nectar-producing plants in your specific area and their typical bloom times. This knowledge allows you to time your interventions perfectly.
The Value of Diverse Forage
Monoculture crops can provide a massive, but short, nectar flow. A landscape with diverse and overlapping bloom times provides a more stable and prolonged source of nutrition.
If possible, plant pollinator-friendly flowers or establish relationships with landowners who have clover, alfalfa, or wildflower fields. Proximity to good forage is key.
Don't Forget Water
Bees need water to regulate hive temperature and humidity, and to dilute honey for consumption. A reliable, clean water source nearby reduces foraging stress and frees up bees for nectar collection.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Yield vs. Colony Health
Aggressively pursuing maximum yield can sometimes come at the expense of the bees' well-being. A wise beekeeper understands the balance.
The Danger of Over-harvesting
Never take all the honey. Always leave enough stores for the colony to survive the winter and the early spring.
A common rule is to leave a full deep box or the equivalent amount of honey for the colony's winter needs. Taking too much leads to starvation or expensive emergency feeding.
The Stress of Frequent Inspections
While inspections are necessary, opening the hive too often disrupts the colony's work and internal environment. It breaks the propolis seal and forces the bees to refocus on defense and repair.
Develop an efficient inspection routine. Have a clear goal for each inspection and complete it calmly and quickly.
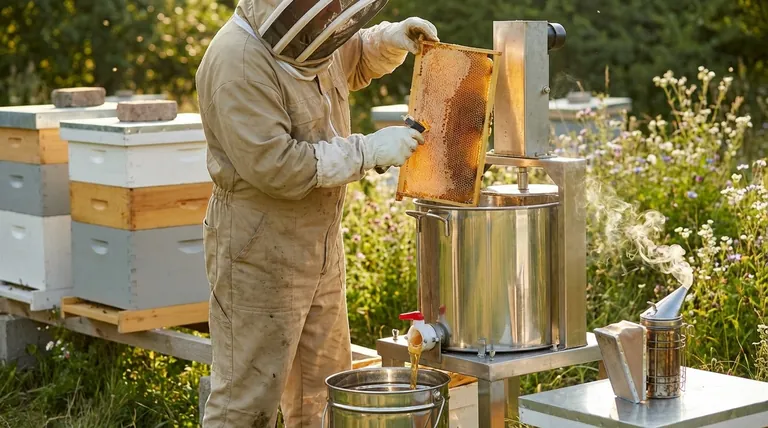
Pillar 3: Executing a Flawless Harvest
How and when you collect the honey directly impacts both your final yield and the colony's recovery.
Identifying Peak Ripeness
Honey is "ripe" when the bees have reduced its moisture content to below 18.6%. Harvesting "wet" honey will lead to fermentation and spoilage.
The visual cue is capped honey. Bees seal the cell with a wax capping when the honey is ready. A frame should be at least 80% capped before you harvest it. A refractometer provides a precise measurement of moisture content for ultimate quality control.
Using the Right Equipment
Efficient harvesting minimizes stress on the bees and maximizes the honey you collect. Essential tools include a hive tool, a smoker, bee-safe escape methods, and an uncapping tool.
For more than a few hives, a centrifugal honey extractor is non-negotiable. It removes honey from the comb efficiently without destroying the drawn-out wax, which saves the bees immense energy on the next flow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach should align with your specific beekeeping objectives.
- If your primary focus is starting out: Concentrate exclusively on colony health, pest management, and helping your bees survive their first year.
- If your primary focus is maximizing surplus: Master swarm control and ensure your hive population peaks precisely with the main nectar flow in your area.
- If your primary focus is efficiency at scale: Invest in high-quality extracting equipment and systems that minimize bee stress during the harvest.
Ultimately, successful honey production is a partnership where you support the natural productivity of a healthy, thriving honey bee colony.
Summary Table:
| Key Area | Critical Action | Impact on Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Colony Strength | Young, prolific queen; proactive swarm & pest control | Creates a large, healthy foraging workforce |
| Forage Environment | Timing with nectar flows; providing diverse flora & water | Ensures abundant, high-quality nectar sources |
| Harvest Execution | Harvesting ripe (>80% capped), moisture-controlled honey | Maximizes collected surplus while preserving colony health |
Ready to equip your operation for maximum honey production?
At HONESTBEE, we supply the durable, high-performance beekeeping supplies and equipment that commercial apiaries and distributors rely on to build strong colonies and execute efficient harvests. From swarm management tools to commercial-grade honey extractors, our wholesale-focused operations are designed to support your scale and success.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and see how we can help you achieve a greater honey surplus.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Stainless Steel Honey Press Wax Press with Tank
- Stainless Steel Manual Honey Press with Guard for Pressing Honey and Wax
- Honey Wax Separating Wax Press with Metal Screw Wax Separator Machine
- Modern Honeycomb Pattern Wooden Honey Dipper for Stirring and Drizzling
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a honey press for Warré or Top Bar beehives? Maximize Your Natural Harvest
- What are the unique characteristics of honey presses? Maximize Honey Yield for Small-Scale Beekeeping
- What are the material advantages of using a stainless steel honey press? Ensure Pure, Lead-Free Honey Extraction
- What are the advantages of using industrial-grade stainless steel honey extractors vs. traditional methods?
- What are the key features of a honey press? Maximize Yield with Durable, Efficient Extraction



















