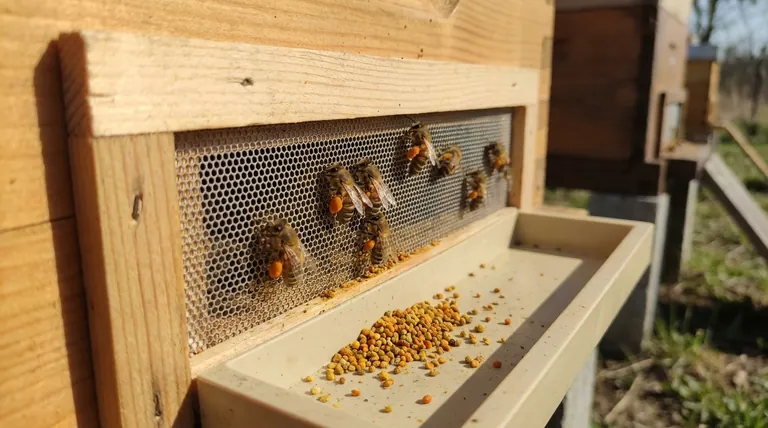
In essence, a pollen trap works by scraping pollen off a bee's legs. The device fits over a hive's entrance and forces returning forager bees to squeeze through a screen or a plate with small holes. These openings are just large enough for the bee to pass but small enough to knock the compacted pollen pellets from its hind legs, where they fall into a collection tray below for the beekeeper to harvest.
A pollen trap is a mechanical filter placed at the hive entrance. It intercepts a fraction of the pollen carried by returning bees, allowing beekeepers to collect this protein source without completely depriving the colony of its resources.

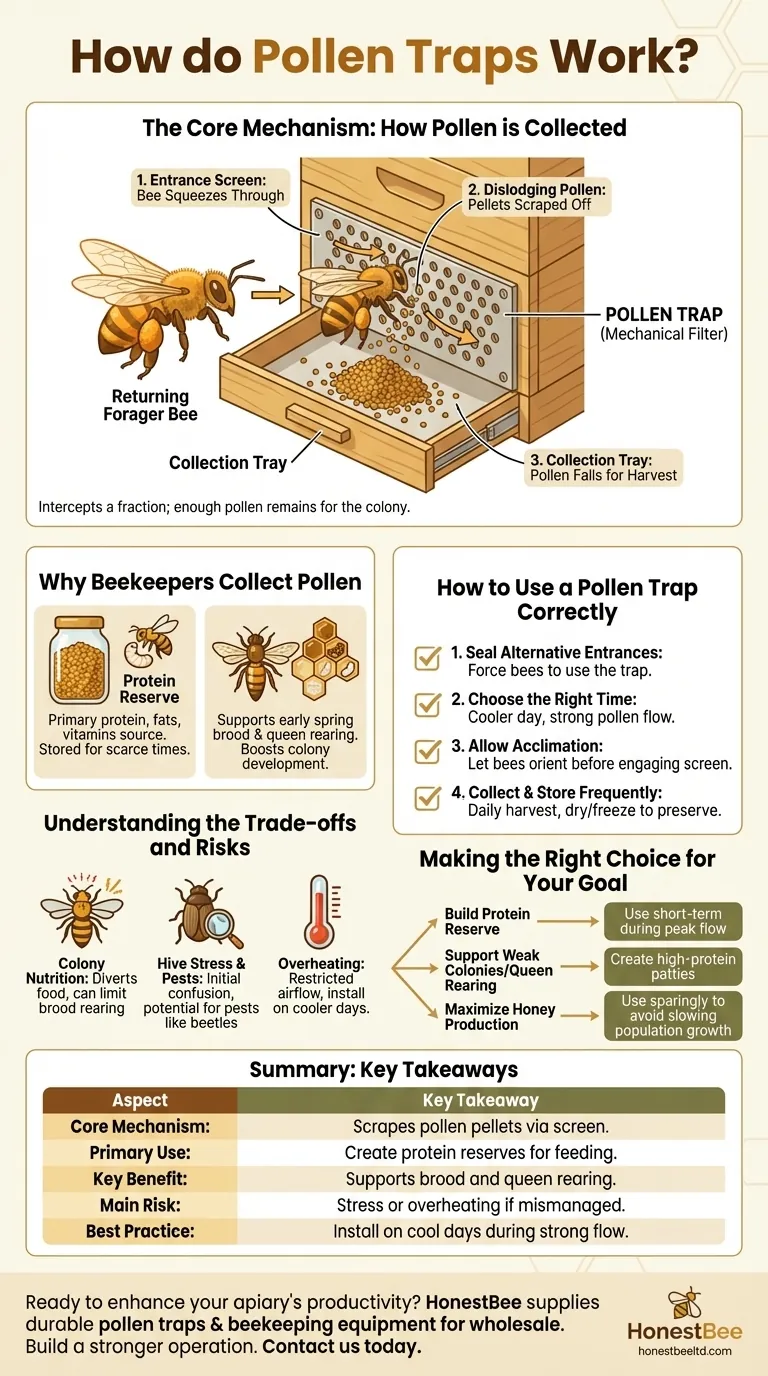
The Core Mechanism: How Pollen is Collected
A pollen trap is a simple but effective device with three main components working in sequence to harvest pollen granules from bees.
The Entrance Screen
The heart of the trap is a screen or perforated plate that partially obstructs the hive entrance. This screen features holes that are specifically sized—typically around 5 millimeters—to allow a worker bee to pass through.
Dislodging Pollen Pellets
As a returning forager bee, laden with pollen packed into its pollen baskets (corbiculae) on its hind legs, squeezes through one of these holes, the edges of the opening scrape against its legs. This action dislodges one or both of the pollen pellets.
The Collection Tray
The dislodged pellets fall through the screen and land in a collection tray or drawer positioned underneath. This tray protects the collected pollen from the elements and the bees, allowing the beekeeper to easily remove and harvest it. The trap is designed so that enough bees still make it through with their pollen loads intact to feed the colony.
Why Beekeepers Collect Pollen
Harvesting pollen isn't just for human consumption; it's a critical beekeeping practice for ensuring colony health and resilience, especially during key moments in the season.
Creating a Protein Reserve
Pollen is the bees' primary source of protein, fats, and vitamins, which are essential for raising new bees (brood). Beekeepers collect pollen during times of abundance to create a reserve. This stored pollen can be fed back to the bees during early spring or other periods when natural pollen is scarce.
Supporting Brood and Queen Rearing
This reserve of high-quality protein is invaluable for stimulating early spring brood rearing before natural sources are available. It is also used to create supplemental pollen patties, often mixed with soybean flour or brewer's yeast, to ensure strong colony development and support robust queen rearing operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While effective, using a pollen trap requires careful management. It is an intervention that changes the hive's natural dynamics and carries potential risks if not implemented correctly.
Impact on Colony Nutrition
The most obvious trade-off is that you are diverting food from the colony. A trap only collects a portion of incoming pollen, but continuous use during a poor pollen flow can stress a hive and limit its ability to raise brood.
Potential for Hive Stress and Pests
Forcing bees through a new, constricted entrance can cause initial confusion and stress. It can take them hours or even a few days to adjust. Furthermore, some trap designs can inadvertently attract and harbor pests like small hive beetles.
Risk of Overheating
By restricting the main entrance, a pollen trap can reduce airflow and ventilation within the hive. Installing a trap on a very hot day can contribute to overheating, making it crucial to choose a cooler day for installation.
How to Use a Pollen Trap Correctly
Proper installation and management are key to a successful and safe pollen harvest that doesn't harm your colony.
Seal All Alternative Entrances
For the trap to be effective, the bees must be forced to use the entrance it covers. Before installation, ensure you have sealed any other cracks or holes in the hive bodies that bees might use as an alternative entrance.
Choose the Right Time to Install
Install the trap on a cooler day to mitigate the risk of overheating from reduced ventilation. It's also best to install it during a strong pollen flow so you are only harvesting a true surplus.
Allow for an Acclimation Period
Once the trap is installed, give the bees time to orient themselves to the new entrance. Do not engage the pollen-stripping screen immediately. Let them use the new entrance for a day or two before you begin collecting pollen. For top-entrance traps, it's wise to orient the bees to a simple top entrance for a week or two before installing the trap itself.
Collect and Store Pollen Frequently
Harvest pollen from the collection tray daily to prevent mold, spoilage, and pest infestation. Fresh pollen must be dried or frozen immediately to preserve its nutritional quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using a pollen trap is a strategic decision that depends entirely on your objectives as a beekeeper.
- If your primary focus is to build a protein reserve for next season: Use the trap for short periods during peak pollen flows to harvest surplus without impacting the colony's current needs.
- If your primary focus is to support weak colonies or queen rearing: The harvested pollen is an invaluable resource for creating high-protein patties to boost brood production when it's needed most.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: Use pollen traps sparingly, as diverting protein resources can slow the population growth required to forage for a large nectar surplus.
Ultimately, a pollen trap is a powerful tool for proactive hive management when used with a clear understanding of its impact.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Scrapes pollen pellets from bees' legs as they pass through a screen. |
| Primary Use | Harvesting pollen to create protein reserves for colony feeding. |
| Key Benefit | Supports early spring brood rearing and queen rearing operations. |
| Main Risk | Can stress the colony if not managed correctly, especially in heat. |
| Best Practice | Install during a strong pollen flow on a cooler day. |
Ready to enhance your apiary's productivity with the right equipment?
HONESTBEE supplies durable, well-designed beekeeping supplies and equipment—including pollen traps—to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations. Let us help you build a stronger, more resilient operation.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our products support superior hive management.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
- Removable Washable Hive Beetle Trap Attractants for Small Hive Beetles
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
- Professional Hive Front Entrance Bee Feeder
- Wooden Bee Brush with Double-Row Horsehair Bristles
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of vacuum packaging systems on the sensory quality of bee pollen? Balancing Flavor and Stability
- How does high-concentration honey reduce bee pollen fungal load? Master Natural Sterilization Techniques
- How does a perforated steel plate pollen trap assist in evaluating honeybee pollination? Data-Driven Colony Insights
- How do precision temperature-controlled drying ovens improve the purity of bee pollen? Achieve High-Quality Dehydration
- What role do pollen traps play in the traceability of royal jelly? Secure Botanical Authenticity and NMR Accuracy
- What is the primary function of a pollen trap in commercial apiculture? Boost Efficiency and Research Accuracy
- What is the function of high-precision constant temperature and humidity incubators? Mastering Bee Pollen Fermentation
- What are the differences between bottom-mounted and top-mounted pollen traps? Choose the Right Trap for Your Hive



















