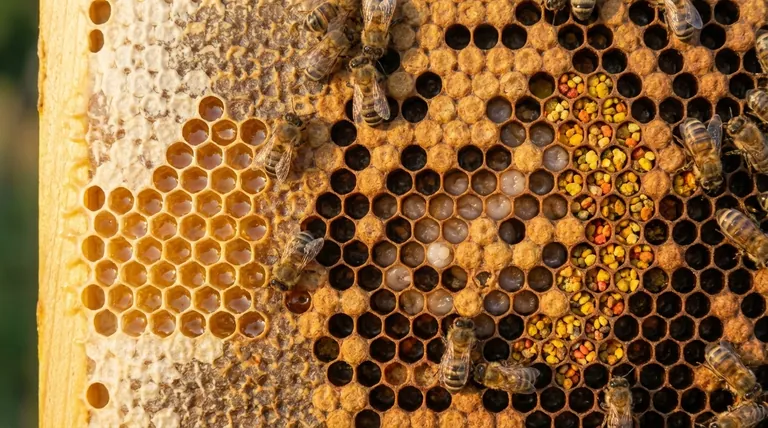
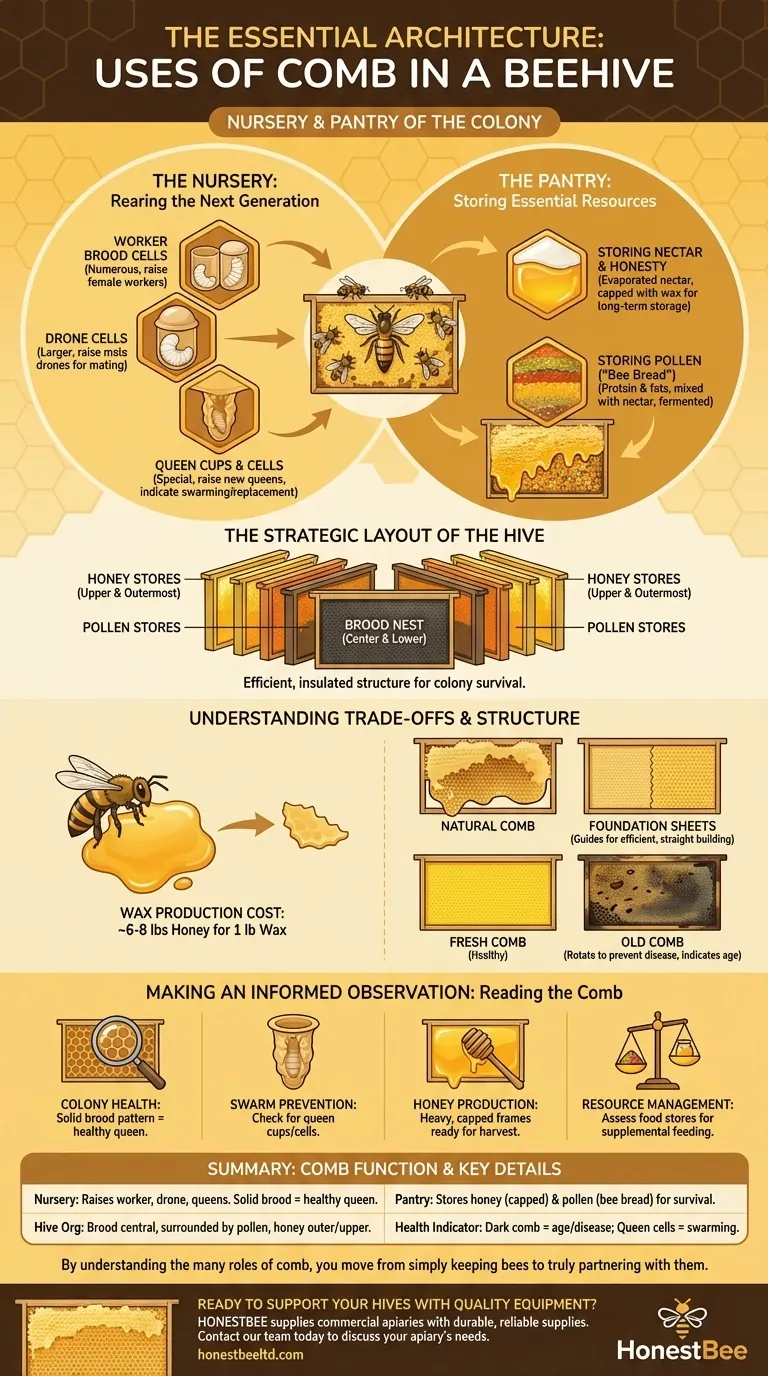
In a beehive, comb is the essential architecture of the colony. It serves as the nursery for raising new bees, the pantry for storing all food, and a physical communication network for the entire population. The two primary functions of beeswax comb are to raise brood (the collective term for eggs, larvae, and pupae) and to store the colony's food supply of honey and pollen.
Beyond simple storage, the comb is a dynamic record of the colony's life. Its structure reveals the queen's health, the availability of resources, and the hive's plans for future growth and reproduction.

The Comb as a Nursery: Rearing the Next Generation
The central purpose of the hive is perpetuation, and the comb is where it all begins. The queen lays eggs in different types of cells, each designed for a specific type of bee.
Worker Brood Cells
These are the most numerous cells in the hive. They are the standard hexagonal cells used to raise female worker bees, which constitute the vast majority of the colony's population. A solid, contiguous pattern of capped worker brood is a key indicator of a healthy, productive queen.
Drone Cells
Drone cells are noticeably larger than worker cells. The colony constructs these to raise male bees, or drones, whose sole purpose is to mate with a new queen. A significant presence of drone comb indicates a strong, well-fed colony that has enough resources to invest in reproduction.
Queen Cups and Cells
To raise a new queen, the workers build special, downward-facing cells that resemble a peanut shell. They begin as small queen cups and are elongated into full queen cells once the queen lays an egg inside. Observing these is critical for the beekeeper, as it signals the colony is preparing to swarm or replace its current queen.
The Hive's Pantry: Storing Essential Resources
A colony's survival depends on its ability to store food for periods when outside resources are scarce, such as winter or during a nectar dearth.
Storing Nectar and Honey
Bees collect nectar and store it in comb cells. They then fan their wings to evaporate the water content, transforming the nectar into honey. Once the honey is "cured" to the right consistency, the bees cap the cell with a fresh layer of white beeswax for long-term storage.
Storing Pollen ("Bee Bread")
Pollen is the colony's primary source of protein and fats, essential for feeding developing larvae. Bees pack pollen into cells, mix it with a small amount of nectar, and allow it to ferment slightly, creating what is known as bee bread.
The Strategic Layout of the Hive
The comb is not arranged randomly. Bees typically organize their hive with the brood nest in the center and lower portions of the frames. This is surrounded by a ring of pollen, with the honey stores located in the upper and outermost areas of the hive, creating an efficient and insulated structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Structure
The comb is a costly resource for the colony to produce, and its management has significant implications for hive health.
The Cost of Wax Production
Producing beeswax is metabolically demanding. Bees must consume large quantities of honey—estimates suggest around 6-8 pounds of honey—to produce just one pound of wax. This is a significant energy expenditure for the colony.
Natural Comb vs. Foundation
To ease this burden and ensure straight, manageable combs, beekeepers often provide foundation sheets—thin sheets of beeswax or plastic with the hexagonal pattern imprinted on them. Bees use this as a guide, building out the comb structure much more quickly and efficiently than they would with no guide.
The Lifespan of Comb
Over time, comb used for brood rearing becomes dark and saturated with old cocoons and traces of pathogens. To maintain colony health and prevent the buildup of disease, beekeepers should periodically rotate out old, dark frames and allow the bees to build fresh comb.
What the Comb Tells You: Making an Informed Observation
Your ability to "read" the comb is the most important skill for successful hive management. The state of the comb provides direct insight into the colony's condition and intentions.
- If your primary focus is colony health: Look for a solid, consistent brood pattern, which indicates a healthy, well-laying queen.
- If your primary focus is swarm prevention: Regularly check for the presence of newly built queen cups or fully developed queen cells.
- If your primary focus is honey production: Identify frames that are heavy and filled with white, capped honey, as these are ready for harvest.
- If your primary focus is resource management: Assess the stores of pollen and honey to determine if the colony has enough food or requires supplemental feeding.
By understanding the many roles of comb, you move from simply keeping bees to truly partnering with them.
Summary Table:
| Comb Function | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Nursery (Brood Rearing) | Raises worker bees, drones, and queens. A solid brood pattern indicates a healthy queen. |
| Pantry (Food Storage) | Stores honey (capped with wax) and pollen (as 'bee bread') for survival. |
| Hive Organization | Brood is central, surrounded by pollen, with honey stored in the upper/outer areas. |
| Colony Health Indicator | Dark comb signals age and potential disease; queen cells indicate swarming or supersedure. |
Ready to Support Your Hives with Quality Equipment?
As a beekeeper, you know that healthy comb is the foundation of a thriving colony. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, reliable supplies needed to build and manage strong hives efficiently.
From high-quality foundations to essential hive tools, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the equipment your bees deserve.
Let's build stronger hives together. Contact our team today to discuss your apiary's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Beeswax Comb Foundation Machine Wax Foundation Mill Embossing Machine
- Colorful Silicone Beeswax Foundation Mold Mould for Beekeeping
- Professional Frame Preparation: The HONESTBEE Electric Wire Embedder
- Electric Beeswax Foundation Machine With Operating Tray and Wax Foundation Roller
- Food Grade Plastic bee Foundation for Bee Frames
People Also Ask
- What texture is embossed on the beeswax foundation machine? The Precise Worker Bee Cell Pattern for Hive Efficiency
- What are the primary applications of fully automatic wax foundation machines? Maximize Your Apiary Production Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a manual honeycomb embossing machine? Create Custom Beeswax Foundations with Ease
- What is the use of a comb foundation mill? Boost Honey Production with Strategic Hive Control
- How does the measurement of wax foundation dimensions assist in honeybee study? Unlock Insights into Breed Evolution



















