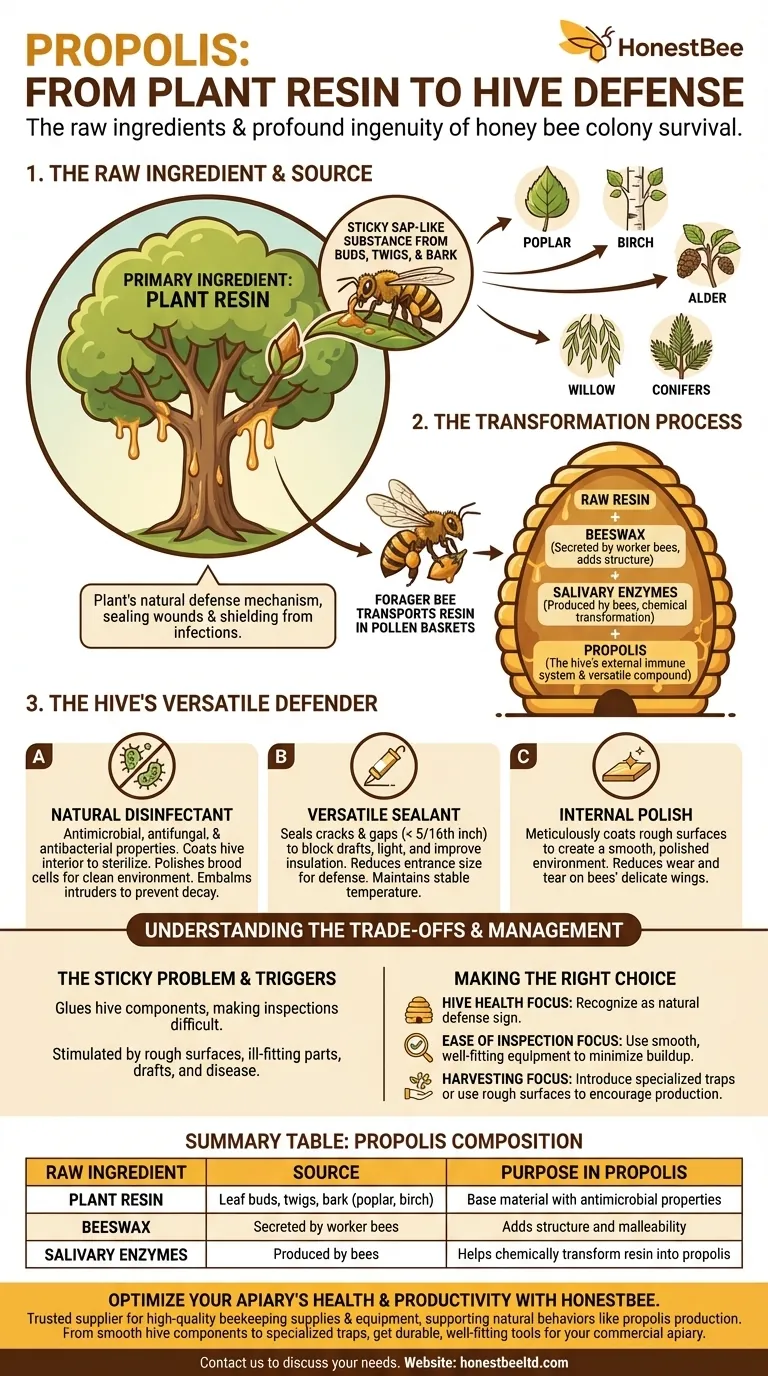
The primary raw ingredient honey bees collect to create propolis is plant resin. This sticky, sap-like substance is gathered from the leaf buds, twigs, and bark of various trees and plants. The bees then process this resin, transforming it into the versatile compound they use to protect and maintain the hive.
Propolis is far more than a simple glue. It is the hive's external immune system, a sophisticated substance borrowed from the plant world and repurposed by honey bees to serve as a disinfectant, a sealant, and a structural reinforcement.

The Source of Propolis: From Plant to Hive
To understand propolis, we must first understand its origin. The bees do not invent it from scratch; they are expert chemists who collect and refine a powerful natural resource.
What is Plant Resin?
Plant resin is a thick, sticky substance that trees exude to protect themselves. It functions as a plant's natural defense mechanism, sealing wounds in the bark and shielding buds from infections, fungi, and insect attacks.
Where Do Bees Find These Resins?
Forager bees seek out specific resin-producing plants in their local environment. Common sources include deciduous trees like poplar, birch, alder, and willow, as well as various conifers. The specific chemical makeup of propolis varies based on the regional flora available to the bees.
The Collection Process
A forager bee uses its mandibles to scrape off the sticky resin from a plant. It then transfers the substance to the pollen baskets on its hind legs, much like it carries pollen. Once its baskets are full, it returns to the hive where other worker bees help unload and process the raw material.
The Purpose of Propolis: The Hive's Versatile Defender
Once back in the hive, the raw resin is mixed with beeswax and salivary enzymes to create the final product: propolis. The colony uses this compound in several critical ways that ensure its health and security.
A Natural Disinfectant
Propolis possesses powerful antimicrobial, antifungal, and antibacterial properties. Bees coat the interior of the hive with a thin layer of it, effectively sterilizing their living space. Brood cells are polished with propolis before the queen lays eggs, providing a clean environment for developing larvae.
Bees also use it as an embalming agent. If an intruder like a mouse or large beetle is killed inside the hive and is too large for the bees to remove, they will encase the carcass in propolis, preventing its decay and the spread of disease.
A Versatile Sealant
Bees use propolis as a construction material to seal any unwanted cracks or gaps in the hive, particularly those smaller than 5/16th of an inch. This caulking action helps to block drafts, prevent unwanted light from entering, and improve insulation, helping the colony maintain a stable internal temperature. They may also use it to reduce the size of the hive entrance for better defense.
An Internal Polish
Rough surfaces inside the hive can damage the bees' delicate wings. The bees meticulously coat these surfaces with propolis, creating a smooth and polished environment that reduces wear and tear on the colony's members.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Beekeeper's Perspective
While essential for the bees, propolis presents a unique challenge for the beekeeper. Understanding what stimulates its production is key to managing a hive effectively.
The Sticky Problem
Bees apply propolis to any uneven surface or small gap, which includes the tiny spaces between hive boxes and around the edges of frames. This can effectively glue the components of a hive together, making routine inspections difficult and requiring a hive tool to pry them apart.
What Stimulates Production?
A colony is more likely to produce large amounts of propolis under specific conditions. These triggers include rough interior surfaces, ill-fitting hive parts, drafts, and the presence of disease. Essentially, anything that compromises the structural or sanitary integrity of the hive will stimulate the bees' instinct to seal and sterilize.
Making the Right Choice for Your Hive
Thinking about propolis production allows you to better understand the state of your colony. You can use this knowledge to manage your hive according to your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is hive health: Recognize that propolis production is a natural and beneficial sign of a colony actively defending itself.
- If your primary focus is ease of inspection: Use smooth, high-quality, and well-fitting hive components to minimize the gaps that encourage excessive propolis use.
- If your primary focus is harvesting propolis: Introduce specialized propolis traps or use rough-sawn lumber to encourage the bees to produce more of this valuable substance for collection.
Ultimately, understanding propolis is understanding the profound ingenuity of a honey bee colony to harness nature for its own survival.
Summary Table:
| Raw Ingredient | Source | Purpose in Propolis |
|---|---|---|
| Plant Resin | Leaf buds, twigs, and bark of trees (e.g., poplar, birch) | Base material with antimicrobial properties |
| Beeswax | Secreted by worker bees | Adds structure and malleability |
| Salivary Enzymes | Produced by bees during processing | Helps chemically transform resin into propolis |
Optimize your apiary's health and productivity with HONESTBEE. As a trusted supplier of beekeeping supplies and equipment for commercial apiaries and distributors, we provide high-quality tools that support natural behaviors like propolis production. Whether you need smooth hive components to minimize propolis buildup or specialized traps for harvesting, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get durable, well-fitting equipment. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Wide Blade Honey Scraper for Beekeeping and Honey Processing
- Professional Long-Handled Silicone Honey Scraper for Beekeeping
- Honey Wax Separating Wax Press with Metal Screw Wax Separator Machine
- Stainless Steel Honey Press Wax Press with Tank
- Stainless Steel Pail Perch Bucket Bench
People Also Ask
- Why is my honey frame not capped? Your Guide to Perfectly Ripe Honey
- Can I extract uncapped honey? Avoid spoilage by trusting the bees' quality control.
- What tools are available for uncapping honey? A Guide to Choosing the Right Tool for Your Operation
- What role does the specialized scraper play in bee venom collection? Optimize Your Yield and Purity
- Why are my bees not capping honey? Understand the Key to Perfect Honey Ripening



















