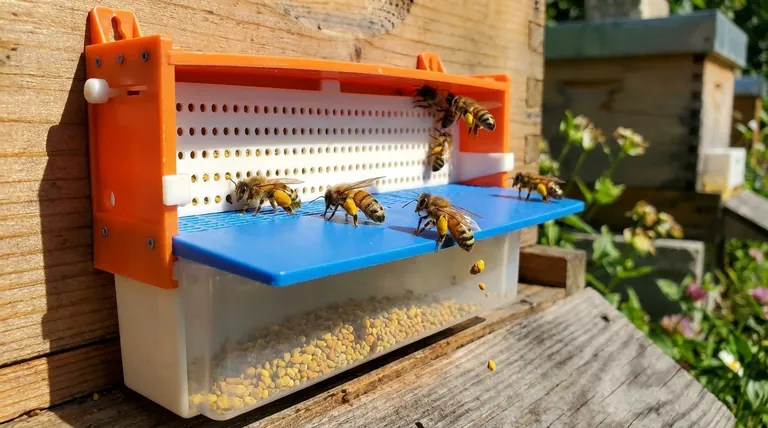
A pollen trap is a specialized beekeeping device that allows for the harvesting of fresh pollen from returning forager bees. It works by fitting over the hive entrance and forcing bees to pass through a screen or small openings, which gently scrape some of the pollen pellets from their legs. These dislodged pellets then fall through a mesh floor into a collection tray below for the beekeeper to gather.
A pollen trap is more than just a harvesting tool; it's a direct intervention in the hive's natural foraging cycle. Its effective use hinges on balancing the desire for collection against the colony's critical need for pollen to feed its young and thrive.

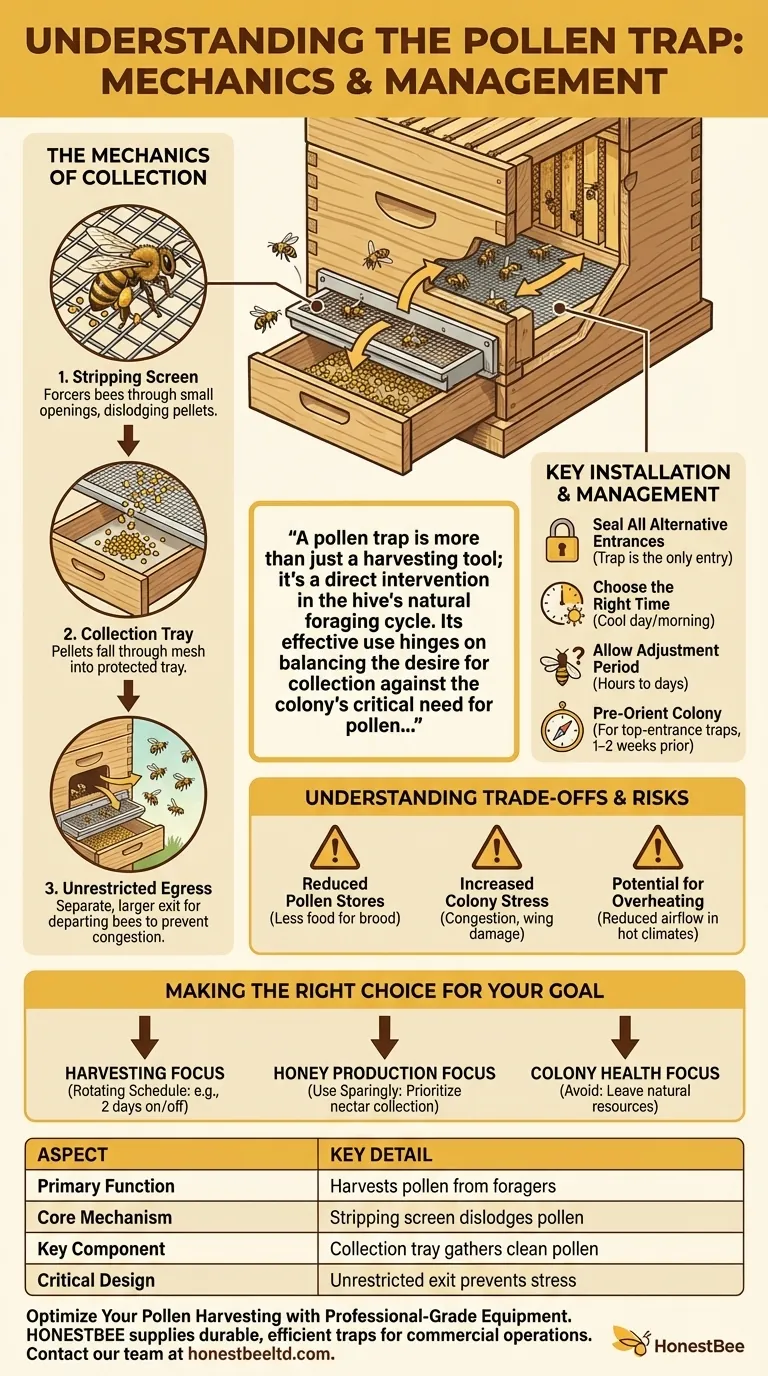
The Mechanics of Pollen Collection
A well-designed pollen trap is engineered to be effective at collection while minimizing disruption to the hive's daily operations.
The Stripping Screen
The core of the trap is the stripping screen. This component contains openings that are just large enough for a bee to squeeze through.
As the pollen-laden forager returns and pushes through an opening, the edges gently scrape against the pollen baskets (corbiculae) on her hind legs, dislodging one or both pellets.
The Collection Tray
Directly beneath the stripping screen lies a mesh floor and a collection tray or drawer. The dislodged pollen pellets fall through the mesh and land in the tray, protected from the bees.
This design keeps the collected pollen clean and allows for easy removal by the beekeeper without significant disturbance to the colony.
Unrestricted Egress
Critically, a good trap is designed to only restrict returning bees. It provides a separate, larger, and unrestricted exit so that bees leaving the hive can do so freely.
This prevents traffic jams at the entrance and reduces unnecessary stress on the colony's foragers.
Key Installation and Management Practices
Proper implementation is essential to ensure the trap is effective and does not harm the colony.
Seal All Alternative Entrances
Before installation, you must ensure the trap is the only way in or out of the hive. Bees are resourceful and will quickly find any other cracks or holes, bypassing the trap entirely.
Choose the Right Time
Install the trap on a cool day or in the morning before foraging activity peaks. A trap can reduce ventilation, so installing it during the hottest part of the day can contribute to overheating.
Allow for an Adjustment Period
Bees will be confused by the new obstacle. It can take anywhere from a few hours to a few days for them to fully adjust and learn how to navigate the new entrance.
Pre-Orient the Colony (Top-Entrance Traps)
If you are using a trap designed for a top entrance, it is vital to get the bees accustomed to using that entrance for 1-2 weeks before you install the trap itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While useful, a pollen trap is not a benign tool. It directly impacts the colony and must be used with care.
Reduced Pollen Stores
The most obvious impact is the removal of a primary food source. Pollen is the bees' only source of protein, which is essential for raising brood. Capturing it reduces the amount available for the nurse bees to feed the larvae.
Increased Colony Stress
Forcing every returning forager to squeeze through a tight opening is stressful. It can damage wings and slows down the process of entering the hive, creating congestion.
Potential for Overheating
By partially blocking the main entrance, a pollen trap can significantly reduce airflow. This is a serious risk in hot climates, as the colony can struggle to regulate its internal temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using a pollen trap should be a deliberate decision based on a clear objective, not a default practice.
- If your primary focus is harvesting fresh pollen: Use the trap on a rotating schedule (e.g., two days on, two days off) to allow the colony time to replenish its own stores.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: Use traps sparingly or not at all. Reduced pollen can lead to a smaller brood area, which in turn means a smaller future workforce available for nectar collection.
- If your primary focus is colony health and observation: Avoid using a trap unless you have a specific, short-term need. Always prioritize leaving all natural resources for the bees.
Ultimately, a pollen trap is a powerful tool when used with a clear understanding of its impact on the colony's delicate balance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Harvests pollen pellets from returning forager bees. |
| Core Mechanism | A stripping screen dislodges pollen as bees enter the hive. |
| Key Component | Collection tray gathers pollen, keeping it clean and accessible. |
| Critical Design | Provides an unrestricted exit to prevent forager stress and congestion. |
| Main Consideration | Balancing harvest with the colony's need for pollen as a protein source. |
Optimize Your Pollen Harvesting with Professional-Grade Equipment
As a commercial apiary or beekeeping equipment distributor, managing hive health while maximizing yield is your top priority. HONESTBEE supplies durable, well-designed pollen traps and other essential beekeeping supplies through our wholesale-focused operations. Our equipment is engineered for efficiency and minimal hive disruption, helping you achieve your production goals.
Ready to enhance your operation? Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and explore our full product catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 30 cm Plastic Entrance Hole Bee Pollen Trap and Collector
- Removable Plastic Pollen Trap With Ventilated Tray for Bees Pollen Collector
- Plastic Bee Pollen Trap Strips Comb Catcher Collector
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the function of pollen-collecting devices in monitoring pesticide exposure? Protect Your Forager Bees Today
- What is the function of a Pollen Trap in large-scale collection? Boost Efficiency with Automated Harvesting
- How do beehive entrance traps facilitate the sustainable harvesting of bee pollen? Optimize Your Apiary Yield
- What is the role of a front-mounted Pollen Trap in primary bee pollen harvesting? Maximize Your Commercial Yield
- What role does a Pollen Trap play in monitoring seasonal honey bee population dynamics? Optimize Your Hive Productivity



















