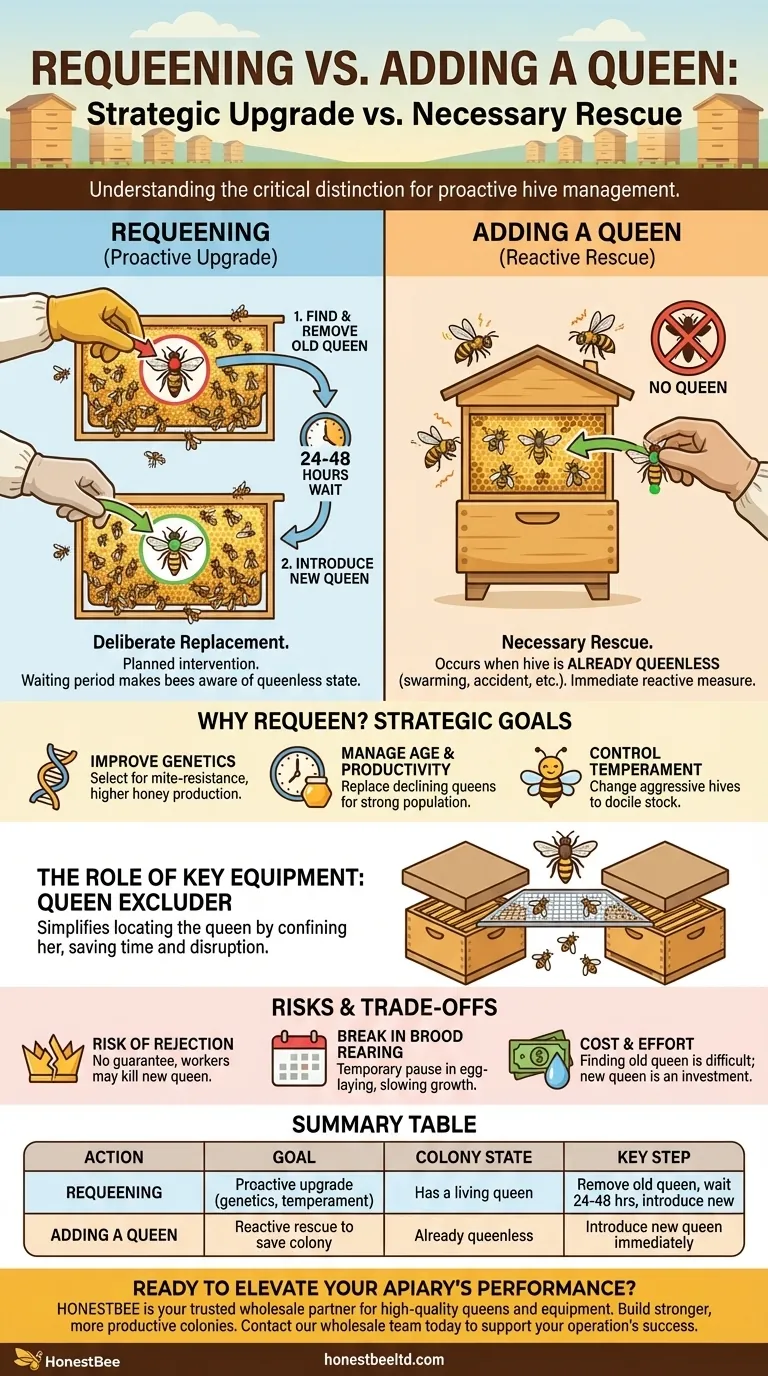
At its core, requeening is the deliberate process of replacing a honey bee colony's existing queen with a new one. This is fundamentally different from adding a queen to a queenless hive, which is a rescue operation. Requeening is a proactive management decision that requires the beekeeper to first find and remove the old queen, wait a specific period, and then introduce her replacement.
The critical distinction lies in intent and circumstance: requeening is a strategic upgrade for an existing colony, while adding a queen to a queenless hive is a necessary rescue to save a colony that has already lost its leader.

The Fundamental Difference: Removal vs. Rescue
The distinction between these two actions hinges on the initial state of the hive. One is a controlled procedure, while the other is a response to an emergency.
Requeening: A Deliberate Replacement
Requeening is a planned intervention. The process involves methodically finding the current queen, removing her from the colony, and then waiting 24 to 48 hours before introducing the new queen. This waiting period makes the bees aware of their queenless state, which increases their likelihood of accepting the newcomer.
Introducing: A Necessary Addition
This action occurs when a hive is already queenless. A colony might lose its queen due to swarming, old age, disease, or an accident during a hive inspection. In this scenario, the bees are already in a state of distress, and adding a new queen is a reactive measure to save the colony from collapse.
Why Requeen? The Strategic Goals of Hive Management
A beekeeper doesn't replace a queen without a good reason. This single decision can radically alter the future of the entire colony by influencing its genetics, behavior, and productivity.
Improving Colony Genetics
The queen determines the genetic makeup of the entire hive. By introducing a new queen from specific stock, a beekeeper can select for desirable traits like mite-resistance, higher honey production, or better overwintering ability. This is the primary driver behind the practice of queen rearing.
Managing Age and Productivity
A queen's egg-laying rate declines significantly after her second or third year. A decline in brood production leads to a smaller workforce and a less productive hive. Requeening with a young, vigorous queen ensures the colony maintains a strong population.
Controlling Colony Temperament
An aggressive hive can be a significant problem for the beekeeper and the surrounding area. Since the queen passes her genetics to all offspring, replacing the queen of an aggressive hive with one from docile stock can completely change the colony's temperament within a few brood cycles.
The Role of Key Equipment
Successfully finding the old queen is the most challenging part of requeening. Certain tools are designed to make this process more efficient.
Using a Queen Excluder
A queen excluder is a grid that is large enough for worker bees to pass through but too small for the queen. By confining the queen to specific boxes in the hive, an excluder drastically simplifies the process of locating her when it's time for replacement. This saves significant time and reduces disruption to the colony.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
Requeening is a powerful tool, but it is not without its challenges. Understanding the potential downsides is critical for success.
The Risk of Rejection
Even with proper procedure, there is no guarantee the colony will accept the new queen. The workers may reject and kill her, forcing the beekeeper to try again. The 24-48 hour queenless period is designed to minimize this risk, but it never eliminates it entirely.
A Temporary Break in Brood Rearing
There will be a gap between the removal of the old queen and the new queen beginning to lay eggs. This pause in brood production can temporarily slow the colony's population growth, which must be timed carefully around major nectar flows.
The Cost and Effort
Finding the old queen can be a time-consuming and difficult task, especially in a very large colony. Furthermore, purchasing a well-bred queen represents a financial investment in the hive's future.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to requeen is a strategic choice based on your specific objectives for the colony.
- If your primary focus is increasing honey production: Requeening with a young, prolific queen can build a massive workforce for the next season's honey flow.
- If your primary focus is managing colony temperament: Replacing the queen from an aggressive hive with one from docile stock is the most effective long-term solution.
- If your primary focus is controlling pests like Varroa mites: Introducing a queen with verified hygienic or mite-resistant genetics is a powerful, proactive management strategy.
Ultimately, successful requeening is about proactive management, shaping your colony's future rather than just reacting to its present.
Summary Table:
| Action | Goal | Colony State | Key Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Requeening | Proactive upgrade (genetics, temperament, productivity) | Has a living queen | Remove old queen, wait 24-48 hours, then introduce new queen |
| Adding a Queen | Reactive rescue to save the colony | Already queenless | Introduce new queen immediately to prevent collapse |
Ready to elevate your apiary's performance?
Successful requeening is a cornerstone of professional beekeeping. For commercial apiaries and distributors, having reliable access to high-quality, well-bred queens and the right equipment is essential for managing genetics, boosting honey yields, and ensuring colony health.
HONESTBEE is your trusted wholesale partner, supplying the beekeeping supplies and equipment you need to implement proactive hive management strategies effectively. We help you build stronger, more productive, and more resilient colonies.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your needs and how we can support your operation's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Multi-Functional Queen Bee Cage
- Multi-Function Queen Roller Cage and Catcher
- Wood and Mesh Push-In Queen Cage
- Durable Galvanized Steel Spring Queen Bee Cage
- Classic Wooden and Mesh California Queen Cage
People Also Ask
- How does relocating a commercial hive by 5 to 10 meters facilitate a multi-queen colony? Master Hive Social Engineering
- Why is high-precision measuring vital for Melipona subnitida yield? Transform Apiary Management with Scientific Data
- Why do smart beehive systems utilize LoRa wireless communication modules? The Key to Long-Range Apiary Connectivity
- Why are specialized transport vehicles critical for seasonal migration? Protect Your Apiary and Boost Efficiency
- What are the technical benefits of using transparent conduits? Enhance Your Honeybee Counting Accuracy
- Why is a high-precision analytical balance necessary for bee patty production? Ensure Hive Health with Precise Testing
- Why are stainless steel or glass containers recommended for the long-term storage of beeswax? Ensure Maximum Purity
- How does modern beekeeping equipment improve honey production? Boosting Yield and Quality in Entomoforestry



















