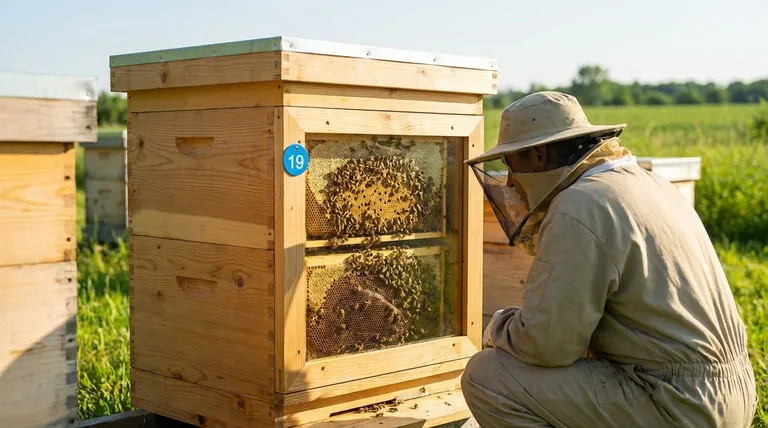
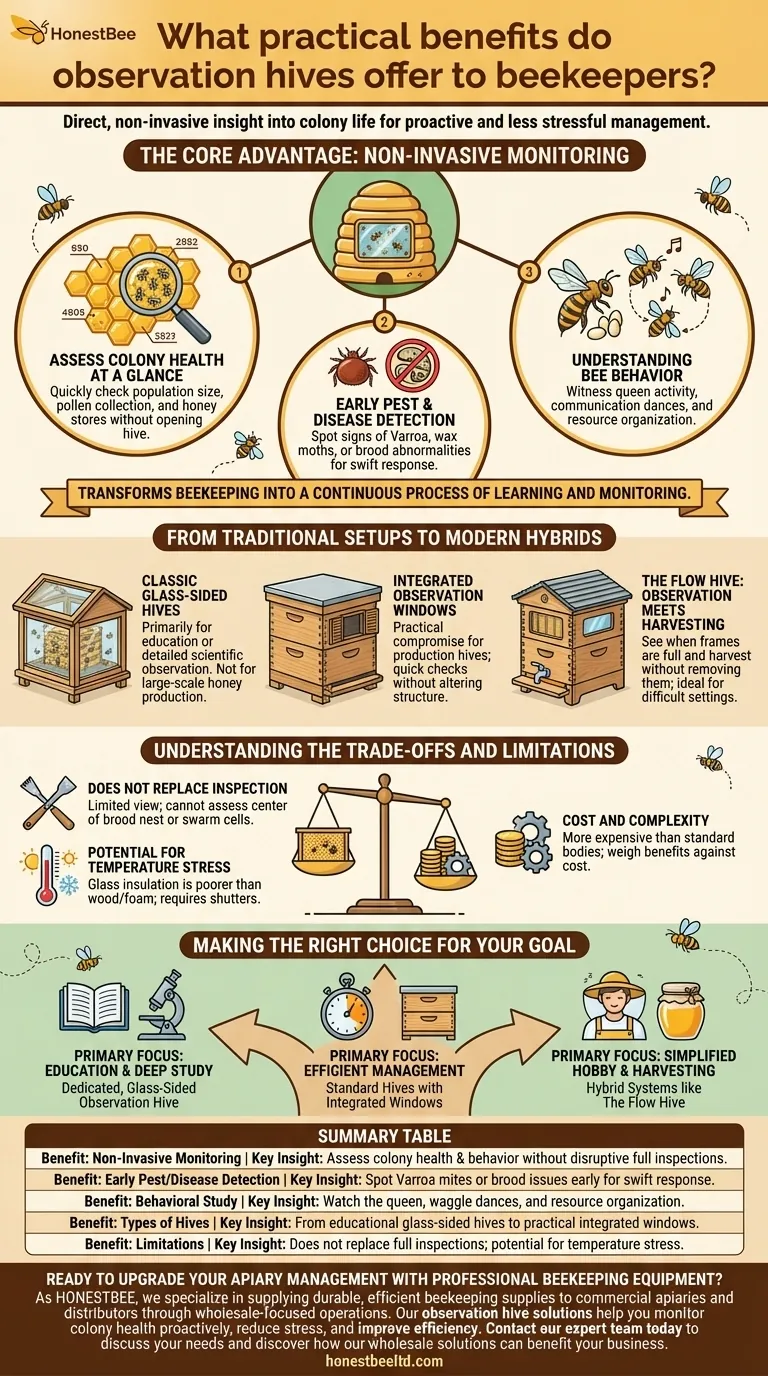
At its core, an observation hive offers a direct, non-invasive window into the life of your colony. This allows you to assess the health, productivity, and behavior of your bees without the disruption of a full hive inspection, enabling a more proactive and less stressful approach to management.
The true value of an observation hive is not replacing inspections, but supplementing them. It transforms beekeeping from a series of disruptive, periodic checks into a continuous process of learning and monitoring, allowing you to spot issues earlier and become a more attuned beekeeper.

The Core Advantage: Non-Invasive Monitoring
The primary benefit of any observation feature is the ability to gather crucial information without cracking open the hive. This minimizes stress on the colony and saves you time.
Assessing Colony Health at a Glance
With a clear view, you can quickly check key health indicators. You can get a sense of the population size, see if bees are actively bringing in pollen, and check the status of honey and nectar stores on the outer frames.
This visual check helps you decide if a full, hands-on inspection is truly necessary.
Early Pest and Disease Detection
Observation windows allow for the early detection of common threats. You might spot signs of a Varroa mite infestation, see evidence of wax moths, or notice abnormalities in the visible brood pattern that could signal disease.
Catching these problems early is critical for a swift and effective response, potentially saving the colony.
Understanding Bee Behavior
For many beekeepers, this is the most rewarding aspect. You can watch the queen lay eggs, witness the famous "waggle dance" used for communication, and observe how the colony organizes its resources.
This deepens your understanding of bee biology and transforms hive management from a chore into a fascinating study.
From Traditional Setups to Modern Hybrids
The term "observation hive" can refer to several different designs, each serving a slightly different purpose.
Classic Glass-Sided Hives
These are often smaller hives, sometimes with only a few frames, enclosed almost entirely in glass or plexiglass. They are designed primarily for educational purposes or detailed scientific observation.
While excellent for learning, they are not typically used for large-scale honey production due to their size and design.
Integrated Observation Windows
Many modern hive bodies, whether wood or EPS foam, now come with small, shuttered windows built into the side.
These offer a practical compromise, providing a quick-check feature on a full-size production hive without significantly altering its fundamental structure or insulation.
The Flow Hive: Observation Meets Harvesting
The Flow Hive is a specific, modern system that integrates observation windows with a unique honey-on-tap harvesting mechanism. This design allows you to see when frames are full and then harvest honey without removing them.
This is particularly useful in difficult settings, such as rooftops, as it eliminates the need to carry heavy, honey-filled boxes down from the apiary.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly beneficial, observation features are a tool with specific limitations. Understanding them is key to using them effectively.
Observation Does Not Replace Inspection
A window provides a limited view, usually of just one or two outer frames. You cannot see what is happening in the center of the brood nest, which is where the queen and youngest larvae reside.
You still must perform regular, full inspections to properly assess queen health, check for swarm cells between brood boxes, and comprehensively manage disease.
Potential for Temperature Stress
Glass is a poor insulator compared to wood or foam. Hives with very large glass panels can lose heat more rapidly in the winter and gain it too quickly in direct summer sun.
This can cause stress on the colony, which must work harder to maintain the stable internal temperature of 35°C (95°F) required for brood development. Most designs mitigate this with insulated shutters.
Cost and Complexity
Hives with integrated observation features or specialized systems like the Flow Hive are generally more expensive than basic, standard hive bodies. You must weigh the added cost against the benefits for your specific beekeeping goals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right observational tool depends entirely on what you want to achieve with your bees.
- If your primary focus is education and deep behavioral study: A dedicated, glass-sided observation hive is your best tool for an immersive view.
- If your primary focus is efficient management of a production apiary: Standard hives that incorporate small observation windows offer the best balance for quick, non-invasive checks.
- If your primary focus is simplified hobby beekeeping with easy harvesting: A hybrid system like the Flow Hive, which combines observation with a unique extraction method, may be the most convenient option.
Ultimately, incorporating observation into your beekeeping practice empowers you to become a more responsive and knowledgeable steward of your colonies.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Non-Invasive Monitoring | Assess colony health & behavior without disruptive full inspections. |
| Early Pest/Disease Detection | Spot Varroa mites or brood issues early for a swift response. |
| Behavioral Study | Watch the queen, waggle dances, and resource organization. |
| Types of Hives | From educational glass-sided hives to practical integrated windows. |
| Limitations | Does not replace full inspections; potential for temperature stress. |
Ready to upgrade your apiary management with professional beekeeping equipment?
As HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying durable, efficient beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors through wholesale-focused operations. Our observation hive solutions are designed to help you monitor colony health proactively, reduce stress on your bees, and improve your operational efficiency.
Let us help you choose the right equipment to meet your specific goals, whether for large-scale production or simplified hobby management. Contact our expert team today to discuss your needs and discover how our wholesale solutions can benefit your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Engraved Round Hive Number Tags for Beekeeping
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
- Professional Hive Front Entrance Bee Feeder
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
People Also Ask
- How can hive straps with hook ends be used to secure a beehive? Adapt Your Straps for Maximum Hive Stability
- What is the function of unique identification numbers and symbols for beehives in biosecurity management? Trace & Protect
- What is the purpose of a hive stand, and why is it beneficial? Elevate Your Hive for Colony Health and Beekeeper Comfort
- Why are weather-resistant numbered plastic tags essential for bee research? Master Long-Term Hive Data Continuity
- What is the purpose of leg straps in beekeeping attire? Secure Your Gear for Maximum Safety



















