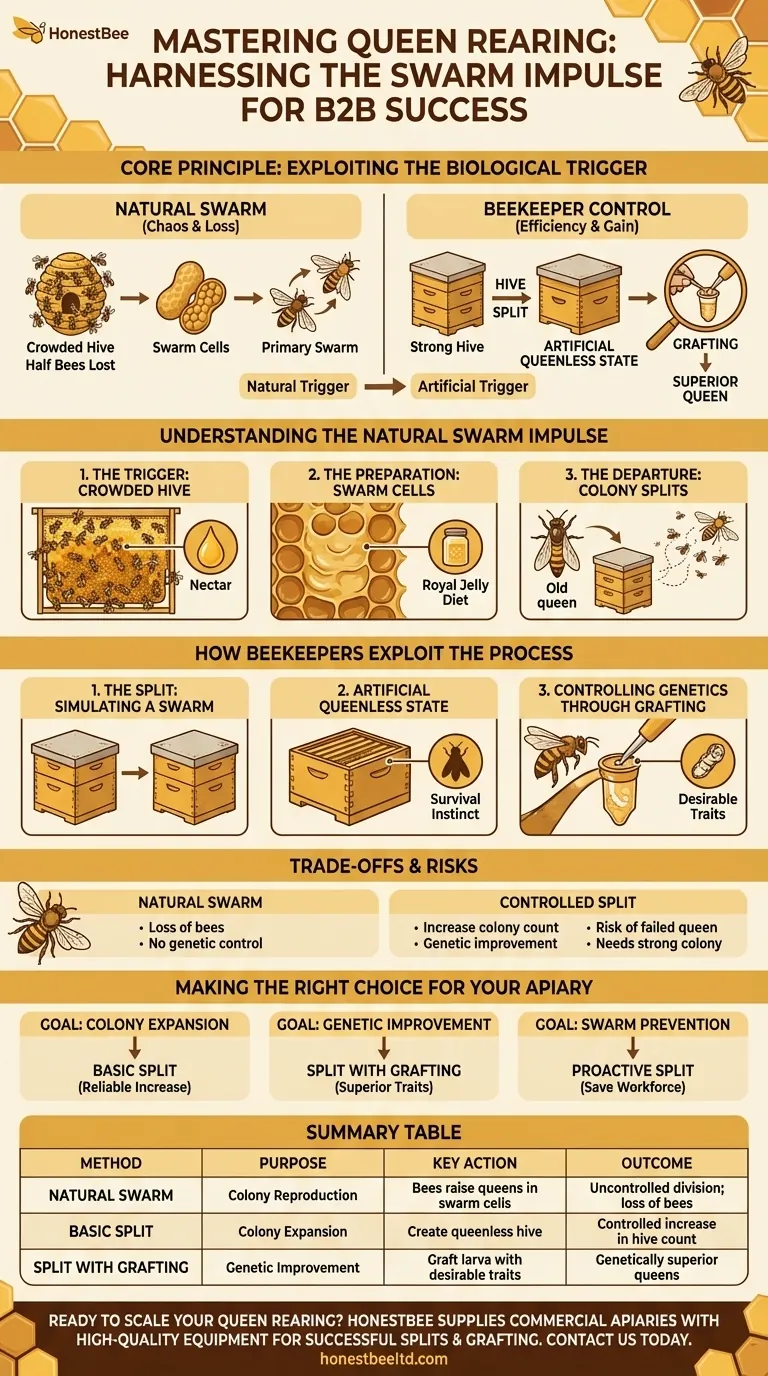
At its core, queen rearing is the practice of manipulating a honey bee colony's natural reproductive impulse—the swarm. Beekeepers do not rely on natural swarms, which are chaotic and inefficient. Instead, they simulate the conditions that precede a swarm to intentionally trigger the bees to raise new, high-quality queens on demand.
The central principle is not to use the swarming process itself, but to exploit the biological trigger behind it. By creating an artificial "queenless" state in a hive or a portion of it, beekeepers compel the worker bees to initiate their emergency procedure: raising a new queen.

Understanding the Natural Swarm Impulse
To understand queen rearing, you must first understand why a colony swarms. It is not a sign of failure; it is the natural method of reproduction for the entire superorganism.
The Trigger: A Crowded, Successful Hive
A strong nectar flow, a rapidly expanding population, and a lack of space are the primary triggers for the swarm impulse. The colony decides it is strong enough to divide itself.
The Preparation: Building Swarm Cells
In preparation for swarming, worker bees will build several specialized, peanut-shaped wax cells called swarm cells. The queen will lay eggs in these cells, and the workers will feed the resulting larvae a rich diet of royal jelly to develop them into new queens.
The Departure: The Colony Splits
Crucially, the old queen leaves with roughly half of the bees before the new virgin queens emerge. This group, the primary swarm, finds a new home. The original hive is left behind with the remaining bees, brood, and the developing queen cells.
How Beekeepers Exploit This Process
A beekeeper rarely wants a natural swarm, as it means losing half their workforce and honey-producing potential. Instead, they use controlled techniques that mimic this natural division.
The "Split": Simulating a Swarm
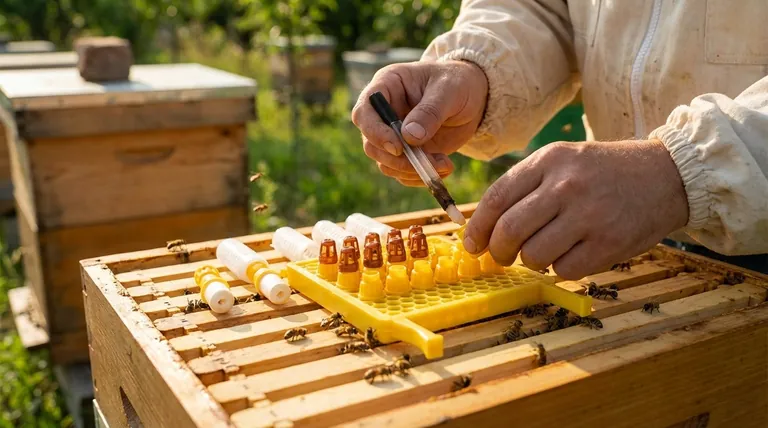
The most common method is creating a hive split. A beekeeper moves frames of bees, brood, and honey from a strong colony into a new hive box. By moving the old queen to one of the boxes, they instantly render the other one queenless.
Creating an "Artificial Queenless" State
This queenless half of the split now faces an existential crisis. Without a queen to lay eggs, the colony is doomed. Their powerful survival instinct kicks in, and they immediately begin the process of raising a new "emergency" queen from existing young larvae.
Controlling Genetics Through Grafting
This is where the beekeeper takes control. Instead of letting the bees choose a random larva, a skilled beekeeper can perform grafting. This involves transferring a day-old larva from a hive with desirable genetics (e.g., gentleness, high honey production) into a man-made queen cup. This cup is then placed in the queenless split, and the bees will raise this hand-picked larva into a genetically superior queen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, manipulating the swarm impulse is a delicate process with potential downsides that must be managed.
Natural Swarm vs. Controlled Split
A natural swarm results in the loss of your bees and no control over where they go or the genetics of the new queen. A controlled split allows you to increase your colony count and, with grafting, actively improve your apiary's genetic stock.
The Risk of a Failed Queen
The new virgin queen raised in a split must still fly out, mate with drones, and return safely to the hive. If she is eaten by a bird, fails to mate, or cannot find her way back, the split will fail and the colony will perish unless the beekeeper intervenes with a new queen or more eggs.
The Need for a Strong Colony
You cannot split a weak hive. A successful split requires a robust population that can afford to be divided and still has enough resources and bees to care for the brood, regulate temperature, and raise a healthy new queen.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
Your approach to using the swarm impulse should align directly with your beekeeping goals.
- If your primary focus is simple colony expansion: Performing basic splits without grafting is a reliable way to increase your hive count by using the bees' natural queen-rearing response.
- If your primary focus is genetic improvement: You must combine the split with grafting to ensure the new queen carries the specific traits you want to propagate in your apiary.
- If your primary focus is swarm prevention: Proactively splitting a strong, congested hive is the single most effective way to satisfy its reproductive urge, preventing the loss of your workforce.
By understanding and directing the hive's powerful natural instincts, you move from simply keeping bees to truly managing them.
Summary Table:
| Method | Purpose | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Swarm | Colony Reproduction | Bees raise queens in swarm cells | Uncontrolled colony division; loss of bees |
| Basic Split | Colony Expansion | Create a queenless hive from a strong colony | Controlled increase in hive count |
| Split with Grafting | Genetic Improvement | Graft a larva with desirable traits into the split | Genetically superior queens for your apiary |
Ready to master queen rearing and improve your apiary's genetics?
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, wholesale-focused supplies needed for successful splits and grafting. From durable hive boxes to precise grafting tools, we provide the reliable equipment that supports your queen-rearing operations.
Let us help you build a stronger, more productive beekeeping business. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and explore our product catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Jenter Queen Rearing Kit Complete Set for Bee Breeding
- Nicot Queen Rearing Kit for Beekeeping and Grafting in Nicot System
- Brown Nicot Queen Cell Cups for Breeding Queen Bees Beekeeping
- No Grafting Queen Rearing Kit: System for Royal Jelly Production and Queen Rearing
- Retractable Chinese Queen Rearing Grafting Tools Equipment
People Also Ask
- What do queen rearers do with queens that fail to lay on time? The Critical Quality Control Decision
- What role do queen rearing systems play in scaling genetic quality? Optimize Your Apiary's Performance and Yield
- What are the five methods of queen rearing? From Simple Splits to Commercial Grafting
- How long can a hive survive queenless? The Critical Countdown to Save Your Colony
- What are the technical advantages of using specialized mating nuclei? Maximize Your Queen Rearing Efficiency



















