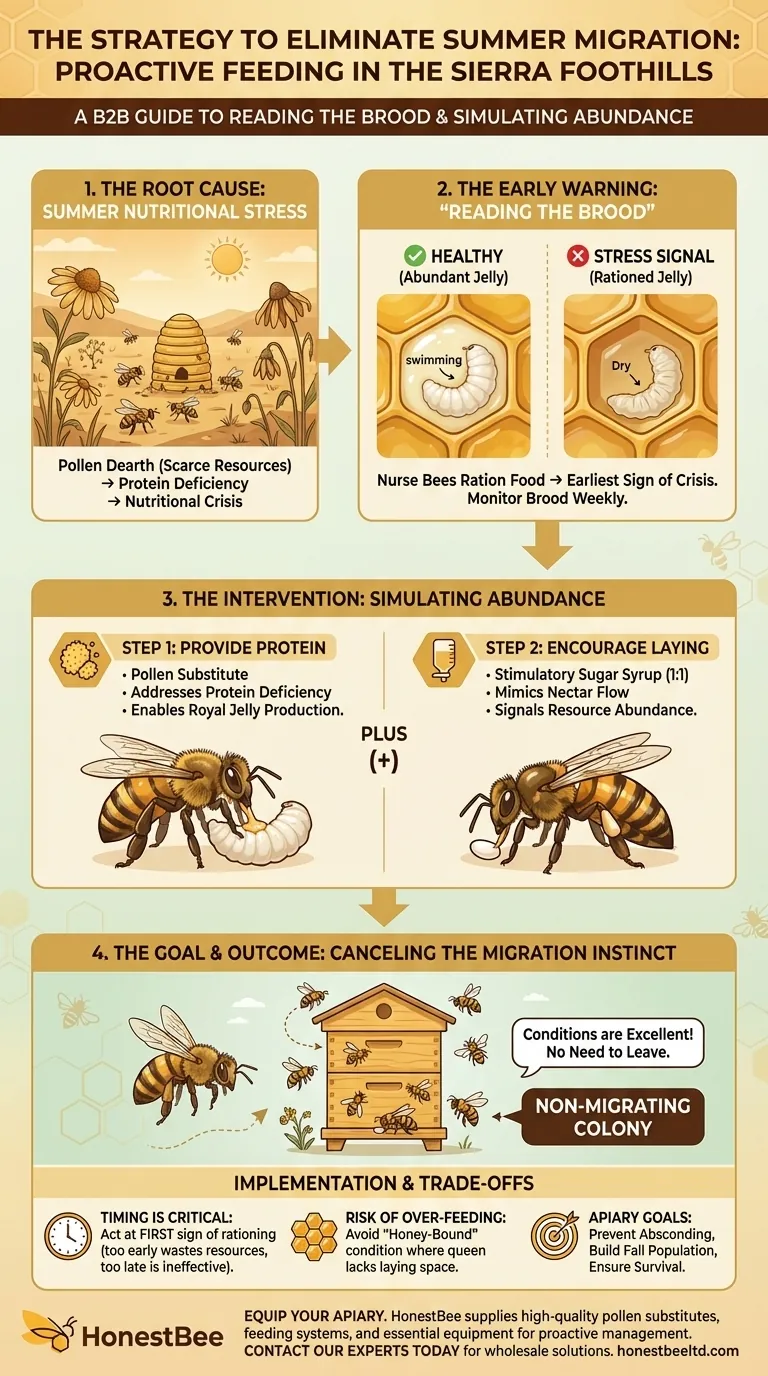
The strategy to eliminate summer migration in honeybee colonies, as demonstrated in the Sierra foothills, is a proactive feeding approach triggered by a specific in-hive indicator. Beekeepers learned to "read the brood" and begin supplemental feeding of pollen substitute and stimulatory sugar syrup at the very first sign that nurse bees were rationing food to the larvae, which signals the start of a nutritional crisis.
The core problem is not the migration itself, but the nutritional stress that forces it. By identifying the earliest warning sign of this stress—rationed larval food—beekeepers can intervene and simulate resource abundance, effectively canceling the colony's instinct to leave.

The Root Cause: Understanding Summer Nutritional Stress
To stop migration, you must first understand its trigger. A colony's decision to leave its home is a desperate survival measure, not a casual choice.
What Triggers Summer Migration?
Honeybee colonies may migrate or abscond when their environment can no longer support them. This is typically driven by a "dearth," a period when essential natural resources—nectar and pollen—become scarce.
The late summer heat in many climates, including the Sierra foothills, often creates such a dearth, killing off the flowering plants that bees rely on.
The Pollen Dearth and its Domino Effect
While nectar provides energy, pollen is the colony's sole source of protein. This protein is critical for nurse bees to produce royal jelly, the food fed to the queen and, most importantly, the developing larvae.
When pollen disappears, the colony's ability to raise the next generation of bees is immediately jeopardized. This puts the entire colony on a path toward collapse.
"Reading the Brood": Your Early Warning System
Experienced beekeepers don't wait for the population to crash. They look for the earliest, most subtle signs of nutritional stress by inspecting the brood nest.
The Critical Sign: Rationing Jelly
A healthy, well-fed larva will be visibly "swimming" in a generous, milky pool of royal jelly within its cell.
When nurse bees lack sufficient protein from pollen, they begin to conserve resources. You will see "dry" or rationed larvae, which have little to no visible jelly in their cells. This is the most reliable and immediate indicator that the colony has entered a state of nutritional stress and is beginning to shut down brood production.
The Intervention Strategy: Simulating Abundance
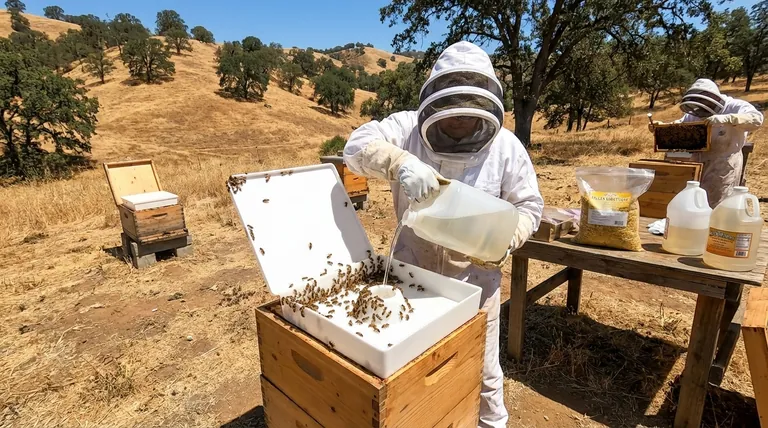
Once jelly rationing is observed, the strategy is to intervene immediately with a two-part feeding plan that simulates the return of a natural nectar and pollen flow.
Step 1: Providing Protein with Pollen Substitute
Feeding a pollen substitute directly addresses the protein deficiency. This gives nurse bees the essential nutrients they need to produce ample royal jelly.
This intervention immediately relieves the stress on the brood-rearing process, ensuring that the developing larvae are well-fed and the colony can continue to produce healthy new bees.
Step 2: Encouraging Laying with Stimulatory Syrup
Simultaneously, feeding a stimulatory sugar syrup (typically a 1:1 ratio of sugar to water) mimics a natural nectar flow. This signals to the queen that resources are abundant.
In response to this signal, a healthy queen will increase her egg-laying rate. The combination of protein for raising brood and energy from the "nectar flow" convinces the colony's collective intelligence that conditions are excellent and there is no need to migrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, this management technique requires careful judgment and is not without risks. Blindly feeding a colony can create new problems.
The Risk of Over-Feeding
Feeding syrup when the colony doesn't need it can lead to the bees storing it in the brood nest. This creates a "honey-bound" condition, where the queen runs out of empty cells in which to lay eggs, effectively halting brood production.
The Importance of Timing
This strategy hinges on precise timing. Feeding too late, after the brood cycle has already been severely impacted, may be insufficient to reverse the colony's decline or its decision to abscond.
Conversely, feeding too early is a waste of money and feed, and it can attract pests like ants or trigger robbing from other nearby hives. The key is to act only when you observe the specific indicator of jelly rationing.
Applying This to Your Apiary
Your goal determines how you apply this knowledge. By monitoring your hives for the specific signs of nutritional stress, you can shift from a reactive to a proactive management style.
- If your primary focus is preventing summer absconding: Monitor your brood frames weekly for "dry" larvae as soon as you notice natural pollen sources declining in your area.
- If your primary focus is building a strong fall population: Begin stimulatory feeding at the first sign of jelly rationing to ensure the colony raises a large, healthy population of "winter bees" needed to survive the cold months.
- If your primary focus is colony survival through a dearth: This two-part feeding strategy is the most direct and effective way to carry a hive through a period of extreme resource scarcity.
By learning to interpret these subtle in-hive cues, you can provide what your bees need exactly when they need it, ensuring their long-term stability and success.
Summary Table:
| Strategy Component | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Early Detection | Monitor brood for "dry" or rationed larvae. | Identify the earliest sign of nutritional stress before the colony decides to migrate. |
| Protein Intervention | Feed a pollen substitute. | Address the protein deficiency, allowing nurse bees to produce royal jelly for larvae. |
| Energy Stimulation | Feed a 1:1 sugar syrup. | Mimic a nectar flow, encouraging the queen to lay eggs and signaling resource abundance. |
| Goal | Simulate resource abundance. | Cancel the colony's instinct to abscond by convincing it conditions are excellent. |
Equip your apiary to master proactive hive management. This strategy relies on precise timing and the right supplies. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality pollen substitutes, feeding systems, and essential equipment needed to implement this successful approach. Stop reacting to colony stress and start preventing it. Contact our experts today to discuss how our wholesale-focused solutions can strengthen your operation's resilience and profitability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Professional Hive Top Bee Feeder Feeding Solution
- Professional Hive Front Entrance Bee Feeder
- HONESTBEE Entrance Bee Feeder Professional Hive Nutrition Solution for Beekeeping
- Boardman Entrance Bee Feeder Durable Galvanized Steel and Wood Construction for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Entrance Bee Feeder Efficient Hive Front Liquid Feeding Solution for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How do I keep bees from drowning in my top feeder? Ensure Safe Feeding for Your Hive
- What is the best way to top feed bees? A Safe, High-Volume Feeding Solution for Your Apiary
- What features make top feeders a reliable choice for beekeepers? A Guide to Safe, Efficient Hive Nutrition
- What safety features are included in top feeders? A Guide to Drowning Prevention and Hive Safety
- How is the plywood floor fitted into the hive-top feeder? Ensure Longevity with a Floating Floor Design



















