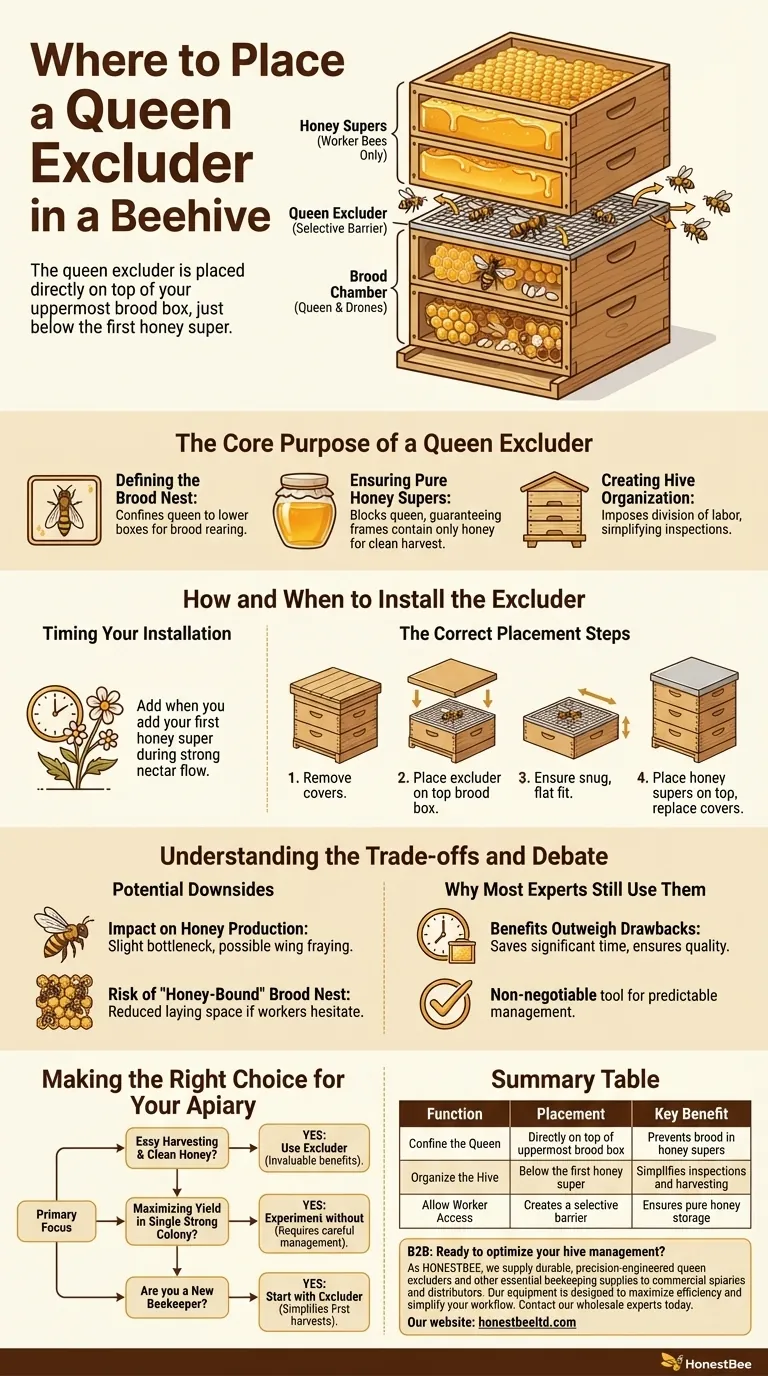
In beekeeping, a queen excluder is placed directly on top of your uppermost brood box. Its position is critical: it sits just below the first honey super you add to the hive. This strategic placement creates a selective barrier that keeps the larger queen and drones confined to the brood chamber while allowing smaller worker bees to pass through to the honey storage areas above.
A queen excluder is not just a barrier; it's a fundamental hive management tool. Its primary function is to ensure your honey supers remain dedicated solely to honey storage—free from eggs and developing brood—which simplifies harvesting and improves honey quality.

The Core Purpose of a Queen Excluder
A queen excluder is a flat screen, made of metal or plastic, with openings precise enough for worker bees to pass through but too small for a queen. Its use centers on creating clear zones within the hive.
Defining the Brood Nest
The primary role of the excluder is to contain the queen within the brood chamber, which consists of the lower boxes of the hive.
This ensures that all brood rearing—the raising of eggs, larvae, and pupae—is confined to a dedicated area, preventing the queen from laying in frames intended for honey.
Ensuring Pure Honey Supers
By blocking the queen's access to the honey supers, you guarantee that these frames will contain only honey.
This is the main benefit. It results in clean honey, free from developing bees or their remnants, making the extraction process much cleaner and more efficient.
Creating Hive Organization
The excluder imposes a clear division of labor within the physical structure of the hive. Brood rearing happens below, while honey storage occurs exclusively above.
This predictable organization simplifies inspections and management, as you know exactly where to look for brood and where to find harvestable honey.
How and When to Install the Excluder
Proper placement and timing are essential for the excluder to function correctly without hindering the colony.
Timing Your Installation
The ideal time to add a queen excluder is at the same time you add your first honey super.
This is typically done during a strong nectar flow when the colony is expanding rapidly and needs more space for honey storage. There is no other specific timing requirement.
The Correct Placement Steps
- First, remove the outer and inner covers from your hive. If you already have honey supers on, take them off and set them aside.
- Place the queen excluder directly on the top bars of the highest brood box.
- Ensure the excluder lies perfectly flat and fits snugly against the hive body, leaving no gaps around the edges where a determined queen might slip through.
- Finally, place your honey supers directly on top of the excluder before replacing the inner and outer covers.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Debate
While highly useful, queen excluders are the subject of some debate among beekeepers. Understanding the potential downsides is key to making an informed decision.
The Impact on Honey Production
Some beekeepers argue that excluders can modestly reduce honey production. The barrier can create a slight "bottleneck" that slows the movement of worker bees as they travel between the brood nest and the supers.
Over time, the sharp edges of some metal excluders can also fray the wings of worker bees as they pass through, slightly reducing their lifespan and foraging efficiency.
The Risk of a "Honey-Bound" Brood Nest
If worker bees are hesitant to cross the excluder, they may begin storing excess nectar in the brood chamber instead.
This condition, known as being honey-bound, reduces the space available for the queen to lay eggs. This can limit colony growth and, in some cases, trigger the colony's instinct to swarm.
Why Most Experts Still Use Them
For many beekeepers, especially those managing multiple hives or selling honey, the benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks.
The guarantee of brood-free honey supers saves significant time during harvest and ensures a higher-quality final product, making the excluder a non-negotiable tool for predictable management.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
Your goal as a beekeeper should dictate whether you use an excluder.
- If your primary focus is easy harvesting and guaranteed clean honey: Use a queen excluder every time you add honey supers. The organizational benefits and simplified extraction process are invaluable.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey yield in a single strong colony: You might experiment with not using an excluder, but be prepared to inspect frames carefully and manage brood placement before you harvest.
- If you are a new beekeeper: Start by using a queen excluder. It removes a major variable, simplifies hive inspections, and makes your first honey harvests much more straightforward.
Ultimately, using a queen excluder is a strategic choice that balances management simplicity against absolute production efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Function | Placement | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Confine the Queen | Directly on top of the uppermost brood box | Prevents brood in honey supers |
| Organize the Hive | Below the first honey super | Simplifies inspections and harvesting |
| Allow Worker Access | Creates a selective barrier | Ensures pure honey storage |
Ready to optimize your hive management? As HONESTBEE, we supply durable, precision-engineered queen excluders and other essential beekeeping supplies to commercial apiaries and distributors. Our equipment is designed to maximize efficiency and simplify your workflow. Contact our wholesale experts today to discuss your apiary's needs and discover how our products can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Wood Framed Metal Wire Queen Bee Excluder
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- Plastic Queen Bee Excluder for Bee Hive Wholesale
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- Metal Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Can a queen get through a queen excluder? A Guide to Preventing Hive Failures
- What are the advantages of using a queen excluder? Maximize Honey Yield & Hive Control
- What considerations should a beekeeper take into account when deciding whether to use an excluder?
- Do I really need a queen excluder? A Guide to Maximizing Your Honey Harvest Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a queen excluder? A Guide to Brood-Free Honey Harvesting



















