Protecting a honey bee colony in spring is about managing a critical transition. This is the most vulnerable time of year, when the colony, weakened from winter, must rapidly expand its population. This explosive growth makes the hive susceptible to resource shortages, unpredictable weather, and emerging pests before it can reach its full, robust strength for the summer.
Spring management is a race against time. The core challenge is ensuring the colony can build its population faster than its threats—starvation, late cold snaps, and pests—can overwhelm its limited resources.
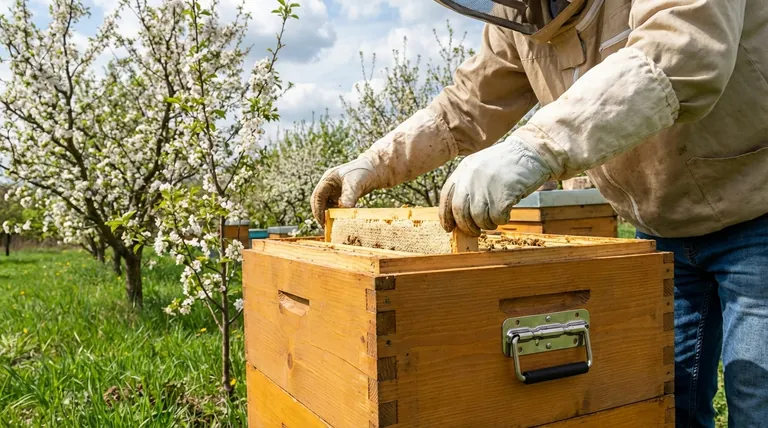

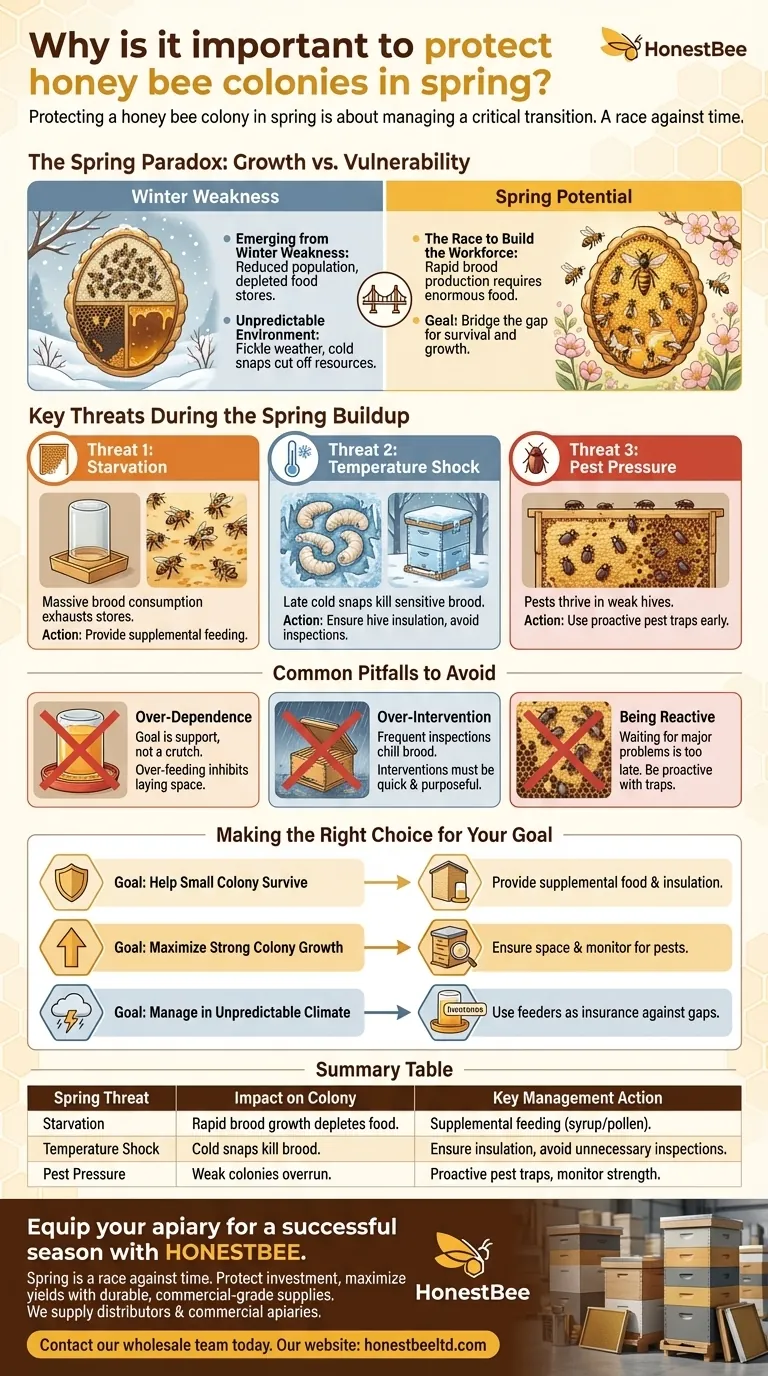
The Spring Paradox: Growth vs. Vulnerability
In spring, a bee colony is simultaneously at its weakest and has its greatest potential. The beekeeper's role is to bridge this gap, ensuring the colony survives the transition and realizes its potential for growth.
Emerging from Winter Weakness
A colony exits winter with a reduced population and depleted food stores. The bees have spent months consuming honey just to generate heat and survive, meaning their energy reserves are at their lowest point.
The Race to Build the Workforce
The queen bee begins laying thousands of eggs per day to build the workforce needed for the main summer nectar flow. This rapid brood production requires enormous amounts of food (pollen and nectar) and stable warmth.
An Unpredictable Environment
Early spring weather is notoriously fickle. A week of warm, sunny days that provide abundant nectar can be immediately followed by a cold, rainy spell that confines the bees to the hive and cuts off all incoming resources.
Key Threats During the Spring Buildup
A colony's rapid expansion creates specific vulnerabilities. Protecting the colony means actively mitigating these three primary threats.
Threat 1: Starvation
Contrary to popular belief, colonies are more likely to starve in early spring than in deep winter. The massive amount of developing brood consumes food at an incredible rate, and a few days of bad weather can completely exhaust the hive's remaining honey stores.
Threat 2: Temperature Shock
A late-season cold snap can be devastating. While the adult bees can cluster for warmth, the developing larvae and pupae (the brood) are highly sensitive to temperature. A sudden chill can kill the brood, setting back the colony's growth by weeks.
Threat 3: Pest Pressure
Pests like the small hive beetle thrive in spring. They target weaker hives that don't have enough bees to effectively police the entire hive area. Managing these pests early prevents their populations from exploding and overrunning the colony.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Effective spring management is a delicate balance. The goal is to support the colony's natural instincts, not to create dependency or introduce new problems through over-intervention.
The Goal is Support, Not Dependence
Supplemental feeding is a critical tool, but it should only be used to prevent starvation, not as a permanent crutch. Over-feeding can inhibit the queen's laying space and lead to other hive issues.
Risk of Over-Intervention
Every time a beekeeper opens a hive, heat and humidity are lost. Frequent inspections during cool spring weather can chill the sensitive brood, causing more harm than good. Interventions should be quick, purposeful, and done only when necessary.
Being Reactive Instead of Proactive
Waiting until you see a major pest problem is often too late. Spring is the time for proactive measures, like setting traps for small hive beetles, when the pest population is small and manageable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific actions should be tailored to the condition of your colony and your local environment.
- If your primary focus is helping a small colony survive: Provide supplemental food to prevent starvation and ensure the hive has adequate insulation to protect it from cold snaps.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the growth of a strong colony: Ensure the bees have enough physical space to expand and proactively monitor for early signs of pests that can hinder their progress.
- If your primary focus is managing colonies in an unpredictable climate: Use feeders as an insurance policy against sudden nectar gaps caused by bad weather, allowing the queen to lay without interruption.
Effective spring management ensures your bees don't just survive this vulnerable period; they enter the main season positioned to thrive.
Summary Table:
| Spring Threat | Impact on Colony | Key Management Action |
|---|---|---|
| Starvation | Rapid brood growth depletes food stores. | Provide supplemental feeding (sugar syrup/pollen). |
| Temperature Shock | Cold snaps kill developing brood. | Ensure hive insulation and avoid unnecessary inspections. |
| Pest Pressure | Weak colonies are overrun by pests like small hive beetles. | Use proactive pest traps and monitor hive strength. |
Equip your apiary for a successful season with HONESTBEE. Spring is a race against time for your honey bee colonies. Protect your investment and maximize summer honey yields with durable, commercial-grade beekeeping supplies from HONESTBEE. We supply beekeeping equipment distributors and commercial apiaries with the reliable tools needed for proactive hive management.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your seasonal needs and ensure your colonies thrive.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Comfort Grip Spring-Loaded Hive Handles
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Classic Pry Bar Hive Tool with High Visibility Finish for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Why is Bilinga wood preferred for tropical forest beehives? The Ultimate Choice for Durability and Honey Yield
- Why is the disinfection of beekeeping tools essential? Protect Colony Health and Stop Disease Spread
- Why is it important to clean and sanitize beekeeping equipment before storage? Protect Your Apiary Investment
- How do industrial-grade hive-making machines and automated honey-filling machines facilitate scaling? Boost Apiary ROI
- How does thermal treatment compare to traditional chemical disinfection in beehive cleaning? Safely Sterilize Your Hives



















