At its core, regular beehive maintenance is the single most important activity for ensuring the health, productivity, and long-term survival of your colony. It is a proactive process of gathering information and taking corrective action to prevent small issues from developing into catastrophic hive failures. Without it, you are not managing bees; you are simply housing them until a problem arises.
Think of regular maintenance not as a chore, but as a diagnostic check-up for a complex superorganism. It allows you to understand the colony's status and make informed decisions that support its natural life cycle and defenses.

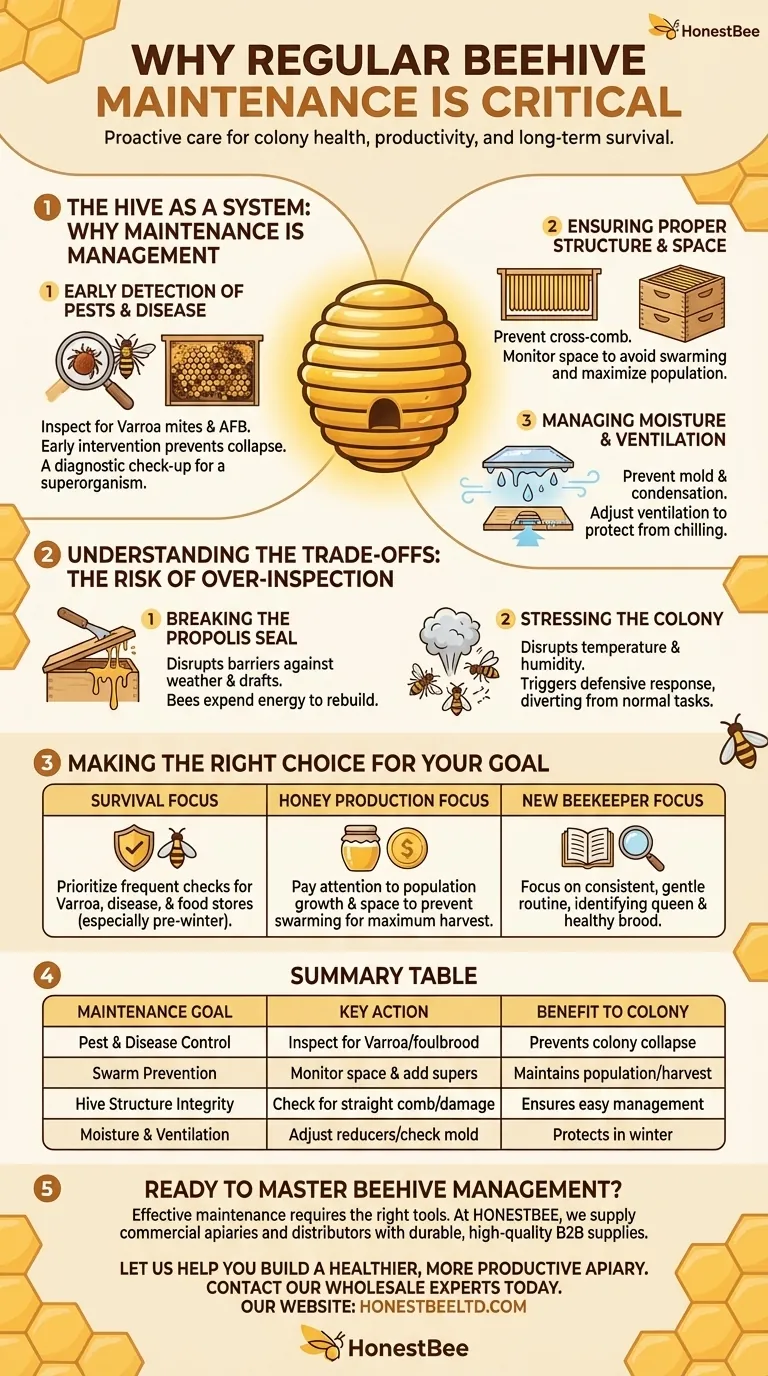
The Hive as a System: Why Maintenance is Management
A beehive is more than a box of insects; it is a finely tuned system. Your maintenance routine is your primary tool for managing that system effectively.
Early Detection of Pests and Disease
The most immediate threat to any modern honeybee colony is pressure from pests and diseases. Regular inspections are your first line of defense.
Pests like the Varroa mite are a primary vector for viruses and can decimate a hive if left unchecked. By looking for signs of infestation on adult bees and in brood cells, you can intervene with treatments before the population collapses.
Similarly, inspecting the brood pattern for signs of diseases like American Foulbrood (AFB) or chalkbrood allows you to act quickly, often saving the colony and preventing spread to other hives in the area.
Ensuring Proper Structure and Space
Bees are master builders, but they work best within the framework you provide. Inspections ensure this framework remains sound.
You are checking that the bees are building straight comb within the frames, which is essential for easy inspections and honey extraction. Damaged frames or foundations must be replaced to prevent cross-comb, a chaotic building pattern that makes the hive nearly impossible to manage.
Furthermore, monitoring hive space is critical for preventing swarming. A colony that feels crowded will raise a new queen and leave with the old one, significantly reducing your bee population and potential honey harvest. Adding boxes (supers) at the right time is a key management task.
Managing Moisture and Ventilation
Moisture is one of the greatest non-biological threats to a colony, especially during winter.
Warm, moist air produced by the bee cluster rises and condenses on cold inner surfaces. This cold water can then drip back down onto the bees, chilling and killing them. Proper ventilation, managed through entrance reducers and upper vents, allows this moisture to escape.
During an inspection, you are looking for signs of excess condensation or mold. This tells you that your ventilation strategy needs to be adjusted to protect the colony's health.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Risk of Over-Inspection
While maintenance is vital, it is not without cost. Every time you open a hive, you disrupt the colony's delicate internal environment.
Breaking the Propolis Seal
Bees use propolis, a sticky plant resin, to seal every crack and seam in the hive. This creates a barrier against drafts, weather, and intruders.
Each inspection requires you to break these seals, forcing the bees to expend significant energy and resources to rebuild them.
Stressing the Colony
Opening the hive disrupts its temperature and humidity regulation. The bees must work hard to restore the carefully controlled climate of the brood nest.
The inspection itself is a stressful event. The smoke, movement, and light trigger a defensive response, diverting the bees from their normal tasks of foraging, nursing brood, and producing honey. Finding a gentle and efficient cadence is key.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance schedule should be guided by the season and your specific objectives as a beekeeper.
- If your primary focus is colony survival: Prioritize frequent checks for Varroa mites, disease symptoms, and adequate food stores, especially leading into winter.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: Pay close attention to population growth and available space to prevent swarming and ensure the bees have room to store nectar.
- If you are a new beekeeper: Focus on building a consistent, gentle inspection routine to learn how to identify a healthy queen, a good brood pattern, and the basic signs of a thriving colony.
Ultimately, effective beehive maintenance is the practice that turns you from a bee-haver into a true beekeeper.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Goal | Key Action | Benefit to Colony |
|---|---|---|
| Pest & Disease Control | Inspect for Varroa mites & foulbrood | Early intervention prevents colony collapse |
| Swarm Prevention | Monitor space & add supers | Maintains population and maximizes honey harvest |
| Hive Structure Integrity | Check for straight comb & damage | Prevents cross-comb and ensures easy management |
| Moisture & Ventilation | Adjust reducers & check for mold | Protects bees from chilling and disease in winter |
Ready to master beehive management?
Effective maintenance requires the right tools and equipment. At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, high-quality supplies needed for successful, large-scale operations—from hive tools and frames to protective gear and mite treatments.
Let us help you build a healthier, more productive apiary. Contact our wholesale experts today to discuss your equipment needs and volume pricing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE 15-in-1 Beekeeper Multi-Tool with Hammer and Pliers for Beekeeping
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Versatile Ratchet Hive Strap with S-Hooks for Secure Fastening
- Professional Bee Frame Wiring Tool with Integrated Tensioning System by HONESTBEE
- Lightweight Durable Plastic Queen Excluder Scraper for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is required to be a beekeeper? Essential Equipment, Knowledge & Mindset
- What is the significance of professional beekeeping tool sets? Scale Your Apiary with Industrial Efficiency
- How do standardized beekeeping tools and equipment management contribute to improved production efficiency?
- What is required for regular inspections in both Flow Hives and Langstroth hives? Essential Beekeeping Tasks Explained
- When is the optimal time for maintenance on beekeeping tools? Boost Commercial Apiary Efficiency in Nov & Dec



















