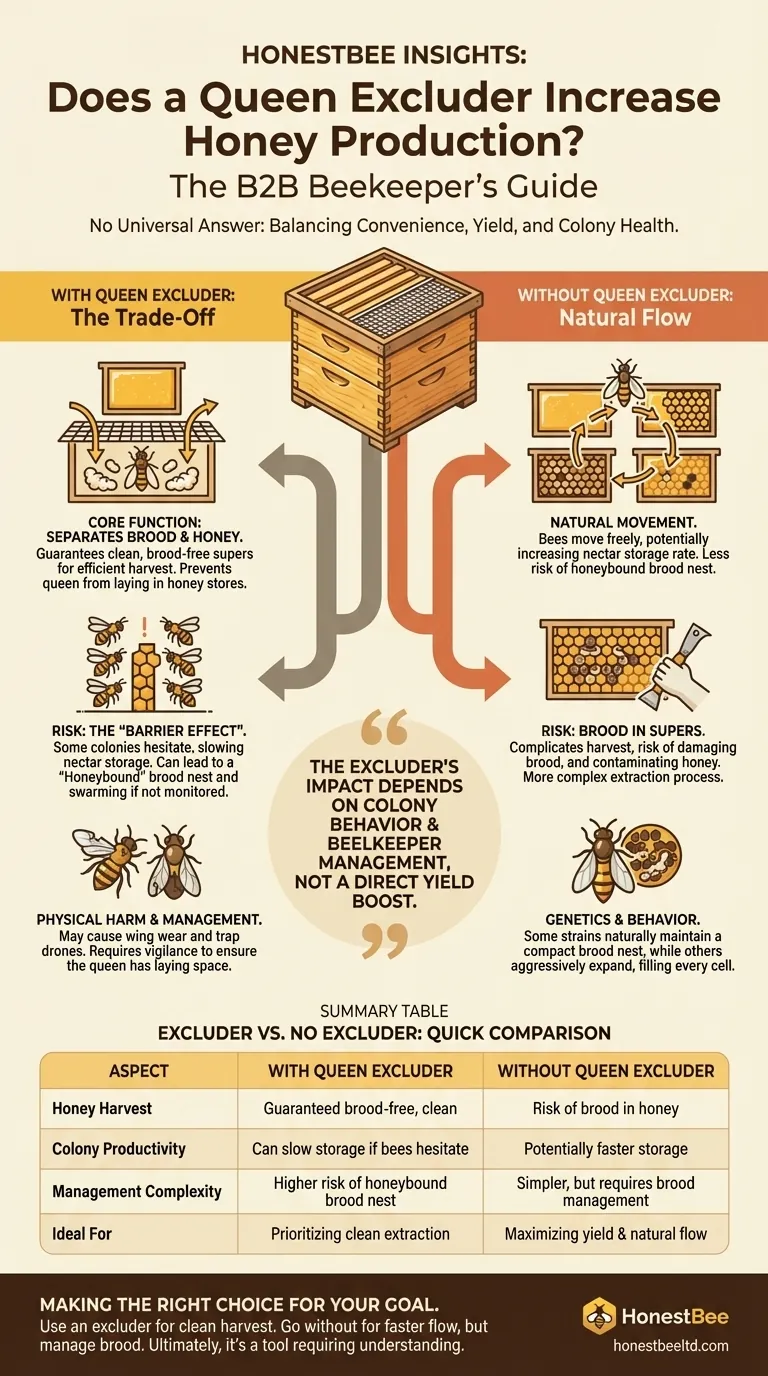
There is no universal answer to whether a queen excluder increases or decreases honey production. Its primary purpose is not to boost yield, but to confine the queen to the brood boxes, ensuring honey supers remain free of eggs and larvae. The effect on your honey harvest depends entirely on your colony's behavior and your management practices.
The queen excluder introduces a fundamental trade-off: it guarantees the convenience of brood-free honey at the cost of potentially creating a barrier that can slow honey storage and increase the risk of a "honeybound" brood nest if not managed carefully.

The Core Function: Separating Brood from Honey
A queen excluder is a simple grid, wide enough for worker bees to pass through but too narrow for the larger queen and drones. Its placement between the brood chamber and the honey supers physically separates the two areas of the hive.
Why Separation Simplifies Harvest
The single greatest benefit of an excluder is the guarantee of clean, honey-only frames in your supers.
This makes the extraction process significantly more efficient. You do not have to worry about damaging bee larvae or contaminating your honey harvest with brood, which is a major advantage for both new and commercial beekeepers.
The "Barrier Effect" on Productivity
The primary drawback is that some colonies are reluctant to move through the excluder. This hesitation can create a "traffic jam" and slow the rate at which bees deposit nectar in the supers above.
This reluctance is not universal. Some colonies show no hesitation and work the supers readily, while others may treat the excluder like a ceiling, significantly reducing the honey stored above it.
Colony Genetics and Behavior
The tendency for a queen to move into honey supers is also influenced by genetics. Some bee strains, particularly those locally adapted, naturally maintain a more compact brood nest.
Conversely, other strains are programmed to expand the brood nest aggressively. In these cases, an excluder becomes a valuable tool to prevent the queen from filling every available cell with eggs, forcing the workers to use the supers for honey.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Using an excluder is not a "set it and forget it" solution. It introduces specific management challenges that can impact hive health and, consequently, honey production.
The Risk of a "Honeybound" Brood Nest
If worker bees are hesitant to cross the excluder, they may begin storing nectar in the brood chamber instead. This is known as the brood nest becoming honeybound or nectar-bound.
When this happens, the queen runs out of space to lay eggs. This severely restricts colony growth, reduces the future forager population, and can trigger the colony to swarm. Active management is required to ensure the queen always has laying space.
Physical Harm to Bees
The excluder is an unnatural barrier that can have physical consequences for the hive.
Drones, unable to pass through, can become trapped and die in the excluder. Furthermore, the repeated passage through the metal or plastic grid can cause cumulative wear and tear on the delicate wings of worker bees over time.
Increased Management Complexity
While an excluder simplifies the harvest, it can complicate routine hive inspections. A beekeeper using an excluder must be more vigilant in monitoring the brood box.
This often involves rotating frames or adding empty comb to the brood nest to prevent it from becoming honeybound, adding a layer of complexity to hive management.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a queen excluder should be based on your specific goals, management style, and what you observe in your colonies.
- If your primary focus is a simple, clean harvest: Using an excluder is the most straightforward way to ensure your honey frames are free of brood.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey with minimal hive manipulation: Going without an excluder may allow for faster honey storage, but you must be prepared to manage brood in your honey frames during extraction.
- If you are a new beekeeper: An excluder can simplify your first harvests and help you learn hive dynamics, but requires you to watch carefully for a honeybound brood nest.
Ultimately, the queen excluder is a tool, and its value is determined by the beekeeper's understanding of its impact on the colony.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | With Queen Excluder | Without Queen Excluder |
|---|---|---|
| Honey Harvest | Guaranteed brood-free, clean supers | Risk of brood in honey frames |
| Colony Productivity | Can slow honey storage if bees hesitate | Potentially faster honey storage |
| Management Complexity | Higher risk of honeybound brood nest | Simpler, but requires brood management |
| Ideal For | Beekeepers prioritizing clean extraction | Beekeepers focused on maximizing yield |
Optimize your apiary's efficiency and honey yield with the right equipment. At HONESTBEE, we supply durable, high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment—including reliable queen excluders—to commercial apiaries and distributors. Let our wholesale-focused expertise help you make informed decisions for your operation. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and boost your honey production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- Premium Wood Framed Metal Wire Queen Bee Excluder
- Plastic Queen Bee Excluder for Bee Hive Wholesale
- Metal Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the specific function of a queen excluder? Boost Success in Queenright Rearing Methods
- Does using a queen excluder lead to more or less honey production? Optimize Your Hive's Yield & Efficiency
- How does a queen excluder function? A Guide to Optimizing Hive Management and Honey Purity
- What is a queen excluder, and how does it function? A Guide to Hive Management
- Why is a plastic queen excluder installed at the entrance of a lightweight pollination hive? Maximize Colony Stability
- Why is the installation of a queen excluder critical for honey production? Ensure Pure, High-Quality Harvests
- What is the primary function of the queen excluder cage? Key Role in Royal Jelly Production Efficiency
- What is the purpose of a queen excluder in a standard beehive configuration? Master Hive Organization



















