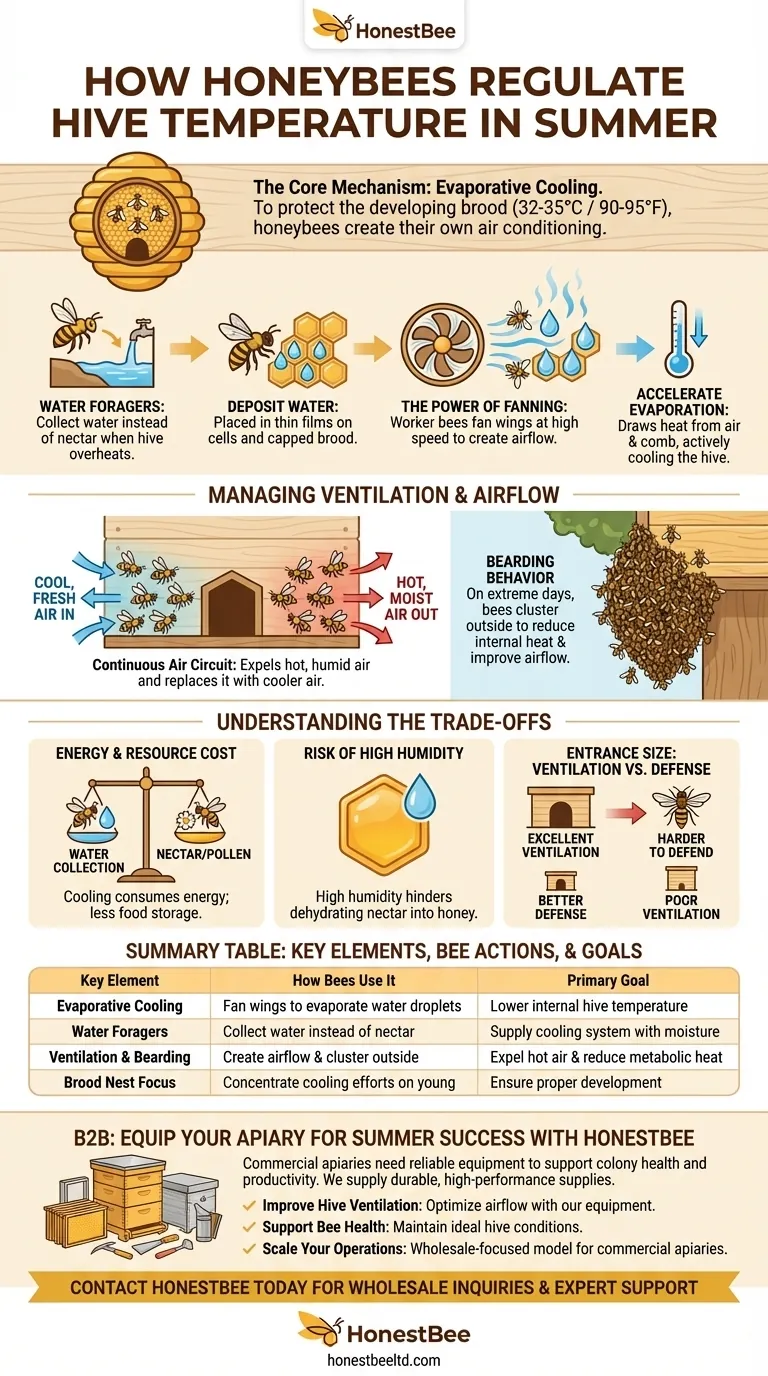
To regulate hive temperature in the summer, honeybees employ a sophisticated system of evaporative cooling, essentially creating their own form of air conditioning. Forager bees collect water and deposit it in droplets throughout the hive, particularly around the crucial brood nest. Other bees then vigorously fan their wings to create airflow, which evaporates the water and actively lowers the hive's internal temperature.
Honeybee temperature regulation is a collective, behavioral process focused on one critical goal: maintaining a stable environment for the developing brood. By using water, fanning, and managing airflow, the colony acts as a single superorganism to combat external heat.
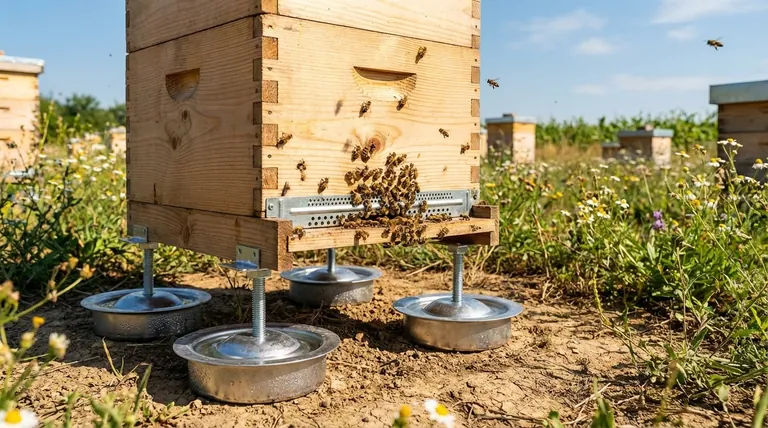

The Core Mechanism: Evaporative Cooling
At the heart of the hive's cooling strategy is the same principle humans use when they sweat. The transition of water from a liquid to a gas requires energy, which it draws from its surroundings in the form of heat.
The Role of Water Foragers
When the hive's internal temperature rises above the ideal range, a specific group of forager bees switches from collecting nectar and pollen to collecting water. They transport this water back to the hive and pass it to house bees, who then deposit it in thin films on the rims of cells or as droplets on the capped brood.
The Power of Fanning
Simultaneously, worker bees position themselves throughout the hive and begin fanning their wings at high speed. This coordinated action creates internal air currents that flow over the deposited water, dramatically accelerating evaporation and pulling heat out of the air and the surrounding comb.
Prioritizing the Brood Nest
This entire effort is focused on protecting the most vulnerable residents: the brood nest. Bee eggs, larvae, and pupae must be kept within a very narrow temperature range (typically 32-35°C or 90-95°F) to develop correctly. The colony will dedicate immense resources to ensure this area remains stable, even if the rest of the hive is warmer.
Managing Ventilation and Airflow
Evaporation alone is not enough. To be effective, the hot, humid air must be expelled from the hive and replaced with cooler, drier air from outside.
Creating Air Circulation
Bees create a highly organized ventilation system. Some bees will line up at the hive entrance facing inward, fanning to draw fresh air in. On the other side of the entrance or at other openings, bees will face outward, fanning to push the hot, moist air out. This creates a continuous, life-saving air circuit.
Behavioral Thermoregulation: Bearding
On extremely hot days, you may see a large cluster of bees hanging on the outside of the hive, a behavior known as "bearding." By moving their bodies outside, the bees reduce the amount of metabolic heat generated within the hive and clear space to improve internal airflow, providing passive cooling assistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The colony's cooling system is effective but comes with significant costs and challenges that reveal the complexity of hive survival.
The Energy and Resource Cost
Cooling is not free. Every forager bee dedicated to collecting water is one less bee collecting nectar or pollen, the food stores the hive needs to survive. The act of fanning also consumes a tremendous amount of energy, which must be replenished from honey stores.
The Risk of High Humidity
While evaporative cooling relies on moisture, excessive humidity inside the hive can be detrimental. High humidity makes it difficult for bees to dehydrate nectar into honey. The ventilation system is therefore critical not only for cooling but also for managing the hive's internal moisture levels.
Entrance Size: Ventilation vs. Defense
The size of the hive entrance presents a classic trade-off. A large entrance is excellent for ventilation and makes it easier for bees to create airflow. However, a large entrance is also much more difficult to defend from predators like wasps or robber bees from other hives.
What This Means for the Hive
Understanding these behaviors provides a window into the colony's priorities and its remarkable ability to adapt.
- If the primary focus is survival: The colony will prioritize cooling the brood nest above all else, even if it means sacrificing foraging efficiency for a day.
- If the primary focus is efficiency: The bees' coordinated fanning and decentralized water distribution represent a highly effective system for climate control without a central command.
- If the primary focus is hive health: Observing behaviors like heavy water foraging and bearding are key indicators that the colony is actively and successfully managing heat stress.
A honeybee hive is not a passive structure; it is an actively managed environment, demonstrating the remarkable collective intelligence of the colony.
Summary Table:
| Key Element | How Bees Use It | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporative Cooling | Fan wings to evaporate collected water droplets | Lower internal hive temperature |
| Water Foragers | Specialized bees collect water instead of nectar | Supply the cooling system with moisture |
| Ventilation & Bearding | Create airflow and cluster outside the hive | Expel hot air and reduce internal metabolic heat |
| Brood Nest Focus | Concentrate cooling efforts on the developing young | Ensure proper development (32-35°C / 90-95°F) |
Equip Your Apiary for Summer Success with HONESTBEE
Just as bees expertly manage their hive's climate, commercial apiaries and distributors need reliable equipment to support colony health and productivity. At HONESTBEE, we supply the durable, high-performance beekeeping supplies and equipment that professionals depend on.
We help you:
- Improve Hive Ventilation: With our range of equipment designed to optimize airflow.
- Support Bee Health: Providing tools that help beekeepers maintain ideal hive conditions.
- Scale Your Operations: Through our wholesale-focused model, perfect for commercial apiaries and distributors.
Let's discuss how our products can strengthen your beekeeping business. Contact HONESTBEE today for wholesale inquiries and expert support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metal Hive Feet Bee Hive Stand for Ant Protection
- Metal Bee Hive Stand Bee Box Stand for Beekeeping
- Plastic Bee Hive Stand for Beekeeping
- Rigid Pith Style Beekeeper Hat for Square Folding Veils
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to ensure a beehive is level and elevated off the ground during setup? Optimize Health and Yield
- Why should beekeeping operations utilize specialized hive stands? Protect Your Assets and Boost Apiary Efficiency
- How do specialized iron stands protect wooden beehives? Expert Solutions for Pest Isolation and Hive Longevity
- How do beehive stands improve hive ventilation? Boost Colony Health with Superior Airflow & Moisture Control
- What is the placement recommendation for cedar bases? Expert Tips to Maximize the Lifespan of Your Beehive Foundations



















