The fundamental value of a nuc hive in mite control lies in its ability to facilitate targeted interventions and disrupt the Varroa mite's reproductive cycle. By creating smaller, isolated colonies, you can treat infestations more efficiently and implement brood breaks that leave mites vulnerable and exposed.
The core strategy is not about the box itself, but about how it enables you to break a large, complex mite problem into smaller, manageable parts. Using nucs shifts your approach from reactive, apiary-wide chemical applications to proactive, targeted colony management.
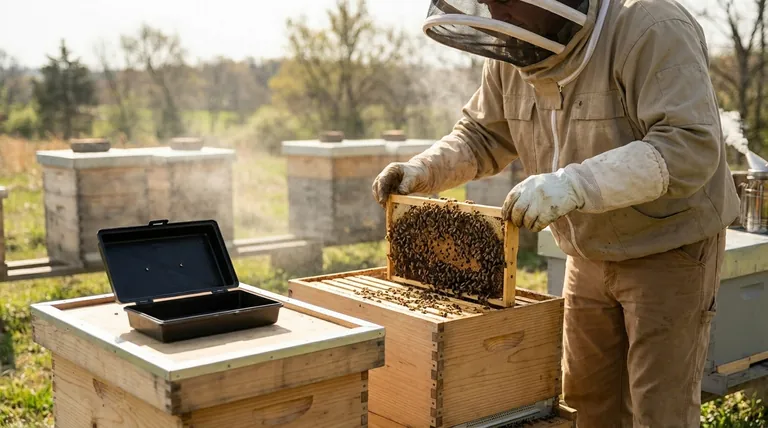

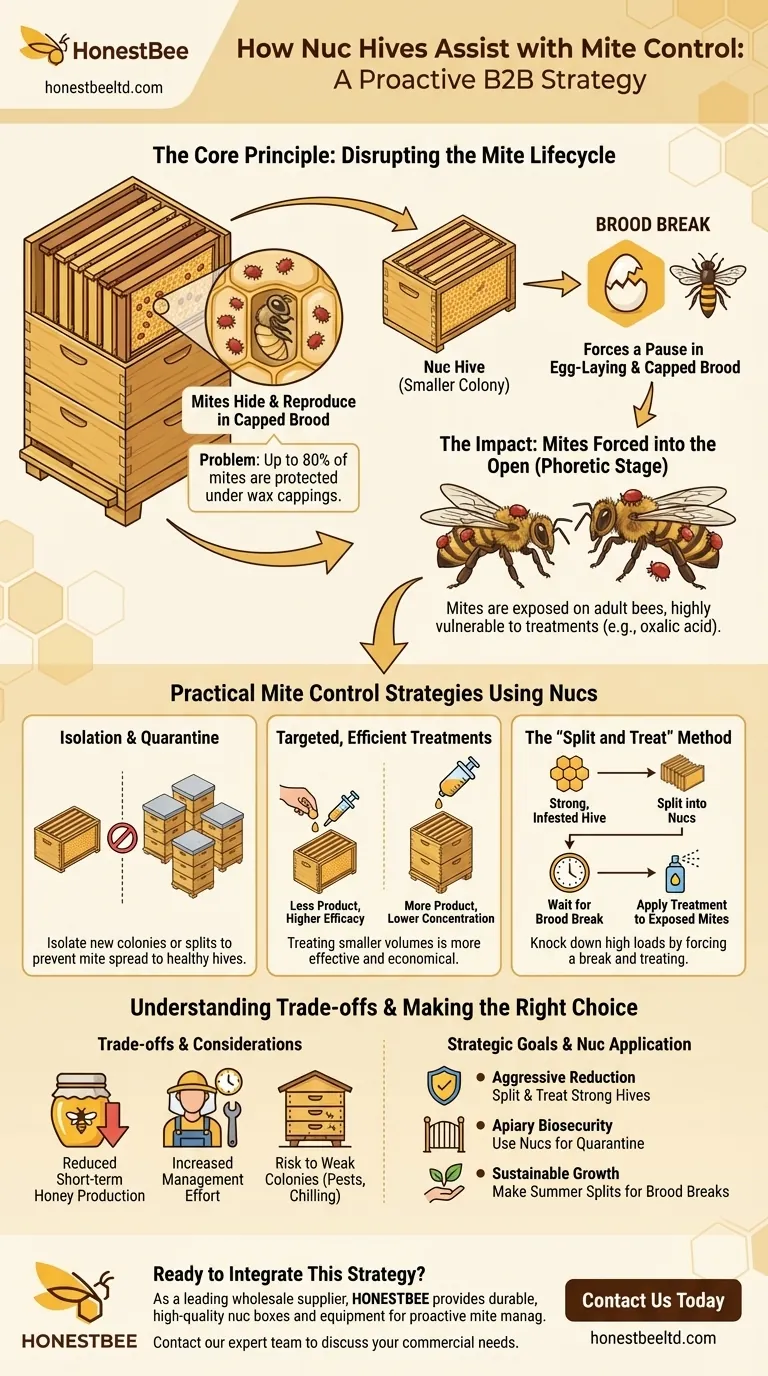
The Core Principle: Disrupting the Mite Lifecycle
To understand why nucs are effective, you must first understand the enemy. The Varroa destructor mite's lifecycle is inextricably linked to honey bee brood.
How Varroa Mites Reproduce
Varroa mites are parasites that reproduce almost exclusively inside capped honey bee brood cells. An adult female mite enters a cell just before it is capped, lays her eggs, and they mature alongside the developing bee pupa.
This means that at any given time in a healthy colony, the majority of the mite population (often 50-80%) is hidden and protected under the wax cappings, safe from many common chemical treatments.
Creating a "Brood Break"
A "brood break" is a deliberate interruption in the queen's egg-laying, resulting in a period where the colony has no capped brood.
When you create a nuc by splitting a larger hive, you often move the queen to the new box or introduce a new queen cell. This process naturally creates a period where no new eggs are being laid and capped, forcing a break in the brood cycle.
The Impact on Mite Populations
During a brood break, the entire mite population is forced out into the open and onto the bodies of adult bees. This is known as the phoretic stage.
Mites in this stage are highly vulnerable. With no brood cells to hide in, treatments that target mites on adult bees (like oxalic acid vaporization or dribble) become dramatically more effective, capable of eliminating a much higher percentage of the total mite load.
Practical Mite Control Strategies Using Nucs
A nuc is a tool. Its effectiveness depends entirely on the strategy you employ.
Isolation and Quarantine
The most straightforward use of a nuc is for biosecurity. By placing new colonies, swarms, or splits from infested hives into a nuc, you can physically isolate them from the rest of your apiary.
This allows you to assess their mite levels and perform treatments without risking the spread of mites to your healthy, established production hives.
Targeted, Efficient Treatments
Treating a small nuc is far more efficient than treating a full-sized, multi-box colony.
The smaller volume requires less treatment product and ensures a higher concentration of the active ingredient, leading to a more effective and economical application.
The "Split and Treat" Method
This is a powerful technique for knocking down high mite loads in a strong hive.
First, you split the strong, mite-infested colony into two or more nucs. Then, you wait for the natural brood break to occur in the queenless split(s). Once all brood has hatched, you can apply a highly effective phoretic-stage treatment like oxalic acid.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, using nucs for mite management is not without its costs and considerations.
Reduced Honey Production
Splitting a strong production colony will inevitably reduce its foraging workforce. This means the parent colony will produce less honey in the short term.
Increased Management Effort
Managing multiple small nucs requires more attention and labor than managing a few large hives. You must monitor their queen status, food stores, and population growth more frequently.
Risk to a Weak Colony
A nuc is a small, vulnerable entity. It is more susceptible to robbing, pests, and chilling than a large, populous colony. A poorly timed split can result in the loss of the colony.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Integrating nucs into your mite management plan should be a deliberate decision based on your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is aggressive mite reduction: Use the "split and treat" method on your strongest colonies before the main honey flow to drastically lower mite loads.
- If your primary focus is apiary biosecurity: Use nucs as dedicated quarantine boxes for all incoming bees to prevent the introduction of new pests and diseases.
- If your primary focus is sustainable growth: Use nucs to make summer splits, creating brood breaks and new colonies simultaneously while keeping mite levels in check.
By leveraging nucs to create brood breaks and isolate colonies, you gain a powerful advantage in controlling Varroa mite populations.
Summary Table:
| Strategy | Key Action | Primary Benefit for Mite Control |
|---|---|---|
| Split and Treat | Split a strong hive into nucs. | Forces a brood break, exposing mites for highly effective treatment. |
| Isolation & Quarantine | House new colonies or splits in nucs. | Prevents mite spread to healthy production hives. |
| Targeted Treatment | Apply treatments to the smaller nuc volume. | Increases treatment efficacy and reduces chemical use and cost. |
Ready to integrate this powerful mite management strategy into your operation?
As a leading wholesale supplier to commercial apiaries and equipment distributors, HONESTBEE provides the durable, high-quality nuc boxes and beekeeping equipment you need to implement these proactive techniques effectively. Our products are designed for the rigors of commercial use, helping you protect your investment and improve colony health.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our supplies can support your mite control and business growth goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Black Plastic Beetle Barn Hive Beetle Trap for Beehives
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
- 4 Frame Plastic Nuc Boxes for Beekeeping Bee Nuc Box
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Professional Multi-Function Stainless Steel Hive Tool
People Also Ask
- What is the recommended number of beetle traps per hive? Optimize Your Hive's Beetle Defense
- How do specialized physical traps and isolation devices assist in the management of Small Hive Beetle (Aethina tumida)?
- How should filled beetle traps be handled? Safely Remove and Dispose to Protect Your Hive
- How should beetle traps be placed in the hive? Achieve Perfect Flush Placement for Maximum Control
- When is the best time to use small hive beetle traps in cold climates? Protect Your Honeybee Winter Stores Now



















