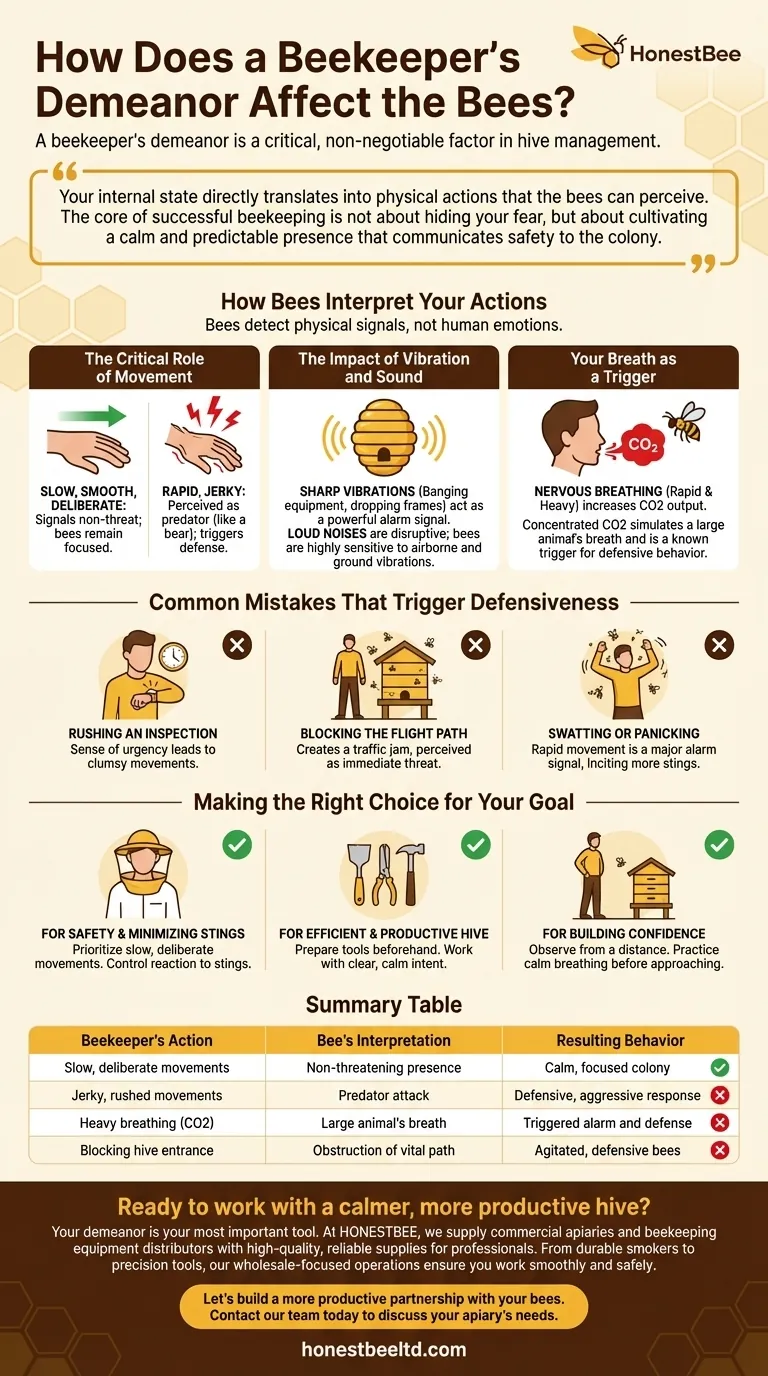
A beekeeper's demeanor is a critical, non-negotiable factor in hive management. Bees are highly sensitive to their environment, and they interpret a beekeeper's actions as either benign or threatening. A calm, deliberate presence results in a calmer colony, while anxious, jerky movements can quickly trigger a defensive response.
Your internal state directly translates into physical actions that the bees can perceive. The core of successful beekeeping is not about hiding your fear, but about cultivating a calm and predictable presence that communicates safety to the colony.

How Bees Interpret Your Actions
Bees do not understand human emotions, but they are masters at detecting potential threats. Your demeanor manifests as physical signals that they can easily interpret.
The Critical Role of Movement
Slow, smooth, and deliberate movements are crucial. Bees perceive rapid, jerky motions in the same way they would a predator, like a bear tearing at the hive.
Think of your movements as a form of communication. Fluid, predictable actions signal that you are not a threat, allowing the bees to remain focused on their own tasks rather than on defending the colony.
The Impact of Vibration and Sound
An anxious or clumsy beekeeper is more likely to bang equipment, drop a frame, or stumble near the hive. These actions create sharp vibrations that travel through the hive structure, acting as a powerful alarm signal for the entire colony.
Likewise, loud noises can be disruptive. While bees don't "hear" in the human sense, they are exceptionally sensitive to vibrations carried through the air and ground.
Your Breath as a Trigger
When a person is nervous or exerting themselves, their breathing becomes more rapid and heavy. This increases the output of carbon dioxide (CO2).
For bees, a concentrated puff of CO2 is a known trigger for defensive behavior, as it can simulate the breath of a large animal attempting to raid the hive.
Common Mistakes That Trigger Defensiveness
Understanding the theory is one thing; avoiding common pitfalls is another. Many defensive reactions are triggered by simple, avoidable mistakes rooted in a beekeeper's unease.
Rushing an Inspection
Feeling nervous often creates a desire to get the inspection over with as quickly as possible. This sense of urgency leads to rushed, clumsy movements that agitate the bees.
Blocking the Flight Path
A nervous or distracted beekeeper may inadvertently stand directly in front of the hive entrance. This blocks the bees' flight path, creating a traffic jam that is perceived as an immediate threat to the colony's operations.
Swatting or Panicking
If you do get stung, the instinctive human reaction is to swat at the bee or flail your arms. This rapid movement is a major alarm signal to other bees and is far more likely to incite more stings than the original pheromone alarm. A calm beekeeper learns to simply scratch the stinger out and move away slowly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to beekeeping should be a conscious practice. By focusing on your own actions, you gain significant influence over the colony's response.
- If your primary focus is safety and minimizing stings: Prioritize slow, deliberate movements and learn to control your reaction if a sting occurs.
- If your primary focus is an efficient and productive hive: Prepare all your tools beforehand to avoid fumbling and work with a clear, calm intent.
- If your primary focus is building confidence: Spend time simply observing the hive from a distance, practicing calm breathing until you feel ready to approach.
Ultimately, beekeeping is a partnership where your calmness fosters the colony's trust.
Summary Table:
| Beekeeper's Action | Bee's Interpretation | Resulting Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Slow, deliberate movements | Non-threatening presence | Calm, focused colony |
| Jerky, rushed movements | Predator attack | Defensive, aggressive response |
| Heavy breathing (CO2) | Large animal's breath | Triggered alarm and defense |
| Blocking the hive entrance | Obstruction of vital path | Agitated, defensive bees |
Ready to work with a calmer, more productive hive?
Your demeanor is your most important tool, and having the right equipment supports a calm and confident approach. At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, reliable supplies that professionals trust. From durable smokers to precision tools, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you have what you need to work smoothly and safely.
Let's build a more productive partnership with your bees. Contact our team today to discuss your apiary's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
- HONESTBEE Classic Pry Bar Hive Tool with High Visibility Finish for Beekeeping
- Professional Frame Comb Fork and Lifter for Efficient Handling
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
- Yellow Plastic Bucket Pail Perch for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Why are modern movable frame hives preferred over traditional hives? Boost Your Commercial Apiary Efficiency
- Why is the implementation of movable frame hives necessary for internal inspections? Master Precision Colony Care
- What are the technical considerations for limiting a single apiary to 150 beehives? Optimize Forest Honey Production
- Why is the use of movable-frame beehives recommended? Enhance Your Commercial Apiary's Efficiency and Yield
- What technical advantages do movable-frame hives offer? Boost Modern Beekeeping Management and Honey Yields



















