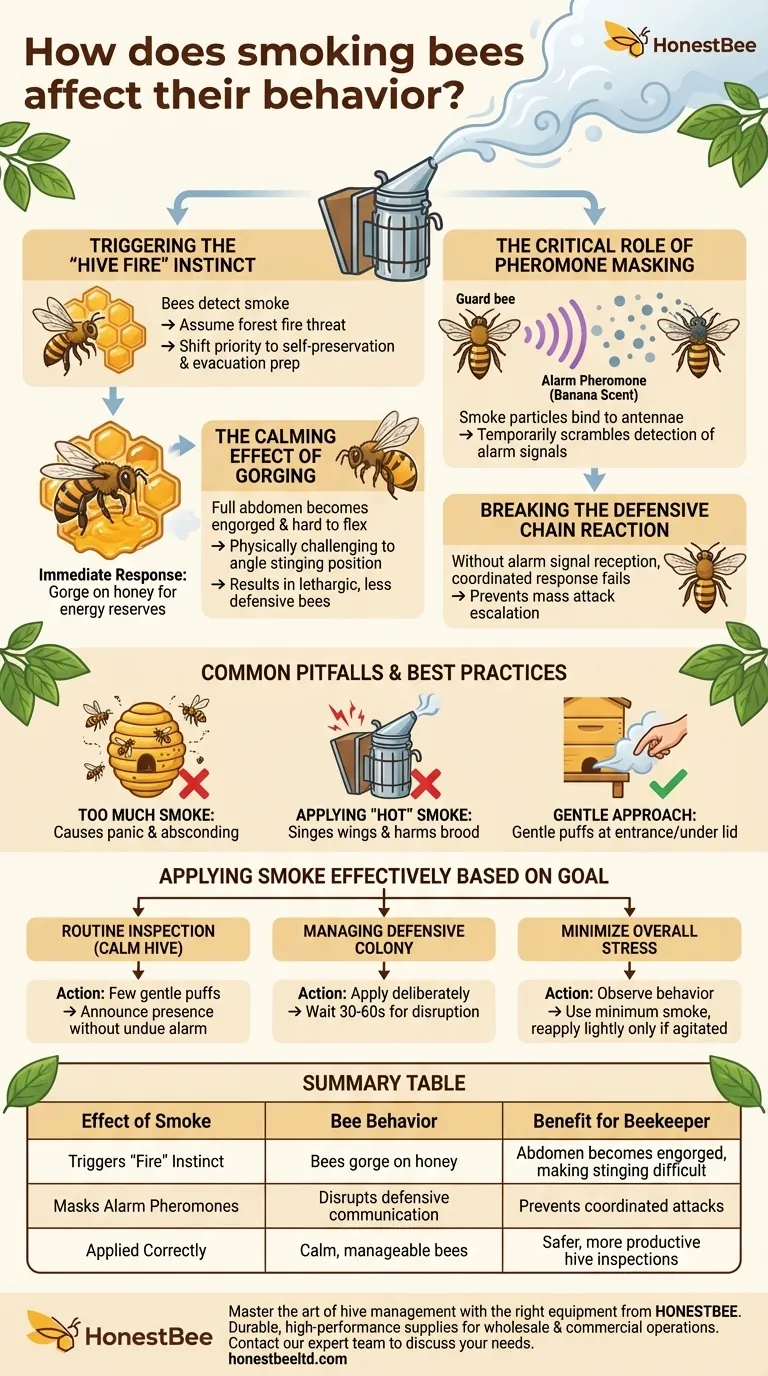
At its core, smoking bees triggers their primal survival instinct. When bees detect smoke, they don't get sleepy or sedated. Instead, they assume a forest fire is threatening their home, which fundamentally shifts their priorities from hive defense to self-preservation and preparing for a potential evacuation.
Smoke works not by sedating bees, but by cleverly redirecting their focus. It simulates a large-scale emergency, compelling them to gorge on honey and simultaneously masking the chemical alarm signals they use to coordinate a defensive attack.

The Two-Pronged Effect of Smoke
A bee smoker is a communication tool that leverages a bee's evolved behaviors. Its effectiveness comes from a combination of two distinct, simultaneous reactions within the colony.
Triggering the "Hive Fire" Instinct
A bee's most valuable resource, besides the queen, is the honey stored in the hive. It is the colony's sole source of energy.
When smoke is introduced, the bees' evolutionary programming kicks in, telling them a fire is nearby and they may have to abandon their home.
Their immediate response is to prepare for this journey by consuming as much honey as possible. This ensures they have the energy reserves needed to fly a long distance and build a new wax comb if necessary.
The Calming Effect of Gorging
This act of gorging on honey has a convenient side effect for the beekeeper. A bee's abdomen, when full of honey, becomes engorged and difficult to flex.
This makes it physically challenging for the bee to angle its body into the proper "stinging" position. While not impossible, it makes them far more lethargic and less inclined to sting.
The Critical Role of Pheromone Masking
The second, and arguably more important, function of smoke is its ability to disrupt the bees' primary method of communication: pheromones.
Disrupting the Alarm System
When a guard bee perceives a threat, it releases an alarm pheromone. This chemical signal, which smells like bananas to humans, instantly alerts other bees in the vicinity to the danger.
The thick, carbon-rich particles in cool smoke effectively bind to the bees' sensitive antennae, temporarily scrambling their ability to detect these specific pheromones. It's the equivalent of jamming an army's radio communications during an attack.
Breaking the Defensive Chain Reaction
Without the ability to receive the alarm signal, a coordinated defensive response never materializes. One agitated bee cannot incite a mass attack.
This disruption is why smoke is so effective at preventing a few stings from escalating into a major event where hundreds of bees join the defense.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Using a smoker is a skill that requires finesse. Misusing it can be counterproductive and harmful to the colony.
Using Too Much Smoke
Over-smoking a hive is a common mistake. It can cause panic, leading bees to become agitated and run erratically instead of calming down. In extreme cases, it can even cause the colony to abscond, or abandon the hive entirely.
Applying "Hot" Smoke
The goal is to produce cool, white smoke. If your smoker is puffing out sparks or embers, it can singe the bees' wings and harm the brood. Always ensure your fuel is smoldering gently, not burning aggressively.
The Importance of a Gentle Approach
A few gentle puffs at the entrance and under the cover are usually sufficient. The goal is not to fill the hive with smoke, but to gently inform the bees of your presence and mask any initial alarm pheromones.
Applying Smoke Effectively Based on Your Goal
How you use a smoker should depend on the temperament of the hive and your objective for the inspection.
- If your goal is a routine inspection of a calm hive: Use a few gentle puffs at the entrance and under the lid to announce your presence without causing undue alarm.
- If your goal is managing a known defensive colony: Apply smoke more deliberately, waiting 30-60 seconds for it to take effect before opening the hive to ensure the communication lines are disrupted.
- If your goal is to minimize overall stress: Observe the bees' behavior and the pitch of their buzzing. Use only the minimum amount of smoke needed to keep them calm, reapplying lightly only when they begin to show signs of agitation.
Ultimately, using a smoker is not about subduing your bees, but about communicating with them in a language they have evolved to understand.
Summary Table:
| Effect of Smoke | Bee Behavior | Benefit for Beekeeper |
|---|---|---|
| Triggers 'Fire' Instinct | Bees gorge on honey | Abdomen becomes engorged, making stinging difficult |
| Masks Alarm Pheromones | Disrupts defensive communication | Prevents coordinated attacks |
| Applied Correctly | Calm, manageable bees | Safer, more productive hive inspections |
Master the art of hive management with the right equipment from HONESTBEE.
Whether you're a commercial apiary managing hundreds of hives or a distributor supplying fellow beekeepers, proper technique starts with reliable tools. A well-designed smoker is fundamental to safe and effective beekeeping.
At HONESTBEE, we supply durable, high-performance beekeeping supplies and equipment tailored for wholesale and commercial operations. Let us help you equip your operation for success.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your wholesale equipment needs and ensure every hive inspection is a calm, productive experience.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Honey Bee Smoker Hive and Honeycomb Smoker for Beekeeping
- European Stainless Steel Bee Smoker for Honey Bee Hive
- Economy Galvanized Beekeeping Honey Bee Smoker for Wholesale
- Professional Bee Smoker with Elongated Spout and Durable Bellows for Beekeeping
- Premium Traditional Copper Bee Smoker with Bellows
People Also Ask
- What role does an industrial-grade beekeeping smoker play in mite control? Transform Botanicals into Powerful Treatments
- What is the primary function of a specialized bee smoker? Master Hive Control and Operator Safety
- How to make smoke for a bee hive? Master the Technique for a Calm, Productive Hive
- How does smoke effectively calm honey bees? Master the Science of Chemical Masking for Safer Hive Management
- What is the technical function of an industrial-grade Beekeeping Smoker? Master Hive Control and Safety
- Can smoke harm bees if used incorrectly? Master Gentle Beekeeping Techniques
- What is the operational mechanism of bee smokers? Learn How Cold Smoke Controls Colony Behavior
- What role does a smoker play in the process of opening and inspecting a beehive? Master Hive Control & Safety



















