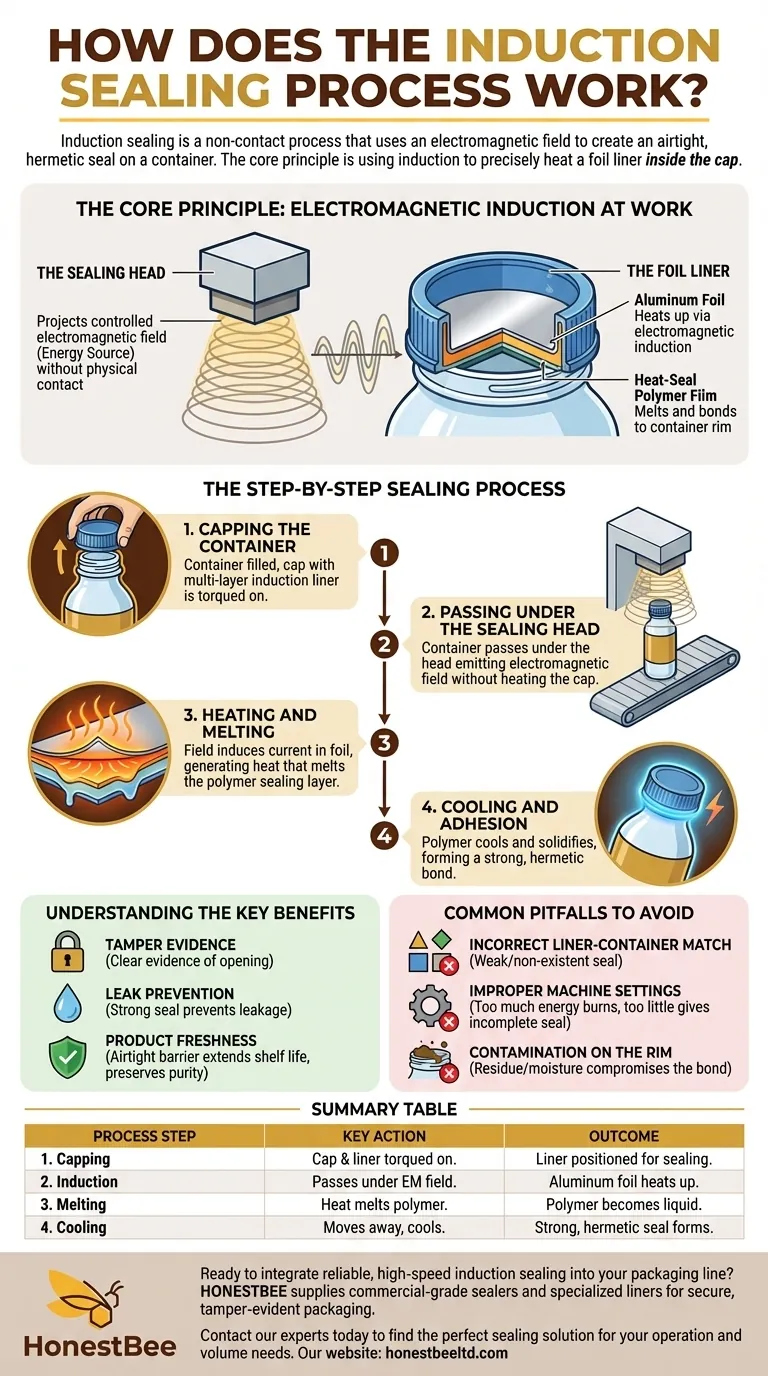
Induction sealing is a non-contact process that uses an electromagnetic field to create an airtight, hermetic seal on a container. After a cap containing a multi-layered foil liner is placed on a container, it passes under a sealing head. The head generates a field that heats the foil layer, which in turn melts a polymer coating on the liner, fusing it to the rim of the container as it cools.
The core principle is not direct heat application, but rather using electromagnetic induction to precisely heat a foil liner inside the cap. This melts a specific sealing layer, bonding it to the container to create a secure, tamper-evident seal without affecting the product inside.
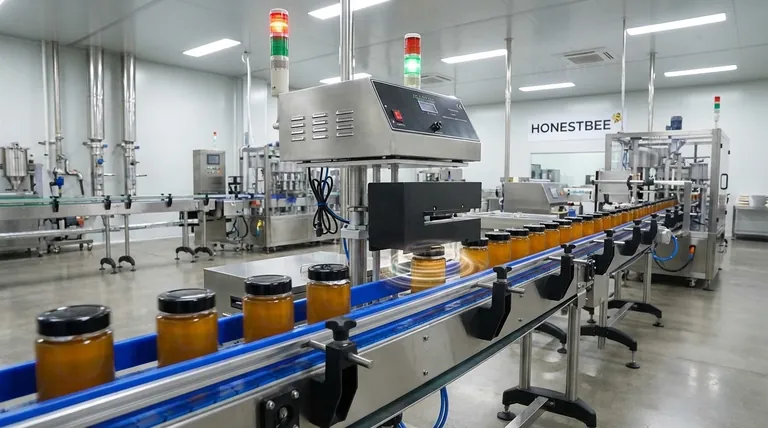

The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Induction at Work
To understand the process, you must first understand the two critical components that interact: the sealing head and the specialized liner inside the cap.
The Sealing Head
The induction sealing machine, or "sealer," has a sealing head that projects a controlled electromagnetic field. This field is the energy source for the entire process.
It operates without any physical contact with the container or cap, allowing it to function cleanly and at high speeds on a production line.
The Foil Liner
The liner, which comes pre-inserted into the cap, is not a simple piece of foil. It is a multi-layered composite.
The most important layers are the aluminum foil, which is conductive and heats up in the electromagnetic field, and the heat-seal polymer film, which is designed to melt at a specific temperature and bond securely to the container's rim.
The Step-by-Step Sealing Process
The elegance of induction sealing lies in its simple, rapid, and repeatable steps, which typically occur on an automated conveyor line.
Step 1: Capping the Container
First, the container is filled with its product. A cap, already fitted with the multi-layer induction liner, is then torqued onto the container.
Step 2: Passing Under the Sealing Head
The capped container moves along a conveyor belt, passing directly underneath the induction sealing head.
As it passes through, the sealing head emits the high-frequency electromagnetic field, which penetrates the plastic cap without heating it.
Step 3: Heating and Melting
The electromagnetic field induces an electrical current in the aluminum foil layer of the liner. This resistance causes the foil to heat up rapidly.
This controlled heat is conducted to the adjacent polymer sealing layer, causing it to melt.
Step 4: Cooling and Adhesion
Once the container moves out from under the sealing head, the process is complete. The melted polymer layer cools and solidifies.
This creates a strong, hermetic bond between the liner and the rim of the container, effectively sealing it.
Understanding the Key Benefits
The primary reasons for using induction sealing are centered around product integrity, safety, and preservation.
Tamper Evidence
The seal provides clear, unambiguous evidence of tampering. If a consumer receives a product with a broken or missing seal, they know it should not be used.
Leak Prevention
The strong, hermetic seal created by the process prevents product leakage, which is critical for liquids and fine powders during shipping and handling.
Product Freshness and Purity
By creating an airtight barrier, the seal protects the product from oxygen, moisture, and other external contaminants, extending shelf life and preserving freshness.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While reliable, the process requires proper setup to be effective. The quality of the seal depends on the precise interaction of the cap, liner, container, and machine.
Incorrect Liner-Container Match
The polymer sealing layer on the liner must be chemically compatible with the container material (e.g., PET, HDPE, glass). Using the wrong liner will result in a weak or non-existent seal.
Improper Machine Settings
The power level of the sealing head and the speed of the conveyor must be carefully calibrated. Too much energy can burn the liner and damage the product, while too little will result in an incomplete seal.
Contamination on the Rim
The rim of the container must be perfectly clean and dry. Any product residue, dust, or moisture can interfere with the polymer's ability to bond, compromising the seal's integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the process allows you to apply it effectively to your specific packaging needs.
- If your primary focus is product safety and tamper-evidence: Induction sealing is a gold-standard technology for providing consumers with confidence in your product's integrity.
- If your primary focus is extending the shelf life of sensitive products: The hermetic seal is exceptionally effective at preventing contamination and degradation from environmental factors.
- If your primary focus is high-speed manufacturing efficiency: The non-contact, rapid nature of induction sealing allows it to be seamlessly integrated into automated production lines without creating bottlenecks.
Ultimately, mastering induction sealing is about controlling a precise energy transfer to create a perfect, protective bond.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Capping | Cap with foil liner is torqued onto container. | Liner is positioned for sealing. |
| 2. Induction | Container passes under a sealing head emitting an electromagnetic field. | The aluminum foil layer in the liner heats up. |
| 3. Melting | Heat melts the polymer sealing layer on the liner. | Polymer becomes liquid and ready to bond. |
| 4. Cooling | Container moves away; polymer cools and solidifies. | A strong, hermetic seal is formed with the container rim. |
Ready to integrate reliable, high-speed induction sealing into your packaging line?
HONESTBEE supplies the commercial-grade induction sealers and specialized foil liners that distributors and large-scale apiaries trust to protect their products. We ensure your packaging is secure, tamper-evident, and preserves product freshness.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sealing solution for your operation and volume needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Water Cooled Induction Sealing Machine for Bottles and Containers
- HONESTBEE Professional Benchtop Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine Capper
- Professional Durable Customizable Blister Packing Machine
- Semi Automatic Electric Bottle Capping Machine
- Automatic Inline Spindle Bottle Capping Machine for Honey Production
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of bottle sealing machine? Achieve Perfect, Tamper-Evident Seals for Your Products
- What role do high-barrier sterile packaging and automatic induction sealing equipment play in honey safety management?
- How does tamper-evident sealing equipment benefit the honey trade? Ensure Product Integrity and Market Trust
- How does an induction sealing machine work? Enhance Honey Packaging with Hermetic Seals & Tamper Evidence
- What is the significance of induction sealing equipment in honey packaging? Protect Your Brand and Product Integrity



















