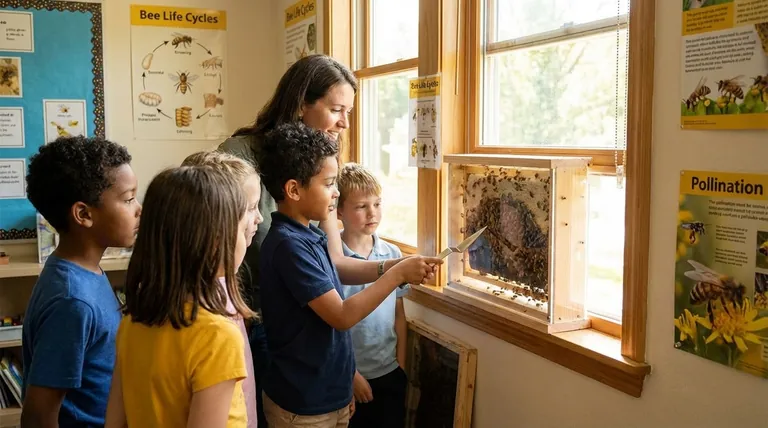
An observation hive is a specially designed, clear-sided beehive that allows for safe, direct viewing of a honeybee colony's inner workings. Its primary benefit for students is its ability to transform abstract biological and ecological concepts into a tangible, living display, making complex science unforgettable.
The true value of an observation hive lies beyond simply watching bees. It functions as a dynamic, living laboratory that makes intricate systems—from social structures to ecosystem dependencies—immediately accessible and deeply engaging for students of all ages.

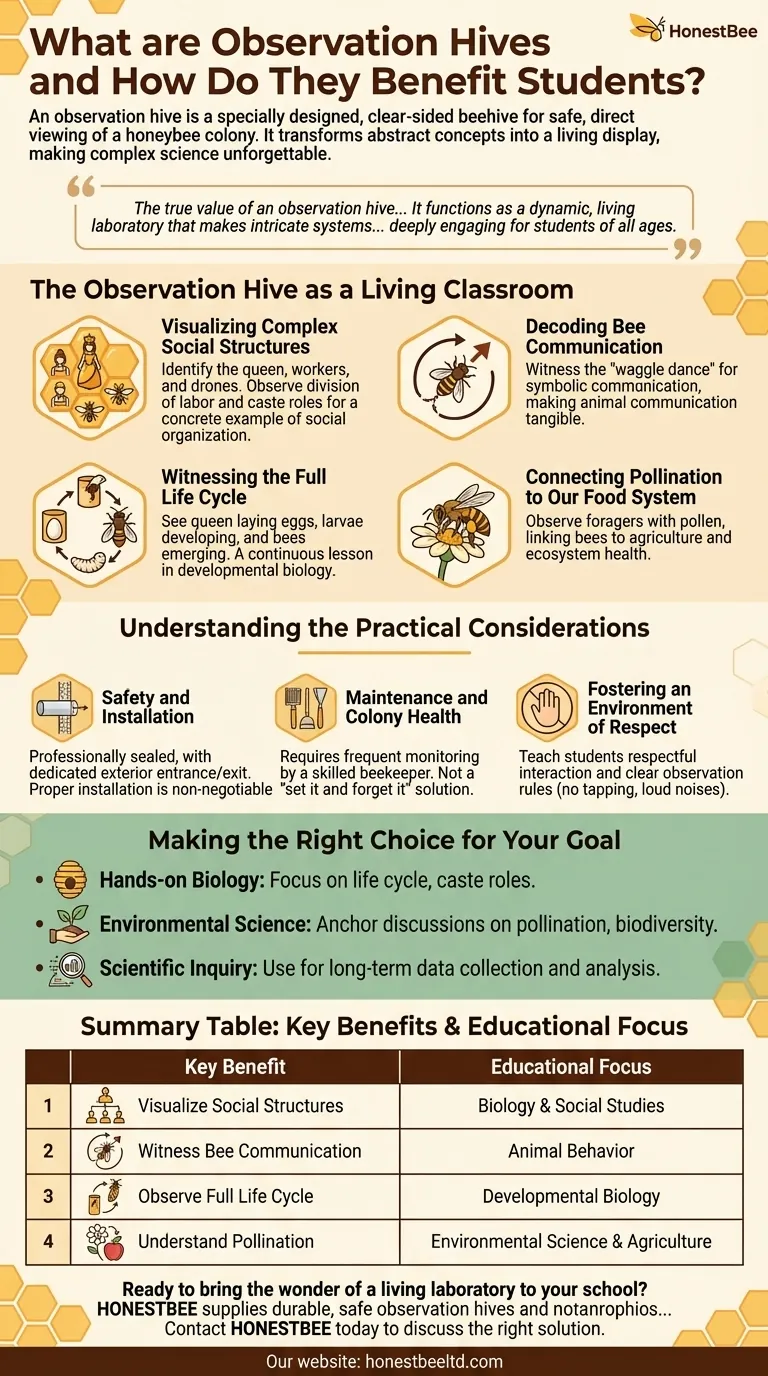
The Observation Hive as a Living Classroom
An observation hive is far more than a novelty; it is a powerful educational tool that brings curriculum to life. It provides a direct window into a functioning superorganism, allowing students to witness key scientific principles as they happen.
Visualizing Complex Social Structures
Students can see firsthand the division of labor that defines a honeybee colony. They can learn to identify the queen, worker bees, and drones, observing how each caste performs its specific duties for the good of the whole.
This provides a concrete example of social organization, specialization, and cooperation—concepts that are relevant in both biology and social studies.
Decoding Bee Communication
The famous "waggle dance" is a primary example of symbolic communication in the animal kingdom. With an observation hive, students can actually witness a forager bee performing this dance to tell her sisters the precise direction and distance to a food source.
This makes the concept of animal communication tangible, moving it from a textbook diagram to a real, observable behavior.
Witnessing the Full Life Cycle
The clear panels allow students to see the queen bee laying eggs, watch larvae develop in their hexagonal cells, and witness young bees emerging as adults.
This presents the complete process of metamorphosis in a way that is far more impactful than static images or videos. It is a powerful, continuous lesson in developmental biology.
Connecting Pollination to Our Food System
Students can observe forager bees returning to the hive with their legs packed with colorful pollen. This simple act provides a powerful visual link to the process of pollination.
It helps them understand the critical role bees play in agriculture and the health of our ecosystem, making the connection between a tiny insect and the food on their plates crystal clear.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While immensely valuable, implementing an observation hive requires careful planning. Understanding the requirements is key to a successful and safe educational experience.
Safety and Installation
Safety is the paramount concern. A professionally designed observation hive is completely sealed from the classroom. The bees enter and exit the hive through a dedicated tube that passes through an exterior wall or window.
Proper installation by someone knowledgeable is non-negotiable to ensure the hive is secure and the bees have no access to the indoor space.
Maintenance and Colony Health
An observation hive is typically smaller and has a different form factor than a standard field hive. This means it requires more frequent monitoring and management by a skilled beekeeper to ensure the colony remains healthy and doesn't run out of space or food.
It is not a "set it and forget it" installation. The health of the bees is an ongoing responsibility.
Fostering an Environment of Respect
The hive serves as a unique opportunity to teach students how to interact with nature respectfully and calmly. It requires establishing clear rules for observation to ensure the bees are not disturbed by tapping on the glass or loud noises.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Integrating an observation hive can serve different educational priorities. Your primary objective will shape how you use this powerful tool.
- If your primary focus is hands-on biology: Emphasize direct observation of the bee life cycle, caste roles, and daily hive activities to illustrate core biological concepts.
- If your primary focus is environmental science: Use the hive to anchor discussions on pollination, biodiversity, and the interconnectedness of ecosystems.
- If your primary focus is developing scientific inquiry: Challenge students to use the hive for long-term projects, such as tracking brood patterns or counting foraging trips to collect and analyze real data.
An observation hive turns a passive learning space into a dynamic hub of discovery.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Educational Focus |
|---|---|
| Visualize Social Structures | Biology & Social Studies |
| Witness Bee Communication | Animal Behavior |
| Observe Full Life Cycle | Developmental Biology |
| Understand Pollination | Environmental Science & Agriculture |
Ready to bring the wonder of a living laboratory to your school?
HONESTBEE supplies the durable, safe observation hives and beekeeping equipment that commercial apiaries and distributors trust. We can help you create an unforgettable, hands-on learning experience that makes complex science tangible for students.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss the right observation hive solution for your educational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Professional Insulated Plastic Bee Hives
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Langstroth Bee Hives Bee Keeping Box for Beginners Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How should beekeepers handle bees when using a hive tool? Master Calm, Deliberate Techniques
- How can a hive tool be used to remove propolis and burr comb? Master Hive Maintenance for a Healthy Colony
- How does standardized beehive manufacturing equipment improve the productivity of commercial apiaries?
- Why use professional beekeeping tools for beehive inspections? Crucial Support for Pollinator Protection Policies
- What are the basic tools for beekeeping? Essential Starter Kit for Safe & Successful Hive Management



















