The single best investment a beekeeper can make after their first hive is a second one. While it may seem like doubling your workload, a second colony provides critical insurance against loss, accelerates your learning curve exponentially, and unlocks management options that are impossible with a single hive. It is the fastest path from being a bee "haver" to a skilled bee "keeper."
A second hive fundamentally changes your role from managing a single, high-stakes colony to overseeing a resilient, self-sufficient system. It provides the redundancy and resources needed to solve problems, compare outcomes, and ensure long-term success.
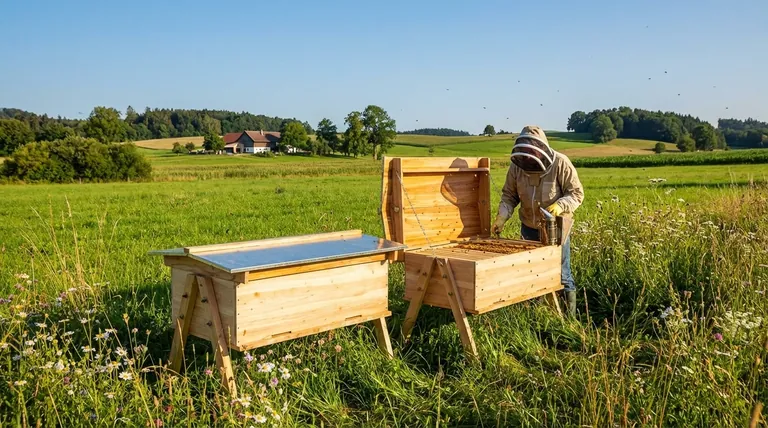

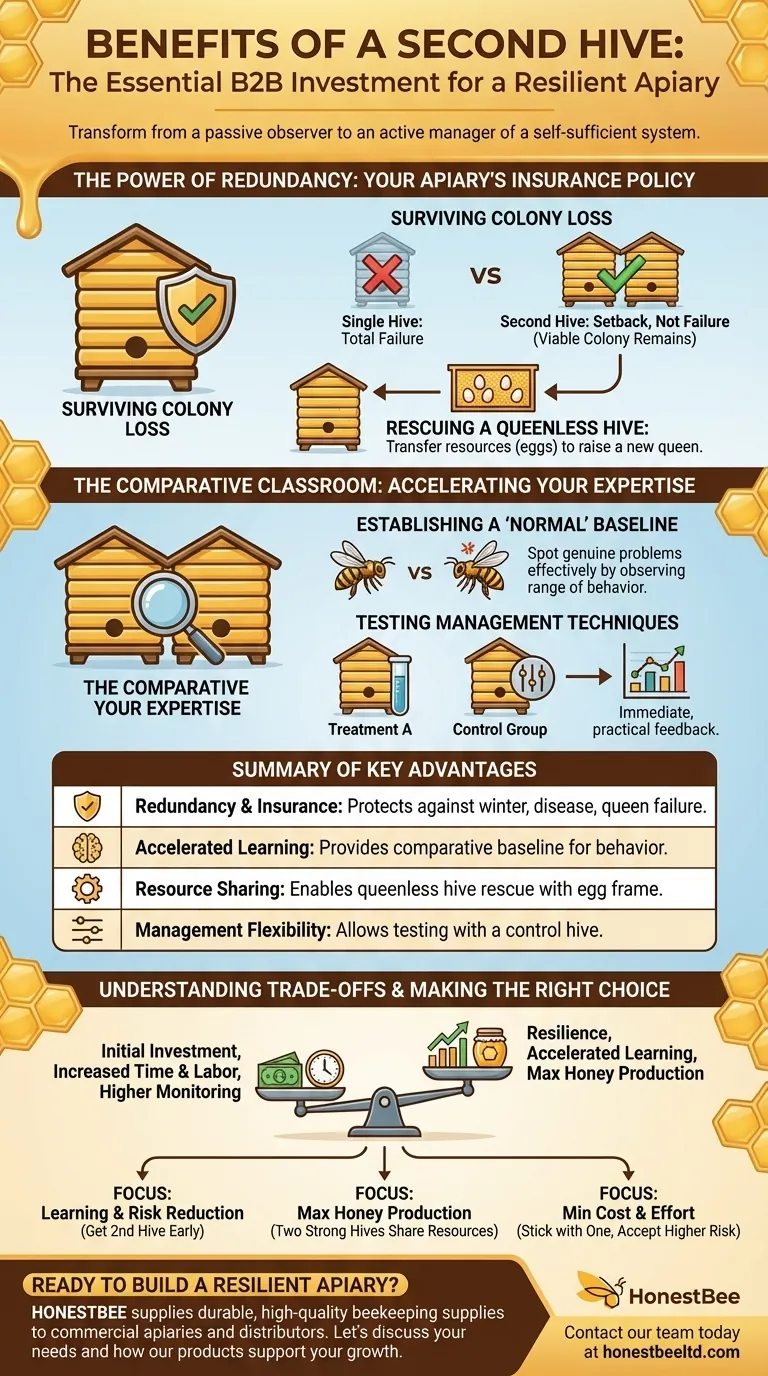
The Power of Redundancy: Your Apiary's Insurance Policy
The most common and painful experience for a new beekeeper is losing their only colony, forcing them to start over from scratch the following year. A second hive is your best protection against this.
Surviving Colony Loss
Losing a hive is a matter of when, not if. Harsh winters, disease, or queen failure can lead to a "deadout." With a second hive, the loss of one is a setback, not a total failure. You still have a viable colony to learn from and can often use it to start a new hive (a "split") in the spring.
Rescuing a Queenless Hive
A colony without a queen is doomed. If you only have one hive, your only options are to hope the bees can raise a new queen (if they have eggs) or buy a new, expensive one. With a second hive, you can simply move a frame containing fresh eggs from the healthy colony to the queenless one. This gives them the genetic material they need to raise their own replacement queen, saving the hive with resources you already own.
The Comparative Classroom: Accelerating Your Expertise
With a single hive, you have no point of reference. Is your colony’s behavior normal or a sign of trouble? A second hive acts as a real-time control group for your beekeeping education.
Establishing a "Normal" Baseline
One hive might be gentle and productive, while another is defensive and slow to build up. By observing two colonies side-by-side, you quickly learn the wide range of what is considered "normal" behavior. This comparative insight helps you spot genuine problems far more effectively.
Learning from Different Genetics
Every colony has a unique "personality" based on its queen's genetics. Managing two different colonies teaches you to be a more flexible and adaptable beekeeper. You'll see firsthand how one colony handles a nectar flow or resists pests differently than its neighbor.
Testing Management Techniques
A second hive allows you to conduct your own experiments. You can try a new mite treatment or feeding strategy on one colony and use the other as a control. This provides immediate, practical feedback on what works and what doesn't in your specific environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While immensely beneficial, adding a second hive is a decision that requires acknowledging the new demands it will place on you.
The Initial Investment
A second hive means a second investment. You will need another complete set of hive bodies, frames, and foundation, as well as a new package of bees or a nucleus colony.
Increased Time and Labor
Two hives require more time for inspections and management. Lifting hive bodies full of honey is also physically demanding, and two hives mean twice the heavy lifting during harvest season.
Higher Monitoring Demands
With two colonies, you have two separate systems to track. This means keeping distinct records for queen health, mite loads, and feeding needs, adding a layer of complexity to your management routine.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
The decision to add a second hive depends entirely on your goals as a beekeeper.
- If your primary focus is learning quickly and minimizing risk: Getting a second hive in your first or second year is the single most effective strategy you can employ.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: Two strong, well-managed hives will produce significantly more honey than one, as you can share resources to ensure both are at peak strength for the nectar flow.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial cost and effort: Sticking with one hive is a valid choice, but you must accept the higher risk of total failure and a much slower learning curve.
Ultimately, a second hive transforms you from a passive observer of one colony into an active manager of a resilient apiary.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Advantage |
|---|---|
| Redundancy & Insurance | Protects against total loss from winter, disease, or queen failure. |
| Accelerated Learning | Provides a comparative baseline to understand normal vs. problematic behavior. |
| Resource Sharing | Enables rescuing a queenless hive with a frame of eggs from the healthy colony. |
| Management Flexibility | Allows testing treatments and techniques with a control hive for better results. |
Ready to build a more resilient and successful apiary?
As a beekeeper, you understand that the right equipment is the foundation of good management. HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment through wholesale-focused operations to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors.
Whether you're adding a second hive or scaling your entire operation, we provide the reliable tools you need to manage your colonies effectively. Let's discuss your needs and how our products can support your growth.
Contact our team today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
- Langstroth Bee Hives Bee Keeping Box for Beginners Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
People Also Ask
- What are the ergonomic and management advantages of Horizontal Top-Bar Hives? Modern Beekeeping with Less Strain
- What are the most popular types of hives besides the Langstroth? Top Bar & Horizontal Hives Explained
- What are the box management requirements for a top bar hive vs. Langstroth? Choose Your Hive Strategy
- What are the specific environmental challenges of using a horizontal Top Bar hive in cold climates? Survival Strategies
- How do top bars function within a top bar hive? Master the Natural Way to Manage Honeybees



















