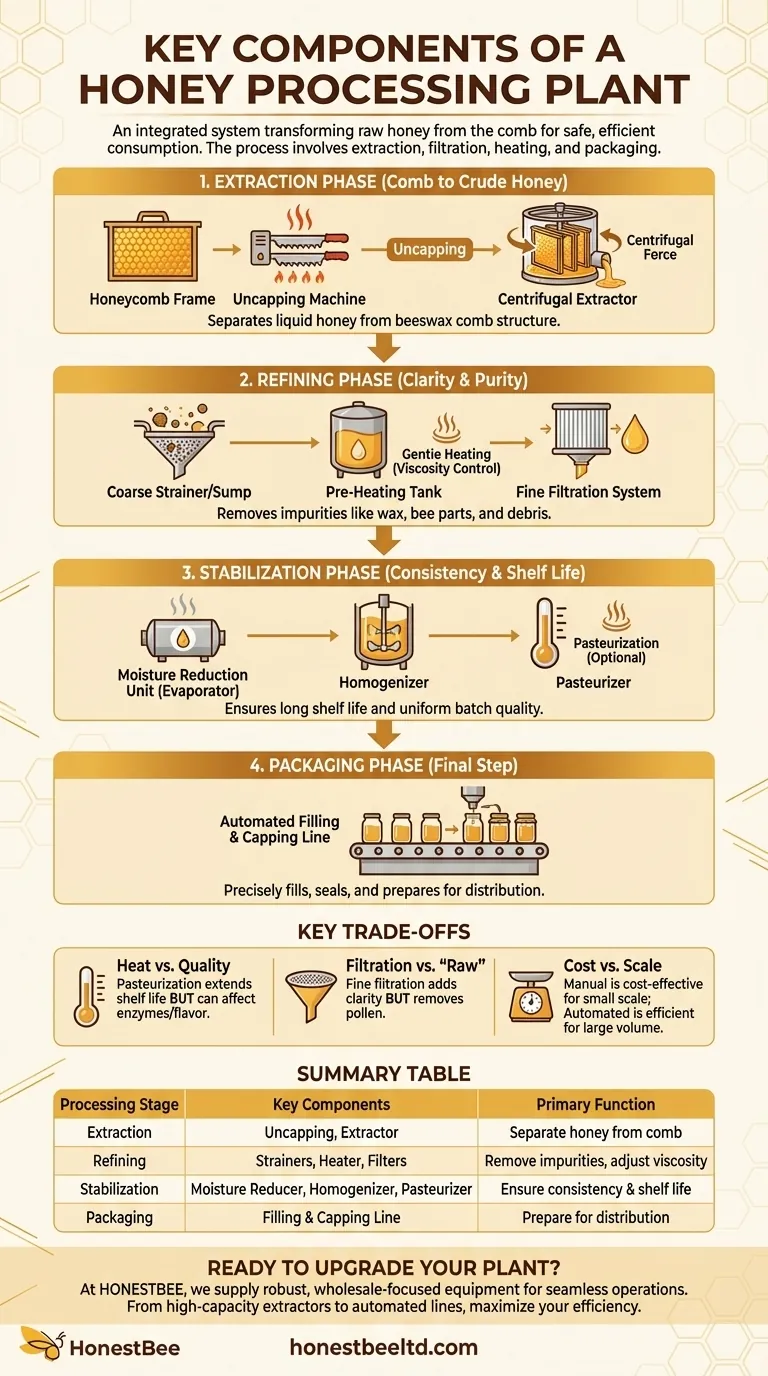
At its core, a honey processing plant is an integrated system designed to take raw honey from the comb and prepare it for consumption safely and efficiently. The essential components that enable this transformation include equipment for extraction, filtration, gentle heating for viscosity control, and finally, packaging.
A successful honey processing operation isn't just about owning the right machinery; it's about understanding how each component impacts the final product. The central challenge is to purify and stabilize the honey for market while preserving its natural enzymes, delicate aroma, and unique qualities.
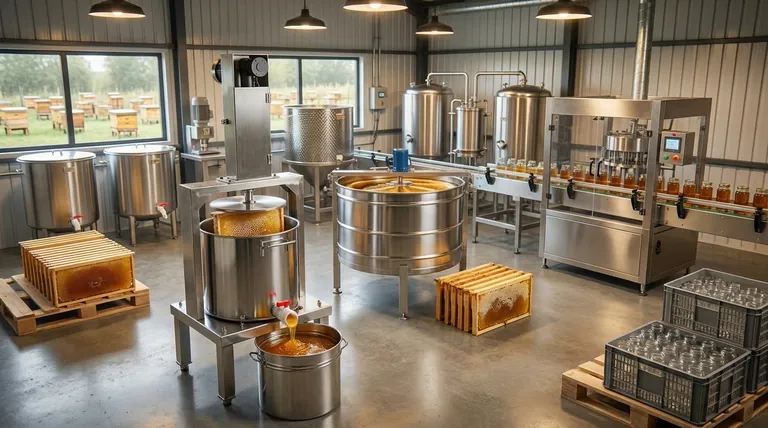

From Comb to Crude Honey: The Extraction Phase
The first stage of processing is dedicated to separating the liquid honey from the beeswax comb structure where the bees stored it.
Honey Reception and Uncapping
Before extraction, honey-filled frames are brought into the plant. The protective wax cappings that seal each honeycomb cell must be removed, typically with heated knives or a specialized uncapping machine.
The Centrifugal Extractor
The uncapped frames are placed inside an extractor. This machine uses centrifugal force, spinning the frames at high speed to pull the honey out of the comb cells without destroying the comb itself.
Refining for Clarity and Purity
Once extracted, the honey contains various impurities like wax particles, bee parts, and other debris that must be removed.
Initial Straining
The raw honey first passes through a coarse strainer or sump. This step is a simple filtration process designed to catch the largest pieces of wax and other visible debris.
Gentle Heating for Fluidity
Raw honey is often highly viscous, making it difficult to filter and pump. It is gently warmed in a pre-heating tank to decrease its viscosity. This must be done carefully to avoid damaging the honey's natural enzymes and flavor.
Fine Filtration
After warming, the honey is pumped through a fine filtration system. This removes smaller suspended particles, including fine wax and sometimes even pollen, resulting in the crystal-clear appearance many consumers expect.
Ensuring Stability and Consistency
This stage prepares the honey for a long shelf life and ensures that every jar in a batch has the same quality.
Moisture Reduction (Optional)
If the honey's natural water content is too high (typically above 18%), it risks fermentation. A moisture reduction unit, often a type of evaporator, can be used to gently remove excess water and ensure stability.
Homogenization
For large-scale operations, a homogenizer is used to agitate and blend honey from different sources. This ensures a consistent color, texture, and flavor profile across the entire production batch.
Pasteurization (Optional)
In some commercial processes, honey is briefly heated to higher temperatures (pasteurization) to destroy any yeast cells and slow down crystallization. This significantly extends shelf life but is a point of debate regarding its impact on quality.
Automated Filling and Packaging
The final step involves an automated filling and capping line. This machine precisely fills jars or containers to the correct volume, seals them, and prepares them for labeling and distribution.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing the right components involves balancing efficiency with the desired quality of the final product.
Heat vs. Quality: The Pasteurization Dilemma
Applying high heat during pasteurization ensures a long shelf life and prevents crystallization, which is desirable for large retailers. However, this heat can destroy beneficial enzymes and alter the honey's delicate flavor and aroma, which is why producers of "raw" honey avoid it.
Filtration vs. "Raw" Honey: The Pollen Debate
Aggressive, fine filtration creates brilliantly clear honey but can remove naturally occurring pollen. Since pollen is often used to verify a honey's floral and geographic origin, some standards prohibit honey that has been ultra-filtered from being labeled with a specific source.
Cost vs. Scale: Manual vs. Automated Systems
For a small-scale beekeeper, a simple extractor and manual bottling may be sufficient. As production volume increases, investing in automated uncapping, pumping, and filling systems becomes essential for efficiency, but it requires significant capital investment.
Selecting Components for Your Goal
The ideal plant configuration depends entirely on your end product and market.
- If your primary focus is artisanal or "raw" honey: Prioritize a quality extractor and coarse straining, while strictly avoiding pasteurization and fine filtration to preserve the honey's natural state.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial distribution: Invest in a fully integrated line with pasteurization and homogenization to ensure product consistency, stability, and a long shelf life for retail channels.
- If your primary focus is balancing quality with scalability: A modular approach is best, starting with core extraction and filtration, then adding components like a moisture reducer or automated filler as your operation grows.
Understanding these components and their functions empowers you to design a process that protects the integrity of your honey while meeting the demands of your market.
Summary Table:
| Processing Stage | Key Components | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction | Uncapping Machine, Centrifugal Extractor | Separate honey from the comb |
| Refining | Strainers, Pre-Heating Tank, Fine Filters | Remove impurities, adjust viscosity |
| Stabilization | Moisture Reducer, Homogenizer, Pasteurizer | Ensure consistency & shelf life |
| Packaging | Automated Filling & Capping Line | Prepare honey for distribution |
Ready to build or upgrade your honey processing plant?
At HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the robust, wholesale-focused equipment needed for a seamless operation. From high-capacity extractors to automated filling lines, our solutions are designed to maximize your efficiency and protect your honey's quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal components for your production goals and scale.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Stainless Steel Honey Press Wax Press with Tank
- Stainless Steel Manual Honey Press with Guard for Pressing Honey and Wax
- Electric Flatting and Embossing Machine with Tray for Beekeeping
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of the stainless steel honey press? Maximize Yield & Guarantee Purity
- What are the benefits of using a honey press for Warré or Top Bar beehives? Maximize Your Natural Harvest
- What are the advantages of using automated stainless steel honey extraction equipment? Boost Your Yield and Purity
- What are the main differences between centrifugal extractors and honey presses? A Guide for Commercial Apiaries
- How does pressed honey compare to extracted or crush-and-strain? Unlock the Full Flavor of the Hive



















