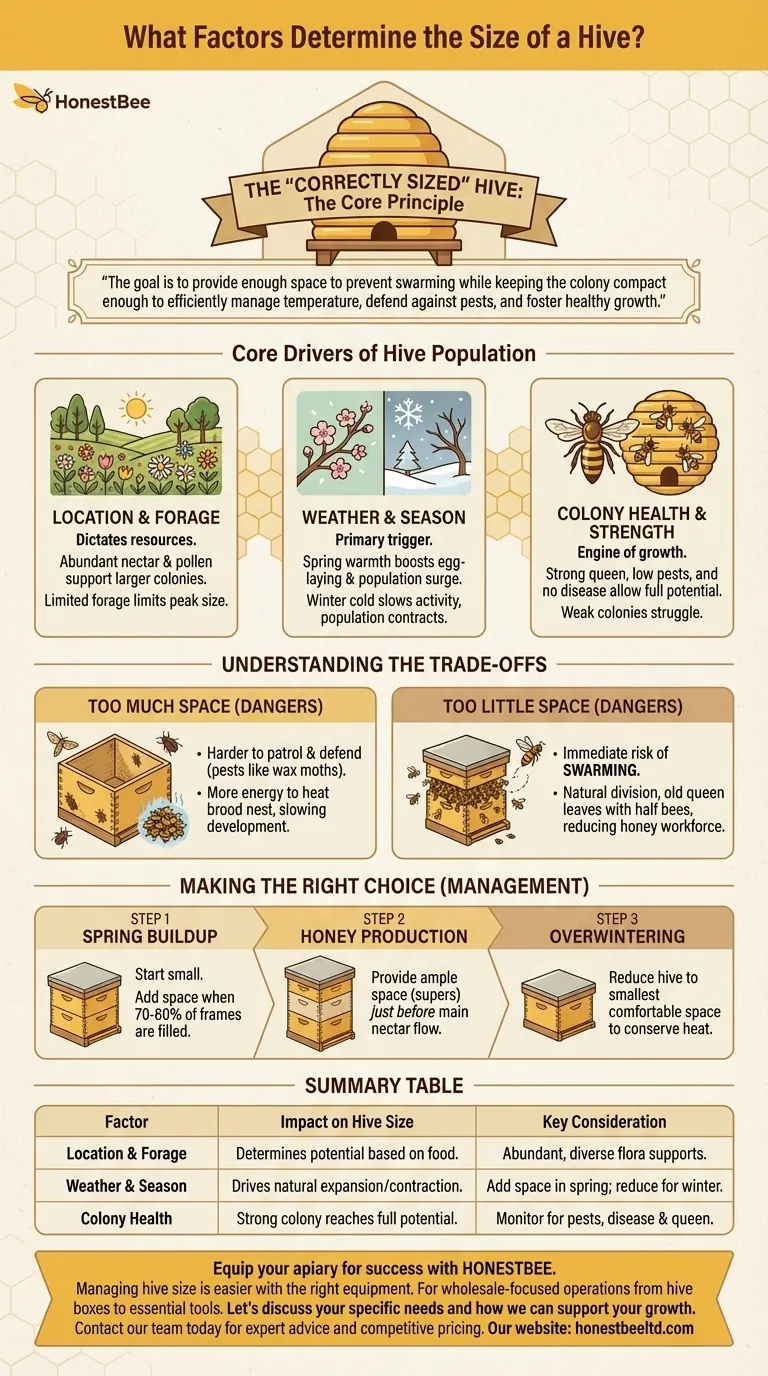
In short, the right size for a hive is determined by the interplay of three key factors. These are the external environment (location and weather), the internal strength of the colony (its health and population), and the time of year. Understanding how these elements work together is the foundation of successful hive management.
The core principle is not to aim for the "biggest" hive, but the correctly sized hive. The goal is to provide enough space to prevent swarming while keeping the colony compact enough to efficiently manage temperature, defend against pests, and foster healthy growth.
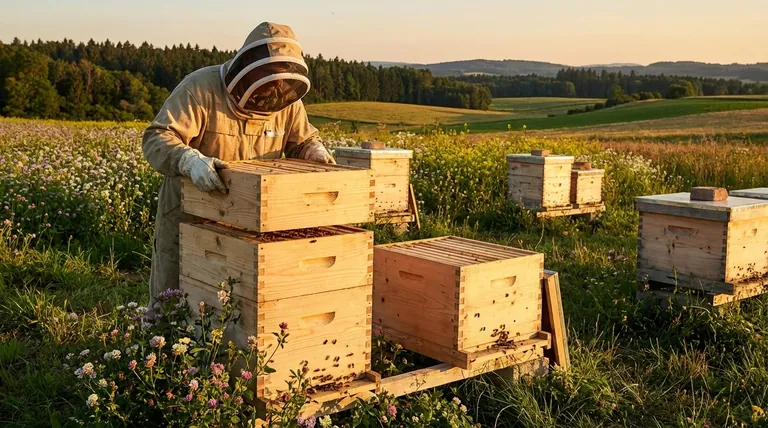

The Core Drivers of Hive Population
A hive is a living, breathing system that expands and contracts based on its needs and resources. The beekeeper's job is to provide the appropriate space for the colony's current and near-future requirements.
The Influence of Location and Forage
The surrounding environment dictates the resources available to the bees. A colony can only grow as large as its food supply allows.
A location rich in diverse, blooming plants provides the nectar (carbohydrates) and pollen (protein) necessary for raising new bees and producing honey. Limited forage will naturally limit the colony's peak size.
The Impact of Weather and Season
Weather is the primary trigger for seasonal bee activity. The colony's population cycle is directly tied to the changing seasons.
In spring, as temperatures rise and flowers bloom, the queen dramatically increases her egg-laying, causing the population to surge. Conversely, as winter approaches, laying slows and the population contracts to conserve resources.
The Strength and Health of the Colony
The internal condition of the colony is the engine of its growth. Two identical hives in the same location can have vastly different outcomes based on their health.
A strong, prolific queen, low pest pressure (like Varroa mites), and the absence of disease will allow a colony to reach its full potential. A weak colony will struggle to expand, even in ideal conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Providing the wrong amount of space at the wrong time can create significant problems for the colony and the beekeeper.
The Dangers of Too Much Space
Giving a colony, especially a small one, an excessive amount of room can be counterproductive and even harmful.
Bees must work to patrol and defend their entire hive. Too much empty space makes it harder to repel pests like wax moths and small hive beetles. It also forces the colony to expend more energy to heat the brood nest, slowing its development.
The Dangers of Too Little Space
A constrained hive presents an even more immediate risk: swarming.
When bees run out of room for brood and food storage, their natural instinct is to divide the colony. The old queen leaves with roughly half the bees to find a new home, drastically reducing your hive's population and honey-producing workforce.
Making the Right Choice for Your Colony
Your role is to anticipate the colony's needs and adjust the hive size accordingly. Observation is your most important tool.
- If your primary focus is spring buildup: Start the colony in a smaller configuration (one or two boxes) and add more space only when they have drawn out and filled 70-80% of the existing frames.
- If your primary focus is honey production: Provide ample space (honey supers) just before the main nectar flow begins to ensure they have room to store honey without clogging the brood nest.
- If your primary focus is overwintering success: Reduce the hive down to the smallest space the bees can comfortably occupy to help them conserve heat and resources through the cold months.
Ultimately, successful hive management is a dynamic process of providing the right space at the right time.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Hive Size | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Location & Forage | Determines maximum potential size based on food supply. | Abundant, diverse flora supports larger colonies. |
| Weather & Season | Drives natural expansion (spring) and contraction (winter). | Add space in spring; reduce for winter. |
| Colony Health | A strong, disease-free colony can reach its full size potential. | Monitor for pests/disease and queen vitality. |
Equip your apiary for success with HONESTBEE. Managing hive size is easier with the right equipment. Whether you're a commercial apiary focused on honey production or a distributor supplying beekeepers, our wholesale-focused operations provide the durable, scalable supplies you need—from hive boxes and frames to essential tools. Let's discuss your specific needs and how we can support your growth. Contact our team today for expert advice and competitive pricing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Langstroth Bee Hives Bee Keeping Box for Beginners Beekeeping
- Ergonomic Two Person Foldable Hive Lifter
- Multi-Functional Sliding Hive Entrance for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Plastic Bee Hive Stand for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How does the measurement of the vertical structure of forest understory vegetation inform beehive hardware design?
- Why is the integration of mechanical lifts necessary for moving beekeeping hives? Protect Your Health and Efficiency
- What is the technical significance of using high-precision digital pH meters to measure honey? Ensure Quality & Purity
- Why is specialized beekeeping infrastructure necessary? Protect Honey Quality and Prevent Spoilage
- Why is it important to remove dead-out hives from a bee yard as soon as possible? Protect Your Apiary Health
- What are the primary types of beehives and how do their designs differ? Choose the Best Hive for Your Apiary
- What are the technical advantages of modern beekeeping hives? Scale Your Honey Yield and Colony Health
- What technical specifications are required for mobile apiary transport platforms? Engineering for Colony Survival



















