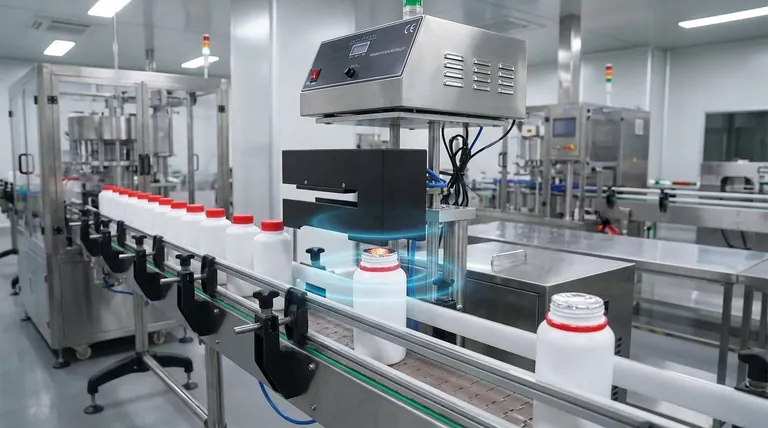
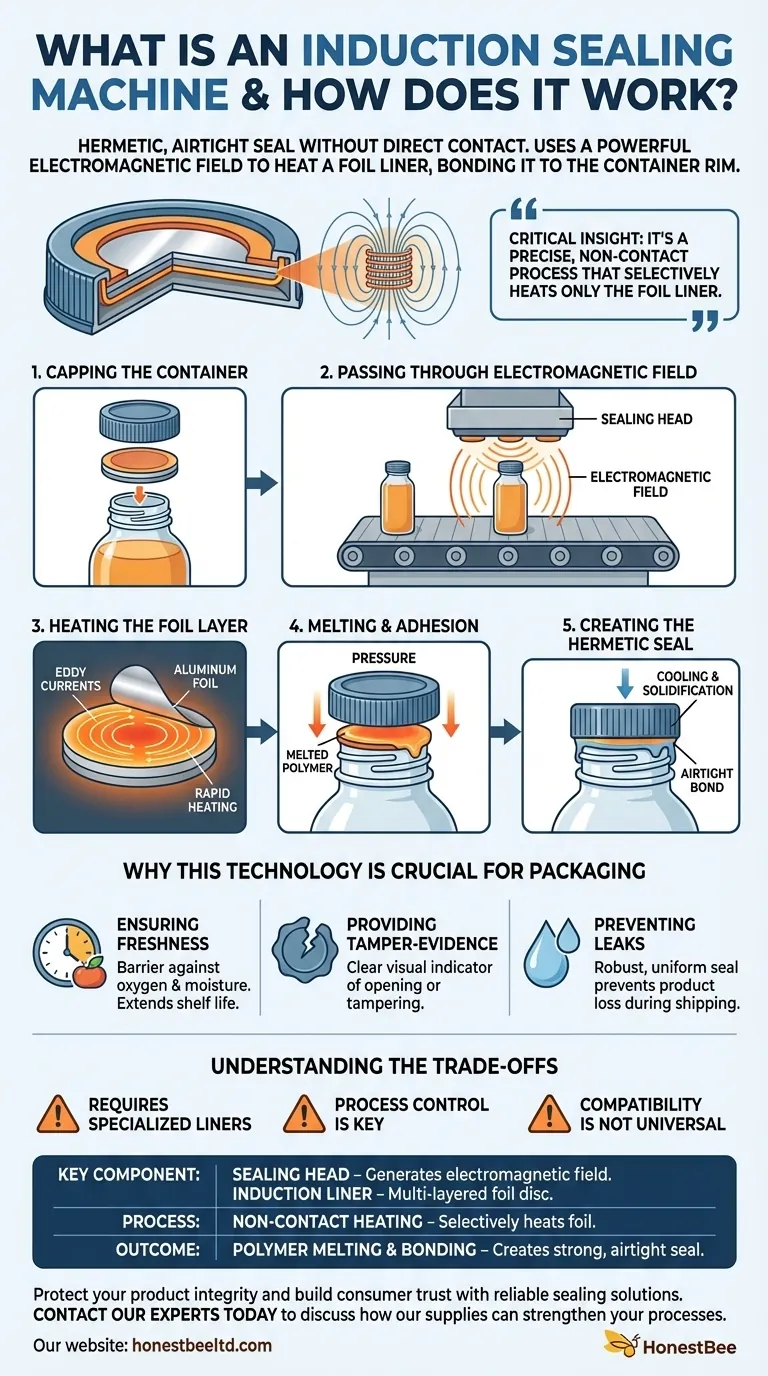
At its core, an induction sealing machine creates a hermetic, airtight seal on a container without direct contact. It uses a powerful electromagnetic field to heat a specialized foil liner inside the cap, which then melts and bonds to the container's rim, locking out contaminants and providing clear evidence of tampering.
The critical insight is that induction sealing isn't about heating the container or the cap. It's a precise, non-contact process that selectively heats only the foil liner, creating a strong, consistent seal that preserves product integrity from the production line to the consumer.

The Core Principle: How Induction Sealing Works
Understanding the induction process reveals a simple yet highly effective method for ensuring product safety and freshness. It relies on a few key components working in perfect sequence.
The Essential Components
The entire process depends on two items: the sealing head of the machine and the induction liner placed inside the container's cap. This liner is typically a multi-layered disc containing foil and a heat-activated polymer.
Step 1: Capping the Container
The process begins before the container ever reaches the sealer. A cap, fitted with the multi-layer induction liner, is placed onto the filled container and tightened.
Step 2: Passing Through the Electromagnetic Field
The capped container then travels along a conveyor belt, passing directly underneath the induction sealing head. This head generates a high-frequency, oscillating electromagnetic field.
Step 3: Heating the Foil Layer
As the container moves through the field, the electromagnetic energy induces electrical currents (known as eddy currents) within the aluminum foil layer of the liner. The foil's natural resistance to these currents causes it to heat up rapidly.
Step 4: Melting and Adhesion
The intense heat generated by the foil instantly melts the polymer coating on the bottom layer of the induction liner. The pressure from the tightened cap forces this melted polymer onto the rim (or "land") of the container.
Step 5: Creating the Hermetic Seal
Once the container moves past the sealing head, the polymer cools and solidifies almost instantly. This creates a strong, airtight bond between the liner and the container, forming a hermetic seal.
Why This Technology is Crucial for Packaging
The benefits of this sealing method are directly tied to preserving the value and safety of the product inside the container.
Ensuring Product Freshness
The airtight seal provides an essential barrier against oxygen, moisture, and other environmental contaminants. This is critical for extending the shelf life of foods, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
Providing Tamper-Evidence
The induction seal must be broken to access the container's contents. This provides a clear, unambiguous visual indicator to the consumer if the product has been opened or tampered with.
Preventing Leaks
The robust, uniform seal ensures that liquid, powder, or solid products will not leak during shipping, storage, or handling, preventing product loss and messes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, induction sealing is a specific tool for a specific job. Its successful implementation depends on understanding its requirements.
Requires Specialized Liners
This process is entirely dependent on using caps fitted with the correct type of induction-ready liner. It cannot be used with standard, unlined caps.
Process Control is Key
Success hinges on a properly calibrated system. The power of the electromagnetic field, the speed of the conveyor, and the tightness of the cap must all be precisely controlled to achieve a perfect seal without damaging the liner or the product.
Compatibility is Not Universal
The container material and the liner's polymer coating must be compatible to ensure a strong bond. Mismatched materials can easily lead to a weak or incomplete seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding the principles, you can leverage this technology to meet specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is product integrity and shelf life: Induction sealing is the industry standard for creating a hermetic barrier that protects against degradation.
- If your primary focus is consumer safety and trust: The tamper-evident nature of the seal is one of the most reliable ways to build consumer confidence in your product's safety.
- If your primary focus is preventing costly leaks: The strong, consistent bond created by induction sealing provides a robust defense against leakage during transit.
Ultimately, mastering induction sealing is a direct investment in protecting the quality and safety of your product from creation to consumption.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Sealing Head | Generates the high-frequency electromagnetic field. |
| Induction Liner | Multi-layered foil disc that heats up to create the seal. |
| Process | Outcome |
| Non-Contact Heating | Selectively heats the foil liner without touching the container. |
| Polymer Melting & Bonding | Creates a strong, airtight, hermetic seal on the container rim. |
Protect your product integrity and build consumer trust with reliable sealing solutions.
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-performance tools needed for efficient, large-scale operations. Just as a perfect seal preserves product quality, the right equipment preserves your productivity and profitability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our wholesale-focused supplies can strengthen your packaging and bottling processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Water Cooled Induction Sealing Machine for Bottles and Containers
- Automatic Inline Spindle Bottle Capping Machine for Honey Production
- HONESTBEE Professional Benchtop Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine Capper
- Semi Automatic Electric Bottle Capping Machine
- Professional Durable Customizable Blister Packing Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a sealing machine? Protect Product Integrity with Airtight Heat & Pressure Seals
- How does a bottle sealing machine work? Ensure Tamper-Evident, Hermetic Seals for Your Products
- What is the function of an induction sealing machine in packaging? Secure Your Brand with Tamper-Evident Seals
- What role do high-barrier sterile packaging and automatic induction sealing equipment play in honey safety management?
- How does tamper-evident sealing equipment benefit the honey trade? Ensure Product Integrity and Market Trust



















