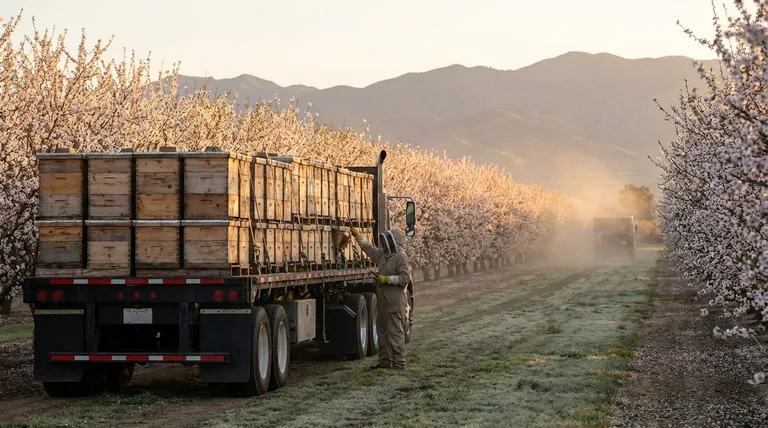
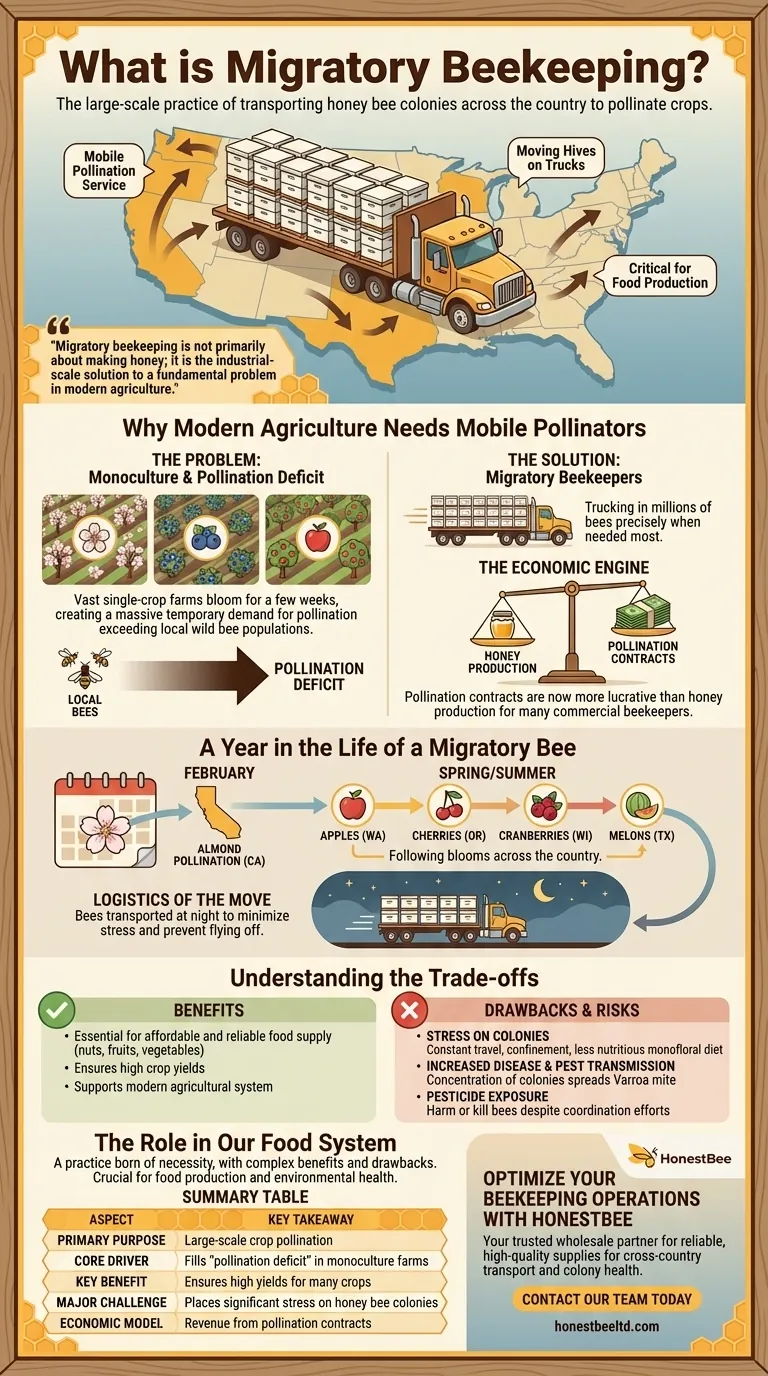
In short, migratory beekeeping is the large-scale practice of transporting honey bee colonies across the country to pollinate different crops as they come into bloom. Rather than keeping bees in one place to produce honey, these beekeepers operate as mobile pollination services, moving their hives on trucks from one agricultural region to another. This practice has become a critical component of modern food production.
Migratory beekeeping is not primarily about making honey; it is the industrial-scale solution to a fundamental problem in modern agriculture: how to pollinate massive, single-crop farms that bloom for only a few weeks a year.

Why Modern Agriculture Needs Mobile Pollinators
The rise of migratory beekeeping is directly tied to the structure of modern agriculture. The system's efficiency creates a challenge that only mobile pollinators can solve.
The Problem of Monoculture
Large-scale farms often practice monoculture, which means planting vast areas with a single crop, such as almonds, blueberries, or apples.
When these millions of plants flower simultaneously, they create a massive, temporary demand for pollination that far exceeds what local, wild bee populations can provide.
A "Pollination Deficit"
Without a sufficient number of pollinators during this short blooming window, the crop would fail or produce a significantly lower yield.
Migratory beekeepers fill this "pollination deficit" by trucking in millions of bees precisely when they are needed most.
The Economic Engine
For many commercial beekeepers, pollination contracts are now more lucrative than honey production.
Farmers pay beekeepers a fee per hive to place their bees in the fields or orchards for the duration of the bloom. This business model is what sustains the entire migratory industry.
A Year in the Life of a Migratory Bee
The life of a migratory bee colony follows the seasons of agriculture, not the natural rhythm of a local environment.
The Cross-Country Journey
A typical year for a migratory beekeeper might begin in February with the almond pollination in California, which requires the vast majority of managed honey bees in the United States.
After the almonds, colonies might be moved to pollinate apples in Washington, cherries in Oregon, cranberries in Wisconsin, or melons in Texas, following the sequence of blooms across the country.
The Logistics of the Move
Hives are loaded onto large flatbed trucks, often thousands at a time.
The bees are transported almost exclusively at night, when the colony is naturally inside the hive, to minimize stress and prevent them from flying off during transit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for our current food system, this practice places significant strain on honey bee colonies and creates systemic risks.
Stress on the Colonies
The constant travel, confinement, and changes in environment are inherently stressful for bees.
Furthermore, a diet based on a single nectar source at each location (monofloral diet) can be less nutritious than the varied diet wild bees enjoy, potentially weakening their immune systems.
Increased Disease and Pest Transmission
Concentrating millions of bee colonies from all over the country into one small area, like California's Central Valley for almond season, creates a perfect breeding ground for diseases and pests.
Pests like the Varroa mite, a major threat to honey bees, can spread rapidly between colonies that would otherwise never come into contact.
Pesticide Exposure
While farmers need the bees, the industrial scale of monoculture farming often involves the use of pesticides, fungicides, and other chemicals.
Despite efforts to coordinate spraying schedules, bees are frequently exposed to these chemicals, which can harm or kill them.
The Role of Migratory Beekeeping in Our Food System
Ultimately, migratory beekeeping is a practice born of necessity, with complex benefits and drawbacks. Understanding its role is crucial for anyone concerned with food production or environmental health.
- If your primary focus is food production: Recognize that migratory beekeeping is currently essential for the affordable and reliable supply of many nuts, fruits, and vegetables.
- If your primary focus is honey bee health: Understand that the practice is a major source of stress on colonies, highlighting the need for more sustainable agricultural practices that can support both bees and crop yields.
- If your primary focus is ecosystem stability: Acknowledge the risk of relying so heavily on a single, managed pollinator species to support a vast and vital part of our food system.
This practice is a powerful illustration of the deeply interconnected, and often fragile, system that brings food to our tables.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Large-scale crop pollination, not honey production. |
| Core Driver | Fills the "pollination deficit" in monoculture farms. |
| Key Benefit | Ensures high yields for many fruits, nuts, and vegetables. |
| Major Challenge | Places significant stress on honey bee colonies. |
| Economic Model | Beekeepers earn revenue from pollination contracts with farmers. |
Optimize Your Beekeeping Operations with HONESTBEE
As a commercial apiary or equipment distributor, the success of your migratory beekeeping business depends on reliable, high-quality supplies. HONESTBEE is your trusted wholesale partner, providing the durable equipment necessary to manage the rigors of cross-country transport and support colony health.
Let us help you build a more resilient and profitable operation. Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and explore our product catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Premium Italian Style Hive Tool with Hardwood Handle
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Wooden Bee Brush with Triple Row Artificial Fiber for Beekeeping
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Long Langstroth Style Horizontal Top Bar Hive for Wholesale
People Also Ask
- Is it advisable to manage a large number of hives alone? The Risks of Solo Beekeeping at Scale
- What is a hive tool used for in beekeeping? Your Essential Guide to Hive Management
- What are the benefits of beekeeping? Boost Pollination, Honey Yield, and Apiary Resilience
- What is the significance of professional hive-making tools? Scale Your Stingless Bee Farm with Precision Equipment
- How is a hive tool used for inspecting the hive? Essential Techniques for Every Beekeeper



















