While there isn't a single "instrument," beekeeping relies on a core set of essential equipment. The most fundamental tools are the hive itself, a hive tool for manipulating frames, a smoker to calm the bees, and protective gear like a veil and gloves to ensure your safety.
Successful beekeeping depends on a small set of specialized tools. This equipment is designed to serve two primary functions: managing the physical structure of the hive and allowing the beekeeper to interact with the colony safely and with minimal disruption.
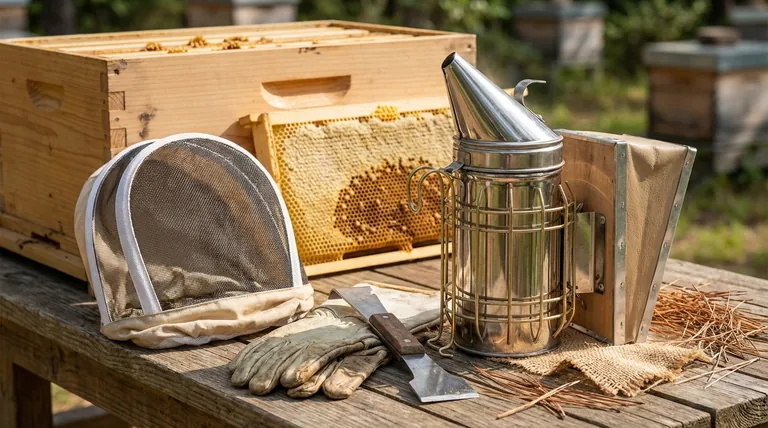

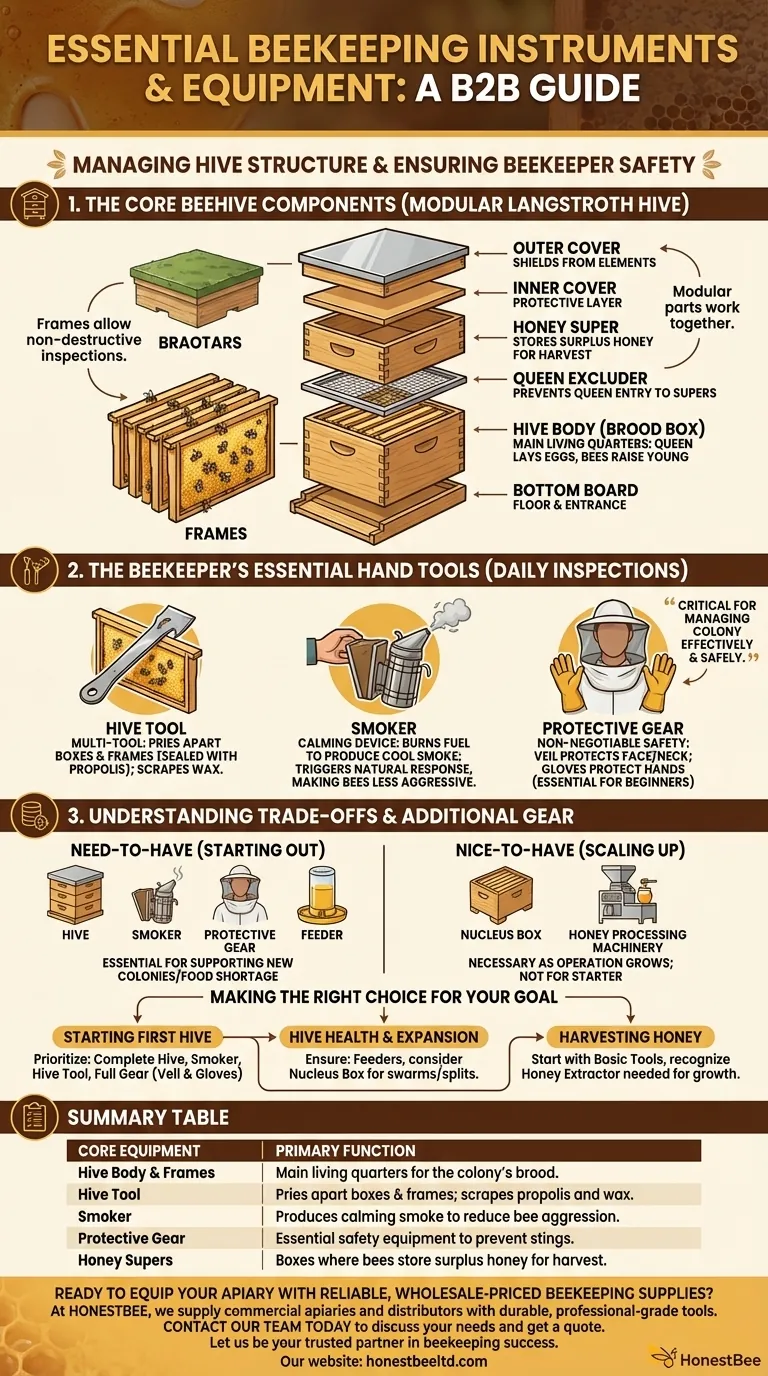
The Core Components of the Beehive
The hive is the bee's home and the beekeeper's primary piece of equipment. Modern Langstroth hives are modular, consisting of several key parts that work together.
Hive Body and Frames
The hive body, or brood box, is the main living quarters for the colony. It's where the queen lays her eggs and the bees raise their young.
Inside are removable frames, which hold the beeswax comb. This design allows beekeepers to inspect the colony's health without destroying the hive structure.
Honey Supers
Honey supers are smaller boxes placed on top of the hive body. Their sole purpose is for the bees to store surplus honey that the beekeeper can later harvest.
A queen excluder, a screen with specific-sized gaps, is often placed between the hive body and the supers. It prevents the larger queen from entering the honey supers to lay eggs.
Covers and Bottom Board
The hive is protected by an inner cover and a telescoping outer cover to shield it from the elements.
The entire structure rests on a bottom board, which serves as the floor and entrance for the hive.
The Beekeeper's Essential Hand Tools
These are the "instruments" you will use during every hive inspection. They are critical for managing the colony effectively and safely.
The Hive Tool
This is the beekeeper's multi-tool. It's a sturdy piece of metal used for prying apart hive boxes and frames, which bees seal together with a sticky resin called propolis.
It's also used for scraping away excess wax and propolis, making it indispensable for hive maintenance.
The Smoker
A smoker is a small, handheld device that burns fuel (like pine needles or burlap) to produce cool, white smoke.
Puffing a small amount of smoke into the hive triggers the bees' natural response to a potential fire, making them gorge on honey. This makes them significantly calmer and less likely to sting during an inspection.
Protective Gear
This is non-negotiable for safety. A beekeeper's veil protects the face and neck, the most common targets for stings.
Gloves protect the hands, though some experienced beekeepers prefer to work without them for better dexterity. For beginners, gloves are essential for building confidence.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Additional Gear
While the tools above are essential, other pieces of equipment support hive health or are needed for larger-scale operations. It's crucial to distinguish between what you need to start and what you might need later.
Need-to-Have vs. Nice-to-Have
A feeder for sugar syrup is essential for supporting a new colony or helping an established one through a food shortage.
However, a nucleus box (a smaller hive for starting new colonies) or specialized machinery for processing honey and beeswax are only necessary as you scale your operation.
The Cost of Entry
Beekeeping has an initial setup cost. Resist the temptation to buy every gadget available. A complete starter kit with one hive, basic tools, and protective gear is all that is required to begin.
Focus on mastering the fundamentals with the core equipment before expanding into more specialized or industrial-grade tools.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your equipment needs will be guided by your specific objectives as a beekeeper.
- If your primary focus is starting your very first hive: Prioritize a complete hive, a high-quality smoker, a hive tool, and full protective gear (veil and gloves).
- If your primary focus is hive health and expansion: Ensure you have feeders for supplemental nutrition and consider adding a nucleus box to your inventory for managing swarms or splitting colonies.
- If your primary focus is harvesting honey: You can start with basic tools, but recognize that a honey extractor will become a critical piece of equipment as your operation grows.
Equipping yourself with the right tools is the first step toward a successful and rewarding partnership with your bees.
Summary Table:
| Core Equipment | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Hive Body & Frames | Main living quarters for the colony's brood. |
| Hive Tool | Pries apart boxes & frames; scrapes propolis and wax. |
| Smoker | Produces calming smoke to reduce bee aggression. |
| Protective Gear (Veil/Gloves) | Essential safety equipment to prevent stings. |
| Honey Supers | Boxes where bees store surplus honey for harvest. |
Ready to equip your apiary with reliable, wholesale-priced beekeeping supplies?
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, professional-grade tools they need to succeed. From essential hive components and smokers to large-scale harvesting equipment, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the quality and value your business depends on.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and get a quote. Let us be your trusted partner in beekeeping success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Honey Bee Smoker Hive and Honeycomb Smoker for Beekeeping
- Premium Traditional Copper Bee Smoker with Bellows
- Stainless Steel Electric Beehive Smoker for Beekeeping and Bee Keeper Use
- Economy Galvanized Beekeeping Honey Bee Smoker for Wholesale
- 54-Piece Smoker Fuel Pellets for Beekeeping Beehive Smoker Fuel
People Also Ask
- How does smoke from a bee smoker affect honeybee behavior? Master the Art of Calm Hive Inspections
- How do simple smokers or torches facilitate honey harvesting? Discover the Science of Bee Smoke Biological Control
- What is the operational principle of a beekeeping smoker for aggressive bees like Apis mellifera adansonii?
- What are the key safety precautions when handling a lit bee smoker? Prevent Fires and Protect Your Apiary
- What technical role does a large smoker play in the honey harvesting process for Apis dorsata? Control & Safety Guide



















