Yes, in many ways, honey bees are incredibly beneficial to have around, primarily for their vital role in pollinating agricultural crops and for the valuable products they create. They are a cornerstone of modern agriculture and provide us with honey, beeswax, and other useful materials.
While honey bees are essential for large-scale agriculture, the most accurate view is nuanced. Their immense value must be balanced against their potential to outcompete and place pressure on native wild bee populations, which are also critical for a healthy ecosystem.

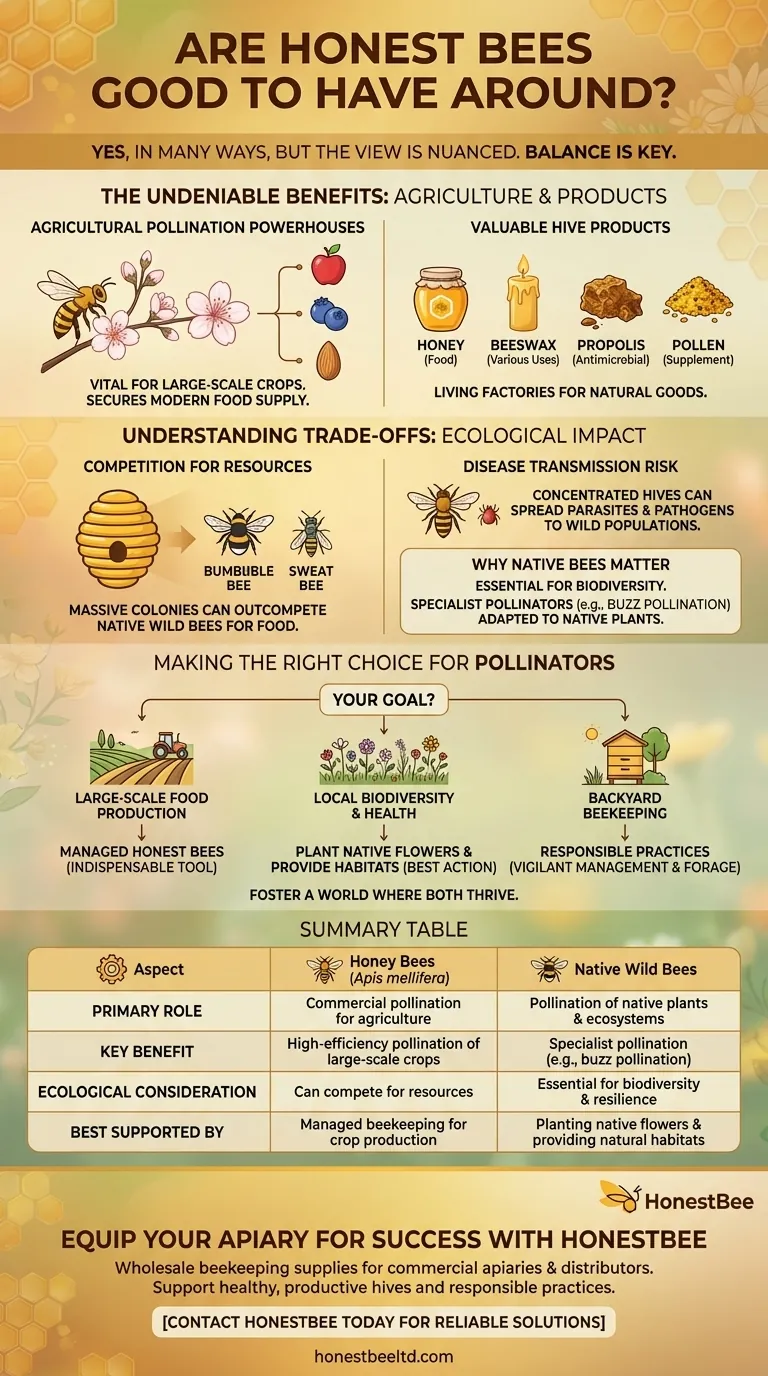
The Undeniable Benefits of Honey Bees
Honey bees (specifically, the Western honey bee, Apis mellifera) are often what people picture when they think of bees. Their benefits are widespread and deeply integrated into our food systems and economies.
Agricultural Pollination Powerhouses
The single greatest benefit of managed honey bees is their work as commercial pollinators. Large, mobile colonies can be transported to farms to pollinate vast monocultures of crops like almonds, apples, and blueberries.
This service is the backbone of much of our modern food supply, ensuring reliable fruit and vegetable production on a scale that would otherwise be impossible.
Valuable Hive Products
As noted, honey bees create several products with direct human uses. They are living factories producing high-quality, natural goods.
These products include honey (a food source), beeswax (used in candles, cosmetics, and food wraps), propolis (a resinous sealant with antimicrobial properties), and pollen (a nutritional supplement).
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Honey Bee's Ecological Impact
The conversation becomes more complex when we move from farms to wild ecosystems. The immense success of the honey bee can create unintended consequences for other pollinators.
The Issue of Competition
In many parts of the world, including North America, the honey bee is a non-native, managed agricultural animal, similar to livestock. A single hive contains tens of thousands of bees.
These massive colonies can monopolize local nectar and pollen resources, effectively outcompeting smaller populations of native wild bees for food.
Why Native Bees Matter
There are thousands of species of native bees (e.g., bumble bees, mason bees, sweat bees) that are essential for a resilient environment. Many are specialist pollinators, uniquely adapted to pollinate native plants that honey bees cannot.
For example, some plants require "buzz pollination," a vibration that honey bees cannot perform but bumble bees can. A diversity of pollinators protects an ecosystem against disease or the decline of a single species.
The Risk of Disease Transmission
Large, concentrated populations of honey bees can become breeding grounds for parasites (like the Varroa mite) and pathogens. These diseases can then spill over from managed hives into wild bee and pollinator populations, placing further stress on these crucial native species.
Making the Right Choice for Supporting Pollinators
Your approach to "helping the bees" should depend on your ultimate goal. Simply adding a honey bee hive is not always the best solution for promoting local biodiversity.
- If your primary focus is large-scale food production: Managed honey bees are an indispensable tool for modern agriculture.
- If your primary focus is supporting local biodiversity and ecosystem health: The best action is to plant a wide variety of native flowers and provide nesting habitats (like bee hotels or undisturbed ground) for native bees.
- If you are considering backyard beekeeping: Commit to responsible practices, including vigilant disease management and ensuring there is enough floral forage to support your hive and local native pollinators.
True environmental support involves fostering a world where both managed honey bees and diverse native pollinators can thrive.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) | Native Wild Bees |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Commercial pollination for agriculture | Pollination of native plants & ecosystems |
| Key Benefit | High-efficiency pollination of large-scale crops | Specialist pollination (e.g., buzz pollination) |
| Ecological Consideration | Can compete with native bees for resources | Essential for biodiversity and ecosystem resilience |
| Best Supported By | Managed beekeeping for crop production | Planting native flowers & providing natural habitats |
Equip Your Apiary for Success with HONESTBEE
Whether you manage commercial honey bee colonies for pollination services or distribute beekeeping supplies, the right equipment is crucial for healthy, productive hives and responsible beekeeping practices. HONESTBEE supplies high-quality, durable beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations.
Let us help you support the vital work of pollinators. Explore our wholesale catalog and get in touch to discuss your apiary's needs.
Contact HONESTBEE today for reliable beekeeping solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- Automatic Honey Flow Beehive 4 Frame Mini Hive for Beekeeping
- Langstroth Bee Hives Bee Keeping Box for Beginners Beekeeping
- All-Stainless Steel Pivoting Honey Uncapping Fork for Beekeeping
- Professional Bent Tine Honey Uncapping Fork with Ergonomic Grip
People Also Ask
- What is the best place to keep bees? Find the Perfect Apiary Site for Your Hives
- What technical factors should be considered when selecting wood for stingless bee hives? Optimize Colony Health
- Why were wooden hives traditionally preferred? For Natural Beekeeping Aligned with Bee Biology
- How does the use of industrial hive-making machinery support ecological balance? Precision for Urban Beekeeping
- How do cement beehives compare to wooden beehives? Durability and ROI vs Traditional Methods



















