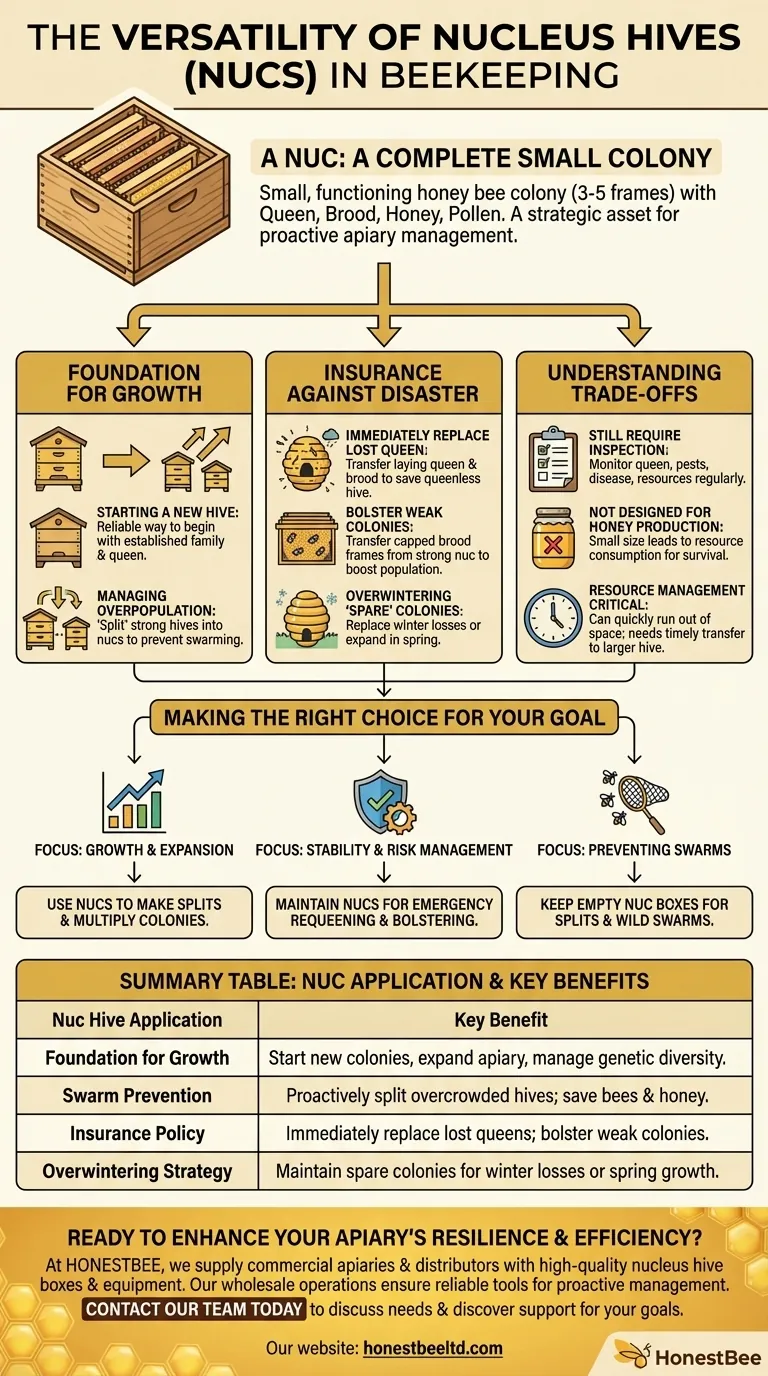
At its core, a nucleus hive, or "nuc," is one of the most versatile tools a beekeeper can possess. It is a small, functioning honey bee colony housed in a smaller-than-standard box, typically holding three to five frames of bees, brood, honey, and pollen. This small scale allows a beekeeper to perform critical management tasks with a level of flexibility and precision that is impossible with a full-sized production hive.
The true value of a nuc is not just as a small hive, but as a strategic asset. It shifts the beekeeper from a reactive problem-solver to a proactive manager, providing ready-made solutions for the most common and costly apiary challenges.

The Nuc as a Foundation for Growth
A nucleus hive is the starting point for all new colonies and the primary tool for expanding your apiary's size and genetic diversity.
What is a Nucleus Colony?
The term "nuc" refers to both the small hive box and the small colony living inside it. This colony is a complete, self-sufficient unit, containing a laying queen, worker bees of all ages, and frames of brood (eggs, larvae, and pupae), honey, and pollen.
Starting a New Hive
For a new beekeeper, purchasing a nuc is the most reliable way to start a colony. Unlike a "package" of bees, a nuc provides an already established family with a proven, laying queen, giving the colony a significant head start on building its population.
Managing Overpopulation and Swarming
When a strong production hive becomes overcrowded, its natural instinct is to swarm, which results in the beekeeper losing half their bees and the old queen. A beekeeper can proactively prevent this by "splitting" the colony, moving a few frames of bees, brood, and resources into an empty nuc box with a new queen or queen cell. This relieves congestion in the main hive and creates a new, viable colony.
The Nuc as Insurance Against Disaster
Experienced beekeepers understand that unexpected problems are a constant. A nuc on hand is the ultimate insurance policy against sudden colony failure.
Immediately Replacing a Lost Queen
A hive that loses its queen (goes "queenless") is on a path to collapse. If this happens during a critical nectar flow, the loss in honey production and brood is immense. Having a nuc with a laying queen allows you to immediately transfer her and a frame of her brood into the queenless hive, saving the colony with minimal downtime.
Bolstering Weak Colonies
Sometimes a colony struggles to build its population, whether due to a harsh winter or a poorly performing queen. You can transfer frames of capped brood from a strong nuc into the weak hive. The emerging bees will dramatically boost the weak hive's population and workforce, helping it recover.
Overwintering "Spare" Colonies
Many beekeepers intentionally create several nucs over the summer and overwinter them. These "spares" serve as immediate replacements for any full-sized production colonies that may die during the winter. If all colonies survive, the extra nucs can be sold or used to expand the apiary in the spring.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a nuc is not a "set-and-forget" tool. Its small size, which is its greatest strength, also creates unique management needs.
They Still Require Inspection
Just like a full-sized hive, a nuc needs regular inspections. You must monitor the queen's laying pattern, check for pests and diseases, and ensure the colony has adequate resources. Their smaller population makes them more vulnerable to collapse if a problem is left unchecked.
Not Designed for Honey Production
A nuc's primary purpose is population management, not honey surplus. Its small size means the bees will consume most of the honey they produce just to survive and grow. They can easily become "honey-bound," filling all available comb with nectar and leaving no room for the queen to lay eggs.
Resource Management is Critical
A nuc can quickly run out of space for brood or food. A beekeeper must be ready to move the colony into a larger, full-sized hive once it has filled the nuc box to prevent it from swarming or starving.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Integrating nucs into your beekeeping practice is a strategic decision that pays dividends in colony health and apiary resilience.
- If your primary focus is growth and expansion: Use nucs to make splits from your strongest hives, allowing you to multiply your colonies quickly and cost-effectively.
- If your primary focus is stability and risk management: Maintain at least one nuc at all times as a resource for emergency requeening and bolstering weaker hives.
- If your primary focus is preventing swarms: Keep an empty nuc box on hand to easily house splits from overcrowded hives or to catch wild swarms in your area.
A nucleus hive empowers you to manage your bees with foresight, turning potential catastrophes into opportunities for growth.
Summary Table:
| Nuc Hive Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Foundation for Growth | Start new colonies, expand apiary size, and manage genetic diversity. |
| Swarm Prevention | Proactively split overcrowded hives to prevent loss of bees and honey production. |
| Insurance Policy | Immediately replace lost queens or bolster weak colonies to ensure stability. |
| Overwintering Strategy | Maintain spare colonies as replacements for winter losses or for spring expansion. |
Ready to enhance your apiary's resilience and efficiency?
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality nucleus hive boxes and equipment needed to implement these powerful strategies. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable tools for proactive beekeeping management.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our supplies can support your growth and stability goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 5 Frame Wooden Nuc Box for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Multi-Function Plier-Style Frame Grip Hive Tool
People Also Ask
- What is a common feature of many 5-frame nuc boxes? The Integrated Feeder for Efficient Colony Growth
- When can nucleus colonies (nucs) be created? Optimal Timing for Apiary Growth and Survival
- How many frames does a typical wooden nuc box hold? A Guide to Choosing the Right Size
- What frames should be moved into the queenless hive when requeening with a nuc? Ensure a Successful Queen Introduction
- What feeding feature is common in 5-frame nuc boxes? Explore Top-Feeding Innovation for Colony Growth



















