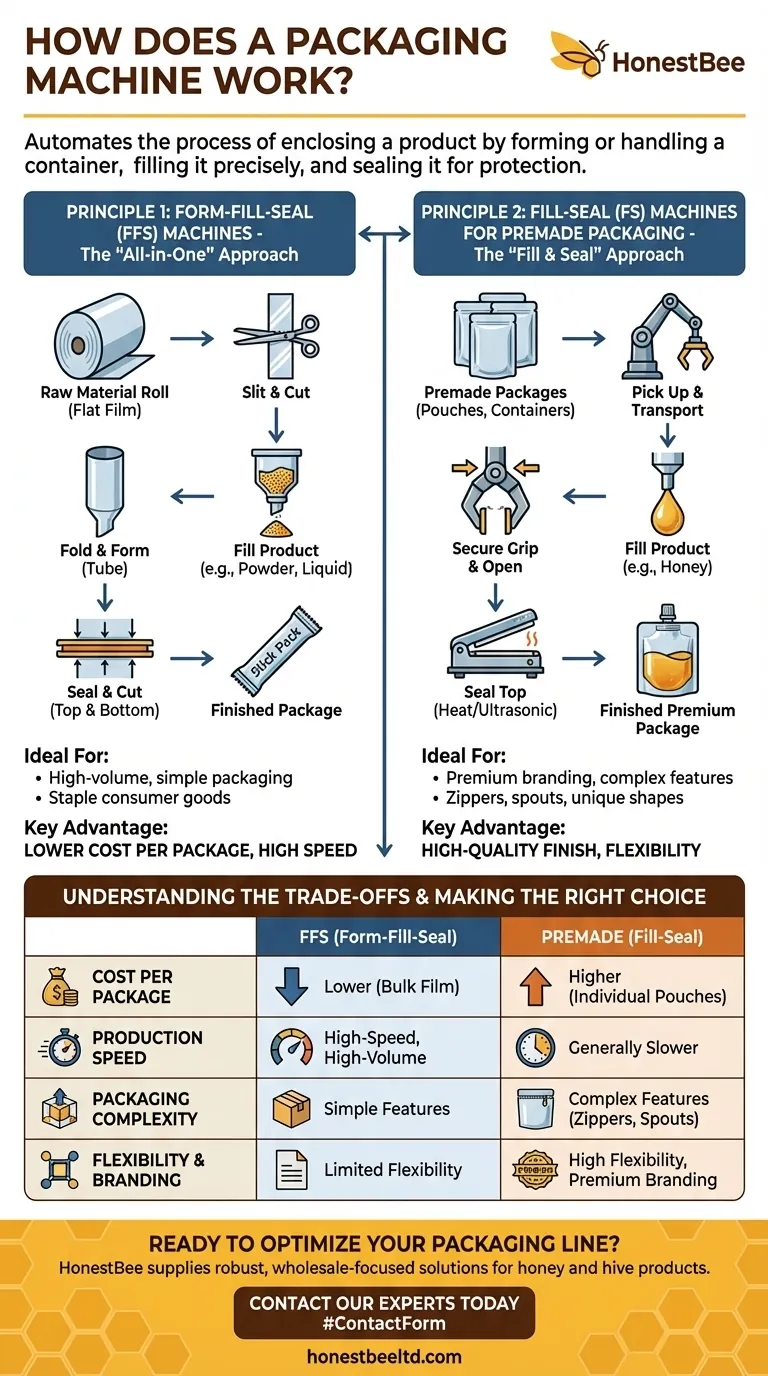
At its core, a packaging machine automates the process of enclosing a product. It systematically takes a container—either by forming it from raw material or by handling a pre-made one—fills it with a precise amount of product, and then seals it shut for protection, consistency, and transport.
The specific mechanics of any packaging machine are dictated by a single, fundamental distinction: whether the machine creates the package from raw materials on the spot, or whether it is designed to fill and seal packages that have already been manufactured.
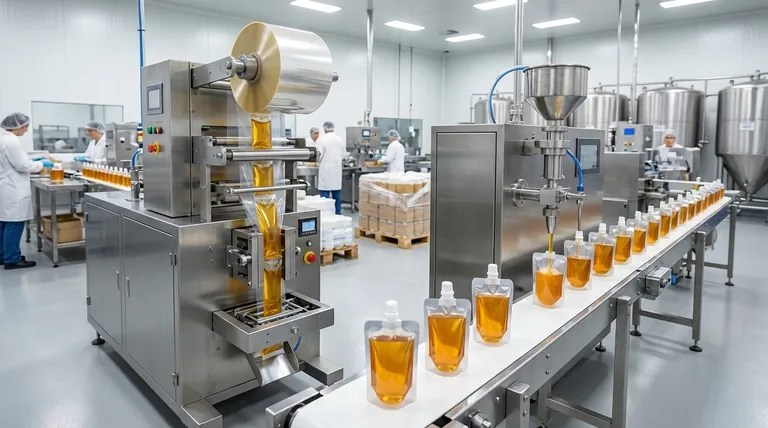

The Two Core Principles of Automated Packaging
While there are countless variations, most packaging machines operate on one of two foundational principles. Understanding these two approaches is the key to understanding how nearly any packaging operation works.
Principle 1: Form-Fill-Seal (FFS) Machines
This is the "all-in-one" approach. An FFS machine starts with a large roll of raw packaging material, typically a flat film, and performs every step of the process in a continuous motion.
The process for a common "stick pack" machine illustrates this perfectly.
First, a special slitting component cuts the large roll of packaging film into narrower strips, one for each "stick" or bag.
Next, each strip is folded and formed into a long, thin tube, which is then sealed along its length to create the basic bag shape.
Finally, the product (often a powder or liquid) is dispensed into the open tube, which is then sealed horizontally at both the top and bottom to create the individual, finished package.
Principle 2: Fill-Seal (FS) Machines for Premade Packaging
This approach separates the manufacturing of the package from the filling process. These machines are designed to handle containers, bags, or pouches that have already been made.
A machine that packages honey into premade pouches is a clear example.
The process begins with a stack of empty, pre-formed pouches being fed into the machine.
Each pouch is individually picked up, transported by a conveyor, and then securely gripped and opened by mechanical arms or suction.
The product is dispensed from a filling nozzle into the open pouch, and then the top of the pouch is sealed shut, typically using heat or ultrasonic methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs: FFS vs. Premade
Choosing between these two principles involves a critical trade-off between material cost, operational speed, and packaging complexity. Neither is universally superior; the right choice depends entirely on the goal.
The Case for Form-Fill-Seal (FFS)
The primary advantage of FFS machines is lower cost per package. Buying raw film in large rolls is significantly cheaper than buying individual, pre-formed pouches.
These machines are also typically built for high-speed, high-volume production, making them ideal for staple consumer goods.
However, the initial investment in FFS machinery is often higher, and accommodating complex package features like zippers or spouts requires more sophisticated and expensive equipment.
The Case for Premade Pouch Machines
Premade pouch machines excel at handling complex and high-quality packaging. Because the pouches are made in a separate process, they can easily incorporate features like resealable zippers, spouts, and unique shapes.
This approach offers greater flexibility for premium branding and produces a more polished final look, which is crucial for retail shelf appeal.
The trade-off is a higher cost for each individual pouch and generally slower production speeds compared to their FFS counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to use one type of machine over another is a strategic one based on product, market, and volume.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with simple packaging: An FFS machine is the most cost-effective solution due to its speed and lower material costs.
- If your primary focus is premium branding and complex pouch features: A premade pouch machine provides the necessary flexibility and high-quality finish for standout retail packaging.
- If your primary focus is running many different products with quick changeovers: A premade pouch machine is often simpler to adapt between different pouch sizes and styles.
Ultimately, understanding how a packaging machine works is about recognizing the fundamental choice between creating the package or simply filling it.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Process | Ideal For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form-Fill-Seal (FFS) | Creates, fills, and seals package from a roll of film. | High-volume, simple packaging (e.g., stick packs). | Lower cost per package, high speed. |
| Fill-Seal (Premade) | Fills and seals pre-manufactured pouches or containers. | Premium branding, complex features (e.g., zippers, spouts). | High-quality finish, flexibility. |
Ready to optimize your packaging line? Whether you're a commercial apiary or a beekeeping equipment distributor, HONESTBEE supplies the robust, wholesale-focused packaging solutions you need to scale your honey and hive product operations efficiently. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you choose the right machinery for your volume and branding goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Durable Customizable Blister Packing Machine
- HONESTBEE Professional Benchtop Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine Capper
- Professional Water Cooled Induction Sealing Machine for Bottles and Containers
- Semi Automatic Electric Bottle Capping Machine
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
People Also Ask
- What is the working process of a sachet filling and packing machine? Optimize Your Packaging Line Efficiency
- What is the function of automated honey bottling machines for increased yields? Scale Your Apiary Production
- How does an automated filling machine contribute to the commercialization of Trigona sp. honey? Scale Your Production
- Why is the establishment of a seasonal flowering calendar critical? Optimize Your Honey Filling Production Today
- Why is specialized honey filling and packaging equipment essential? Boost Competitive Edge for Beekeeping Cooperatives
- What is a semi-automatic filling machine? Boost Efficiency for Small to Medium-Scale Production
- How do honey filling and processing machines ensure zero-residue compliance? Master Regulatory Standards Today
- What bottling equipment is used after honey filtering? Choose the Right System for Your Scale



















