At its core, honey processing is the method of moving honey from the beeswax honeycomb into a container for consumption. The universal steps involve harvesting the honey-filled frames from the hive, uncapping the wax cells, extracting the honey, removing impurities like wax, and finally, bottling the finished product.
The crucial distinction in honey processing lies not in the basic steps, but in the intensity of the filtration and the application of heat. These two factors determine whether the final product is "raw honey," rich with pollen and natural enzymes, or the clear, shelf-stable commercial honey found in most supermarkets.

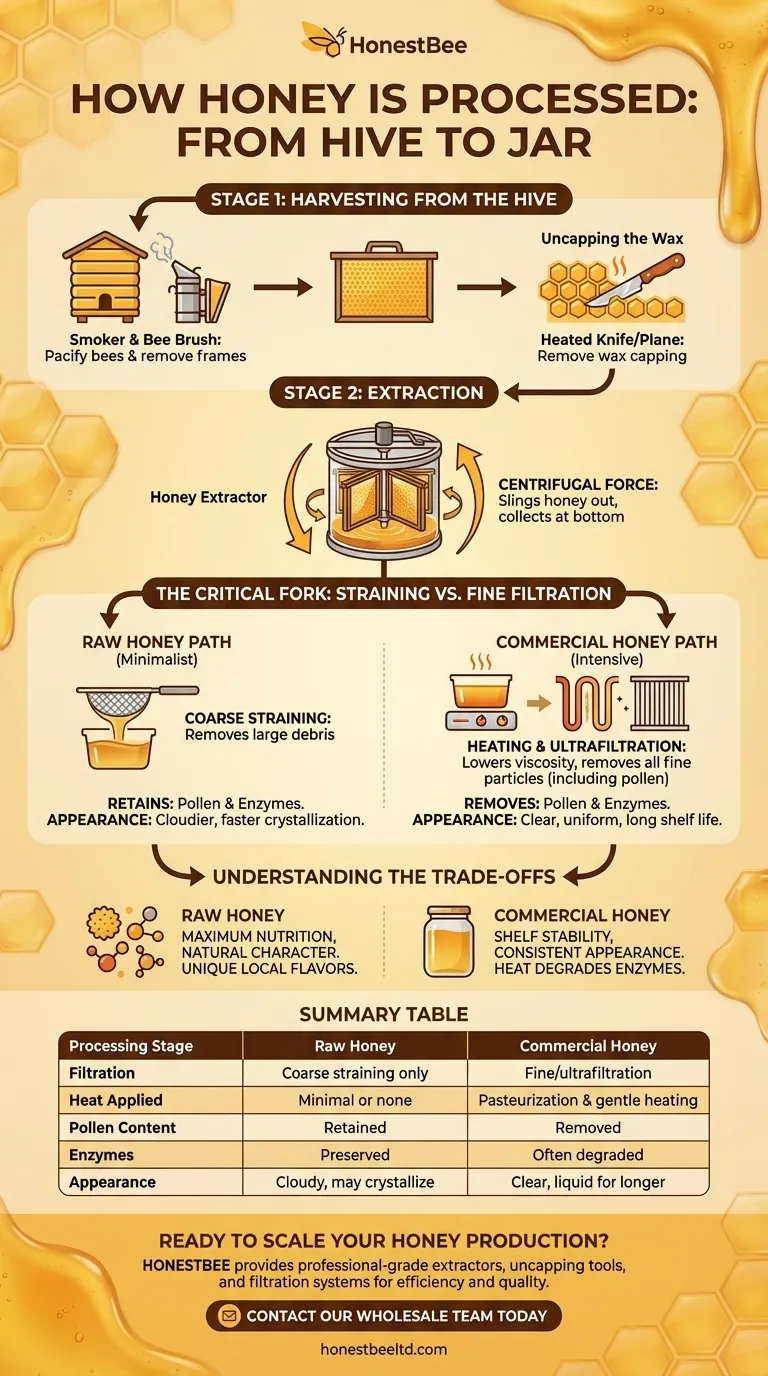
Stage 1: Harvesting from the Hive
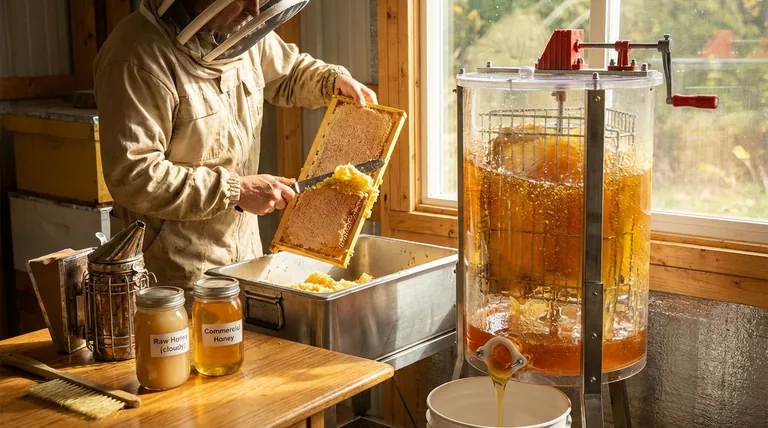
The entire process begins with the careful removal of honey from the beehive, a task requiring precision to minimize stress on the colony.
Removing the Honeycomb Frames
Beekeepers first pacify the bees, often using a smoker, which masks the alarm pheromones of the colony and encourages them to retreat.
Once the hive is calm, the beekeeper removes the frames that are filled with honey and capped with beeswax. A bee brush or a gentle blower is used to clear any remaining bees from the frames before they are taken to an extraction facility.
Uncapping the Wax
Before the honey can be extracted, the protective wax capping that seals each cell must be removed.
This is typically done using a heated knife, a specialized uncapping plane, or a machine with sharp blades that slices off the top layer of wax. This exposes the liquid honey within the comb.
Stage 2: Extraction - Separating Honey from Wax
Once uncapped, the goal is to remove the honey from the comb's hexagonal cells without destroying the comb itself, so it can be returned to the hive.
The Power of Centrifugal Force
The most common method uses a honey extractor, which is a large drum that holds the frames. The extractor spins the frames at high velocity.
Centrifugal force slings the liquid honey out of the cells and onto the interior wall of the drum. The honey then collects at the bottom, ready for the next stage.
The Critical Fork: Straining vs. Fine Filtration
This is the most important stage in defining the final product. After extraction, the honey contains particles of beeswax, pollen, and other hive debris that must be removed. The method used here creates two very different outcomes.
The Minimalist Path: Straining for Raw Honey
To produce raw honey, the liquid is simply passed through a coarse strainer or mesh filter.
This process removes large particles like chunks of wax and debris but leaves the beneficial pollen grains and natural enzymes intact. The resulting honey is often cloudier and may crystallize faster.
The Commercial Path: Heating and Fine Filtration
For large-scale commercial production, the goal is a perfectly clear, uniform product with a long shelf life. This requires a more intensive process.
First, the honey is often gently heated (pasteurized) to lower its viscosity, making it flow more easily through very fine filters.
Next, it undergoes ultrafiltration, a process that removes all fine particles, including all pollen grains. This slows crystallization and creates the crystal-clear appearance many consumers expect. Finally, different batches may be blended, or homogenized, to ensure consistent flavor and color.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each processing method is chosen to achieve a specific outcome, and each comes with distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Why Commercial Processing is Used
The primary drivers for commercial processing are shelf stability and consumer expectation. Ultrafiltration removes the pollen particles that act as nuclei for crystallization, keeping the honey liquid for much longer. Heating also destroys yeast spores that could cause fermentation. This results in a uniform, clear product that looks consistent on the shelf.
What is Lost in the Process
The main trade-off of intensive heating and filtering is the removal of beneficial components. Pollen, which contains proteins and antioxidants, is completely eliminated. High heat can also degrade or destroy the natural enzymes (like diastase and invertase) that are present in raw honey and are valued for their potential health benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the processing journey from hive to jar empowers you to select the honey that best suits your needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum nutritional value and natural character: Seek out honey labeled as "raw" and "unfiltered," which has only been strained to remove large debris.
- If your primary focus is consistent flavor and a long-lasting liquid state: Standard commercial honey is processed specifically to prevent crystallization and ensure uniformity.
- If your primary focus is unique flavor profiles and supporting local apiaries: Buying directly from a local beekeeper often gives you access to minimally processed, single-source honey that reflects regional flora.
Ultimately, knowing how honey is processed allows you to make a truly informed decision based on your priorities.
Summary Table:
| Processing Stage | Raw Honey | Commercial Honey |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration | Coarse straining only | Fine/ultrafiltration |
| Heat Applied | Minimal or none | Pasteurization & gentle heating |
| Pollen Content | Retained | Removed |
| Enzymes | Preserved | Often degraded |
| Appearance | Cloudy, may crystallize | Clear, liquid for longer |
Ready to Scale Your Honey Production?
Whether you're a commercial apiary aiming for large-scale extraction or a distributor looking for reliable equipment, HONESTBEE has the professional-grade solutions you need. We supply durable, high-capacity honey extractors, uncapping tools, and filtration systems designed for efficiency and product quality.
Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your operation's needs and discover how our equipment can help you process honey more effectively.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE 3-Frame Manual Acrylic Honey Extractor
- 6 Frame Manual Stainless Steel Honey Extractor Beekeeping Equipment
- electric honey extractor honey centrifuge 3 frame honey extractor stainless steel honey frame extractor
- Stainless Steel 3 Frame Manual Honey Extractor Spinner for Bee Honey Extraction
- HONESTBEE 8 Frame Electric and Manual Three Use Honey Extractor
People Also Ask
- Which type of honey extractor is generally more durable? Focus on Material & Build Quality for Longevity
- What should be considered when harvesting honey from multiple hives? Scale Your Harvest Efficiently
- How often do beekeepers collect honey? Maximize Your Hive's Sustainable Yield
- What machines are needed in beekeeping besides basic tools? Scale Your Honey Harvest Efficiently
- What equipment is used for honey harvest? Essential Tools for Every Beekeeper



















