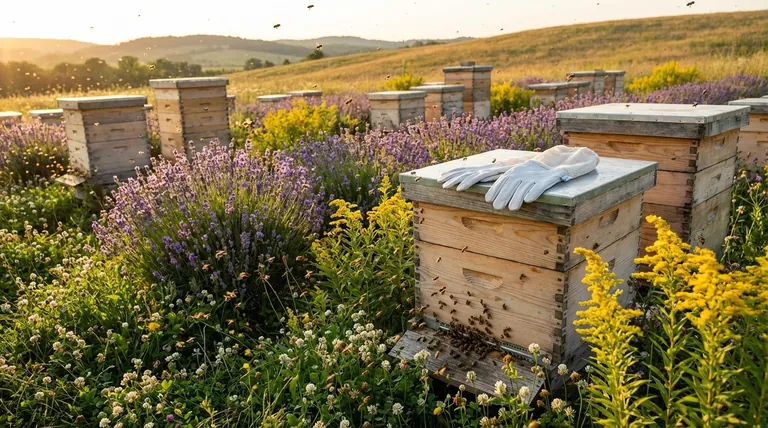
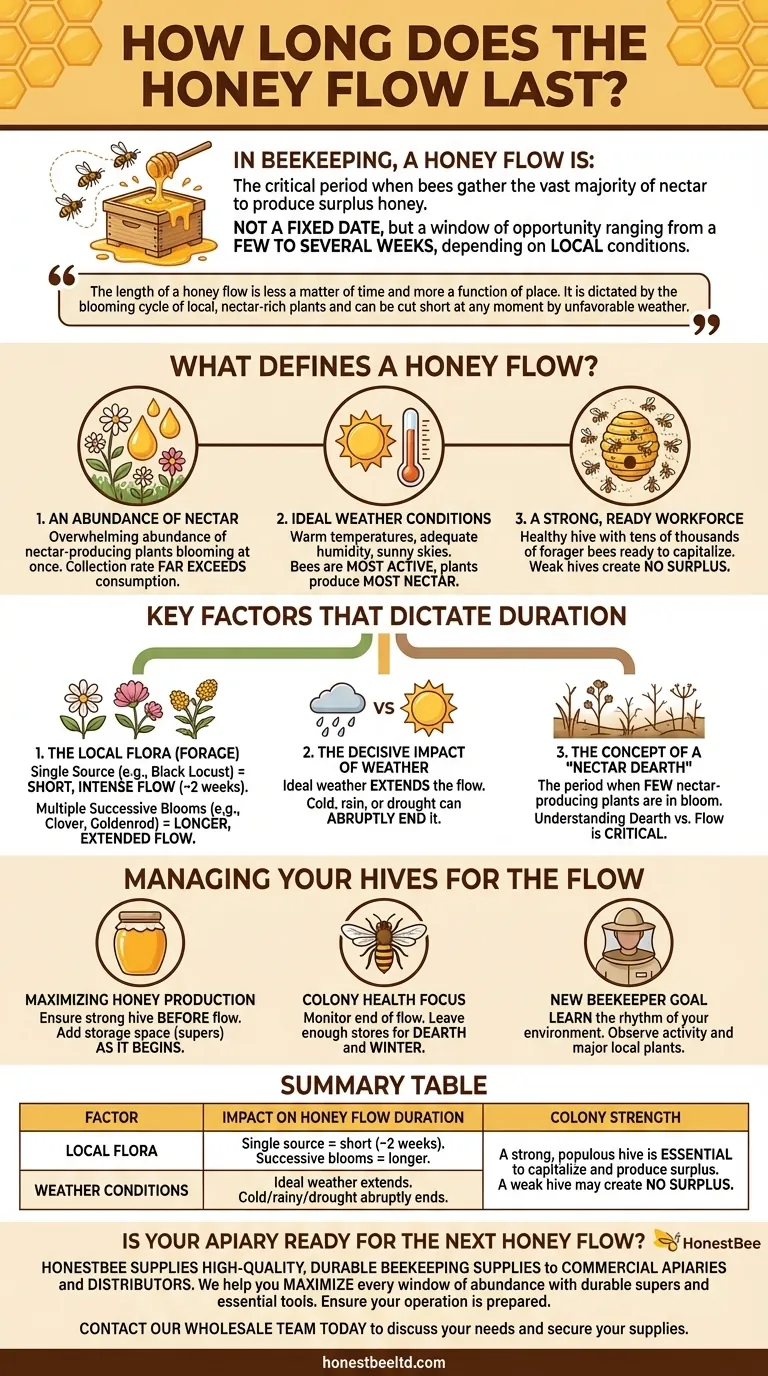
In beekeeping, a honey flow is the critical period when bees gather the vast majority of nectar to produce surplus honey. This period is not a fixed date on the calendar; its duration typically ranges from a few to several weeks, depending entirely on local environmental conditions.
The length of a honey flow is less a matter of time and more a function of place. It is dictated by the blooming cycle of local, nectar-rich plants and can be cut short at any moment by unfavorable weather.

What Defines a Honey Flow?
A honey flow is more than just the presence of flowers. It's a specific window of opportunity where a powerful confluence of factors allows a honey bee colony to thrive and create a surplus.
An Abundance of Nectar
The defining characteristic of a honey flow is an overwhelming abundance of nectar-producing plants all blooming at once. A few scattered flowers will feed the bees, but they won't create the surplus honey beekeepers can harvest.
This period is when the bees' collection rate far exceeds their daily consumption needs.
Ideal Weather Conditions
Weather is the second critical component. Nectar production and bee activity are highly sensitive to the environment.
Optimal conditions include warm temperatures, adequate humidity, and sunny skies. Bees are most active and plants produce the most nectar in this type of weather.
A Strong, Ready Workforce
Finally, a honey flow requires a strong, populous colony ready to take advantage of the opportunity. A weak or small hive may use all the incoming nectar just to feed its brood and expand, creating no storable surplus.
A healthy hive with tens of thousands of forager bees is necessary to capitalize on a strong flow.
Key Factors That Dictate Duration
The "few to several weeks" window is an average. The actual length you will experience is determined by three main variables that are unique to your specific location.
The Local Flora (Forage)
This is the single most important factor. The type of plants in your area dictates the timing and length of your flows.
A region dominated by a single source, like black locust trees, may have a very intense but short flow of only two weeks. An area with a succession of blooming plants, like clover followed by goldenrod, could experience multiple, longer flows throughout the season.
The Decisive Impact of Weather
Weather can extend or, more commonly, abruptly end a honey flow. A week of cold, rainy weather can halt bee flight and wash nectar from the blossoms, effectively pausing or ending the flow.
Conversely, an extended period of ideal weather can prolong a flow and lead to a massive honey harvest. A sudden drought can also cause plants to stop producing nectar, ending a flow prematurely.
The Concept of a "Nectar Dearth"
Just as important as the flow is its opposite: the nectar dearth. This is a period when very few nectar-producing plants are in bloom.
Understanding when the flow ends and a dearth begins is critical for beekeepers. During a dearth, hives can quickly consume their stores, and robbing between hives can become a serious problem.
Managing Your Hives for the Flow
Your role as a beekeeper is to anticipate and react to these natural cycles. Properly managing your hives before, during, and after the flow is the key to both a healthy colony and a successful harvest.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: You must ensure your hive is strong before the main flow and add storage space (supers) just as it begins to prevent swarming and give them room to work.
- If your primary focus is colony health: You must monitor the end of the flow closely, ensuring the bees have enough honey stores left for themselves to survive the coming dearth and winter.
- If you are a new beekeeper: Your goal should be to learn the rhythm of your local environment by observing your bees' activity and identifying which major local plants provide the main nectar flows.
Ultimately, successful beekeeping is about understanding these natural windows of abundance and ensuring your bees are prepared to seize the opportunity.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Honey Flow Duration |
|---|---|
| Local Flora | A single source (e.g., black locust) = short, intense flow (~2 weeks). Multiple, successive blooms = longer, extended flow. |
| Weather Conditions | Ideal weather (warm, sunny) extends the flow. Cold, rainy weather or drought can abruptly end it. |
| Colony Strength | A strong, populous hive is essential to capitalize on the flow and produce a surplus. A weak hive may create no surplus. |
Is your apiary ready for the next honey flow?
A successful harvest depends on having the right equipment at the right time. HONESTBEE supplies high-quality, durable beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations.
We help you maximize every window of abundance. From durable supers for expanding hive storage to essential tools for hive management, our products are designed to support your productivity and your bees' health.
Ensure your operation is prepared. Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your needs and secure your supplies.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Ventilated Goatskin Beekeeping Gloves with Full 3-Layer Mesh Sleeve
- Double Wall Honey Heating Stirring Homogenizer Mixing Machine with Various Capacity
- HONESTBEE Multi Exit Plastic Bee Escape Board for Efficient Honey Harvesting
- Inverted Squeezable Honey Jar with No Drip Flip Top Cap for Easy Pouring
- No Grafting Queen Rearing Kit: System for Royal Jelly Production and Queen Rearing
People Also Ask
- How does the utilization efficiency of beehives and beekeeping consumables impact cost? Maximize Your Apiary ROI
- How are commercial beekeeping apiaries typically organized? Optimize Your Layout for Maximum Efficiency
- What is the primary function of sampling cloths in beehive mortality monitoring? Quantify Hive Health Effectively
- Why is precision weighing equipment necessary for accurate honey yields? Maximize Commercial Apiary Data Precision
- How does the quantity of beehives impact the annual honey yield for a commercial apiary? Maximize Your Production Scale
- What are the primary advantages of vertical beehive designs in cooler or cold climates? Maximize Winter Survival
- What does wax lids covering two-thirds of the honeycomb indicate? Learn the Sign of Honey Maturity & Stability
- What are the advantages of mechanized beekeeping? Transform Your Commercial Apiary for Scalability and Profit


















