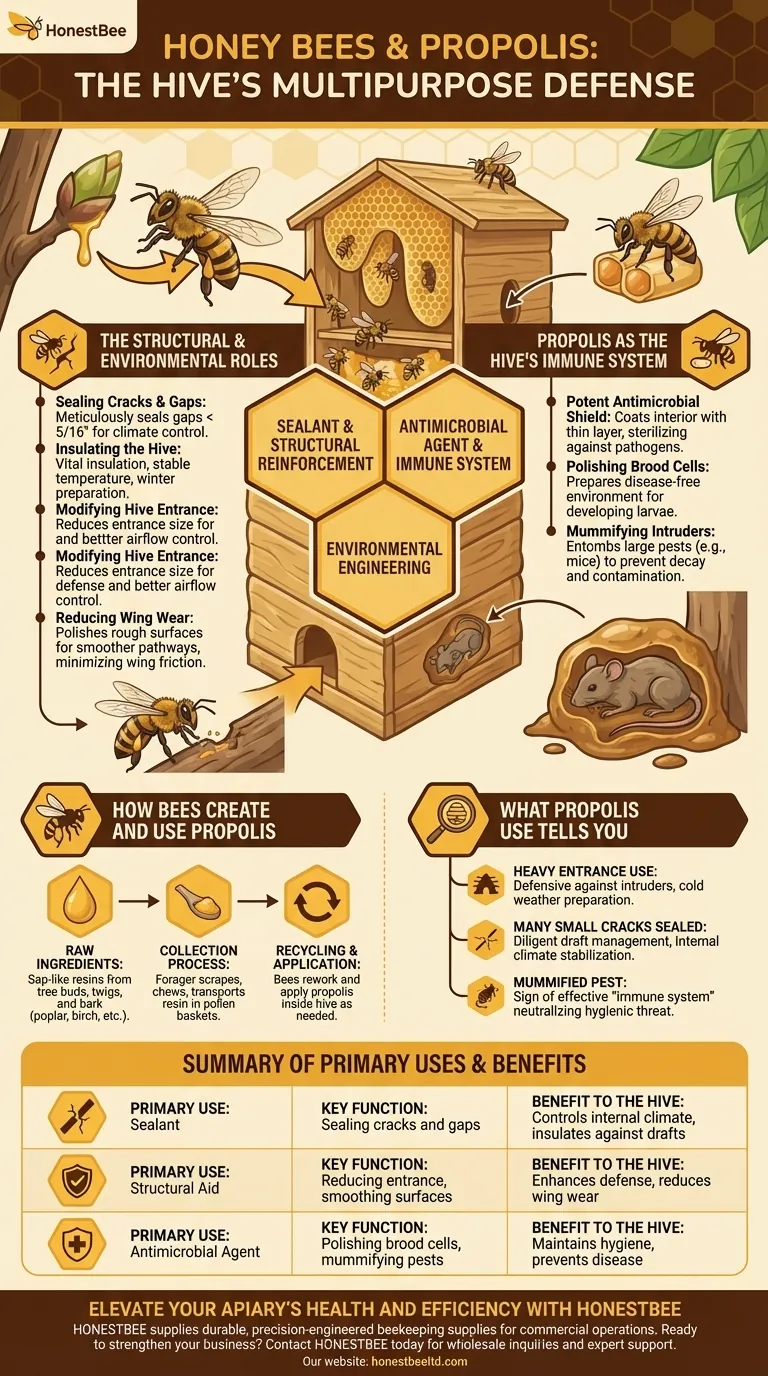
At its core, honey bees use propolis as a multipurpose sealant, structural reinforcement, and antimicrobial agent. This resinous substance is used to seal small cracks, reduce the hive entrance for defense and climate control, polish brood cells for sanitation, and even mummify intruders too large to remove, preventing decay within the hive.
Propolis is far more than just "bee glue"; it is the hive's external immune system and its primary tool for environmental engineering. It allows a colony to control its internal climate, maintain hygiene, and defend against both pathogens and physical threats.

How Bees Create and Use Propolis
The Raw Ingredients
Honey bees create propolis by collecting sap-like resins from the leaf buds, twigs, and bark of various trees. Common sources include deciduous trees such as poplar, birch, cottonwood, and alder.
The Collection Process
A forager bee scrapes these sticky resins from a plant with its mandibles. It then chews and manipulates the resin, transferring it to the pollen baskets on its hind legs for transport back to the hive.
Recycling and Application
Inside the hive, bees can also recycle propolis. They will scrape it from one location, rework it, and apply it wherever it is needed, ensuring this valuable resource is never wasted.
The Structural and Environmental Roles of Propolis
Sealing Cracks and Gaps
Bees meticulously seal any unwanted cracks or gaps smaller than standard "bee space" (about 5/16th of an inch). This activity is crucial for managing the hive's internal environment.
Insulating the Hive
By sealing drafts, propolis serves as a vital insulation material. This helps the colony maintain a stable temperature, which is especially critical in preparing for and surviving winter.
Modifying the Hive Entrance
A colony will often use propolis to reduce the size of its entrance. A smaller opening is easier to defend from predators and robber bees and provides better control over airflow and temperature.
Reducing Wing Wear and Tear
Bees also use propolis to polish and smooth rough surfaces inside the hive. This creates smoother pathways that reduce friction and minimize the wear and tear on their delicate wings over time.
Propolis as the Hive's Immune System
A Potent Antimicrobial Shield
Propolis has powerful antimicrobial properties. Bees coat the interior of the hive with a thin layer of it, effectively sterilizing their home and creating a defensive barrier against bacteria, fungi, and other pathogens.
Polishing Brood Cells
Before the queen lays an egg, worker bees polish the inside of each brood cell with propolis. This ensures the developing larvae are raised in a clean, disease-free environment.
Mummifying Intruders
If a pest like a mouse or large beetle enters the hive and is killed, it is often too large for the bees to remove. To prevent putrefaction and contamination, they entomb the carcass in propolis, safely mummifying it.
What Triggers Propolis Collection
Gaps, Drafts, and Light
Bees are stimulated to collect propolis by physical factors in their environment. Unwanted drafts, cracks, and light leaks are primary triggers for sealing activity.
Rough Hive Surfaces
The presence of rough surfaces inside the hive will also encourage propolis use, as the bees work to create smoother, more efficient pathways.
The Presence of Disease
Finally, a disease infection within the colony can trigger increased propolis collection. This is a direct immunological response, as the bees attempt to leverage its antimicrobial properties to fight off the threat.
What Propolis Use Tells You About a Hive
Observing how your bees use propolis can provide valuable insights into the colony's health, defensiveness, and priorities.
- If you see heavy propolis use at the entrance: The colony may be feeling defensive against intruders or actively preparing for cold weather.
- If you find many small cracks being sealed: Your bees are diligently managing drafts and working to stabilize their internal climate.
- If you notice a mummified pest: This is a clear sign the hive's "immune system" is working effectively to neutralize a major hygienic threat.
Understanding the diverse applications of propolis reveals it as a cornerstone of the honey bee colony's remarkable ability to engineer, defend, and sanitize its home.
Summary Table:
| Primary Use | Key Function | Benefit to the Hive |
|---|---|---|
| Sealant | Sealing cracks and gaps | Controls internal climate and insulates against drafts |
| Structural Aid | Reducing hive entrance, smoothing surfaces | Enhances defense and reduces wing wear |
| Antimicrobial Agent | Polishing brood cells, mummifying pests | Maintains hygiene and prevents disease |
Elevate Your Apiary's Health and Efficiency with HONESTBEE
Understanding the critical role of propolis is key to successful beekeeping. Just as bees rely on this versatile substance, commercial apiaries and distributors rely on high-quality equipment for optimal hive health and honey production.
HONESTBEE supplies the durable, precision-engineered beekeeping supplies and equipment that your operation needs to thrive. Our wholesale-focused operations are designed to support the scale and demands of commercial beekeepers and equipment distributors.
Ready to strengthen your business? Let's discuss how our products can support your success. Contact HONESTBEE today for wholesale inquiries and expert support.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Long-Handled Silicone Honey Scraper for Beekeeping
- Stainless Steel Honey Press Wax Press with Tank
- Electric Flatting and Embossing Machine with Tray for Beekeeping
- Retractable Chinese Queen Rearing Grafting Tools Equipment
- Stainless Steel Manual Honey Press with Guard for Pressing Honey and Wax
People Also Ask
- How does the monitoring of propolis elasticity and moisture content contribute to honey harvest management? Master Quality
- What are the properties of plant resins used by honey bees? A Beekeeper's Guide to Propolis
- Why is multi-stage filtration necessary for propolis extracts? Ensure Purity for Precision Analytical Success
- Why use 70% industrial ethanol for propolis extraction? Maximize your yield and purity with the industry standard.
- What is the function of plastic grids in propolis collection? Boost Purity with Precision Meshes
- What is the technical role of industrial-grade propolis extraction equipment? Master High-Purity Product Conversion
- What role does propolis play in the hive? The Dual-Purpose Secret to Beehive Health
- When is the best time of year to harvest propolis? Timing Your Harvest for Maximum Yield and Colony Health



















