The primary benefit of a pollen trap is its ability to harvest high-protein pollen from returning bees, which can be stored and used as supplemental feed. However, the main drawback is that the trap's design can sometimes attract pests like hive beetles and potentially stress the colony by restricting its entrance.
Pollen traps are a specialized tool for harvesting a valuable resource. Their use represents a trade-off between securing a protein source for strategic colony management and the potential risks of increased pest pressure and hive disruption.
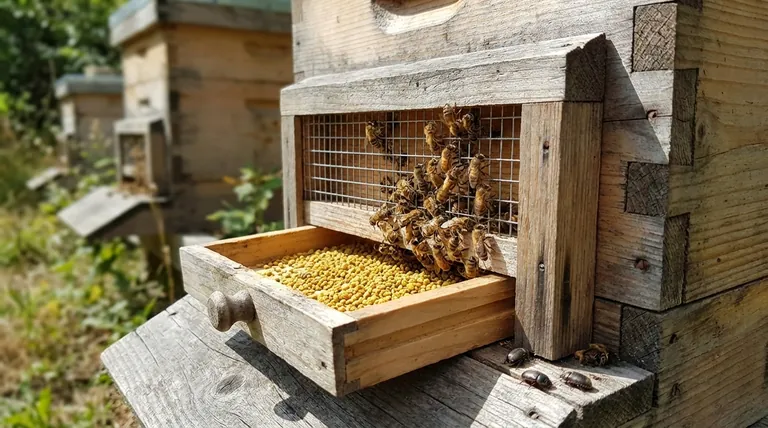

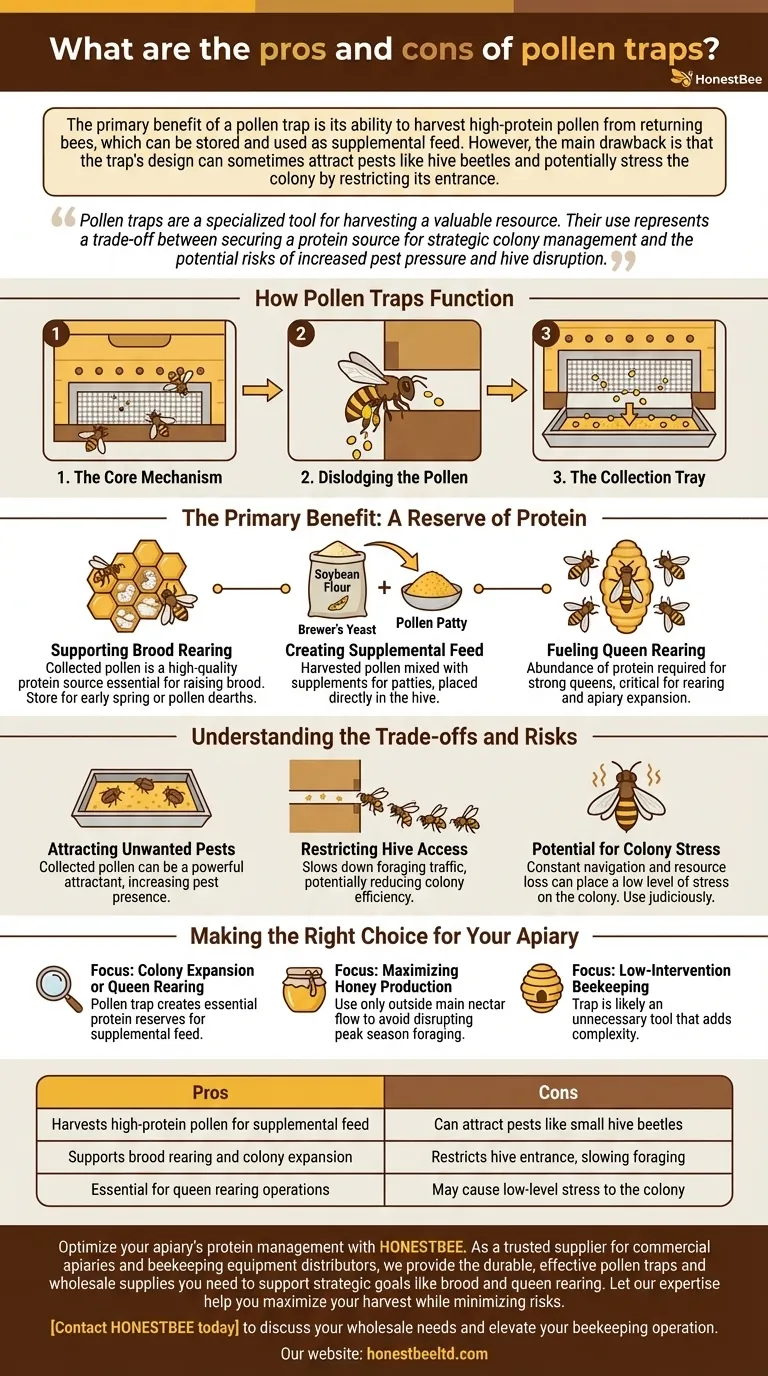
How Pollen Traps Function
The Core Mechanism
A pollen trap works by partially restricting the hive entrance. It forces returning forager bees to pass through small holes in a wire mesh or a punched plate.
Dislodging the Pollen
As a bee squeezes through these narrow openings, the edges scrape against its hind legs. This action dislodges some of the compacted pollen pellets from its pollen baskets.
The Collection Tray
These dislodged pellets fall through the mesh and land in a collection tray below, which the beekeeper can remove to harvest the pollen. The trap is designed so that enough pollen still makes it into the hive to meet the colony's immediate needs.
The Primary Benefit: A Reserve of Protein
Supporting Brood Rearing
Collected pollen is a high-quality protein source essential for raising brood. Beekeepers can store it to feed colonies during early spring or periods of pollen dearth, ensuring strong population growth.
Creating Supplemental Feed
This harvested pollen is often mixed with supplements like soybean flour or brewer's yeast. This mixture is then formed into "pollen patties" that can be placed directly in the hive for the bees to consume.
Fueling Queen Rearing
Raising strong, well-fed queens requires an abundance of protein. Having a pollen reserve on hand is critical for beekeepers focused on rearing their own queens or expanding their apiary.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Attracting Unwanted Pests
The collected pollen in the tray can be a powerful attractant for pests. Small hive beetles, in particular, may be drawn to the trap, increasing their presence around the hive.
Restricting Hive Access
The trap, by its very nature, creates a bottleneck at the hive entrance. This can slow down the traffic of foraging bees, potentially reducing the colony's overall efficiency.
Potential for Colony Stress
Constantly navigating the trap and losing a portion of their collected resources can place a low level of stress on the colony. It should be used judiciously and not for prolonged, uninterrupted periods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
Using a pollen trap depends entirely on your beekeeping goals.
- If your primary focus is supporting colony expansion or queen rearing: A pollen trap provides the essential protein reserves to create supplemental feed for these intensive activities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing honey production: You may choose to use a trap only outside of the main nectar flow to avoid disrupting foraging traffic during peak season.
- If your primary focus is low-intervention beekeeping: A pollen trap is likely an unnecessary tool that adds complexity and interferes with the colony's natural foraging cycle.
Ultimately, a pollen trap is a strategic tool that, when used correctly, can significantly aid in specific management goals.
Summary Table:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Harvests high-protein pollen for supplemental feed | Can attract pests like small hive beetles |
| Supports brood rearing and colony expansion | Restricts hive entrance, slowing foraging |
| Essential for queen rearing operations | May cause low-level stress to the colony |
Optimize your apiary's protein management with HONESTBEE.
As a trusted supplier for commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, we provide the durable, effective pollen traps and wholesale supplies you need to support strategic goals like brood and queen rearing. Let our expertise help you maximize your harvest while minimizing risks.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and elevate your beekeeping operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Dual-End Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Multi-Functional Hive Tool with Ergonomic Wood Handle
- Multi-Function Plier-Style Frame Grip Hive Tool
- Professional Stainless Steel Pry-Bar Hive Tool
- HONESTBEE Professional Mini J-Hook Hive Tool for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of collecting pollen from beehives? Master Hive Nutrition & Growth
- What is the purpose of using a pollen trap when studying bee venom production? Unlock Yield Secrets Through Research
- How do plastic sheets function when used to cover pollen patties? Ensure Maximum Nutrient Intake for Your Honeybees
- What is a basic method for cleaning harvested bee pollen? Manual and Commercial Techniques for High-Purity Results
- What is the specific function of mounted pollen traps in the non-destructive collection of pollen loads? | HONESTBEE
- How do professional pollen traps facilitate the monitoring of bee foraging behavior and protein source analysis?
- Why is it necessary to precisely control the opening duration of a pollen trap? Balance Hive Health and Data Accuracy
- What are the advantages of using a temperature-controlled drying oven for bee pollen? Maximize Purity and Nutrients



















