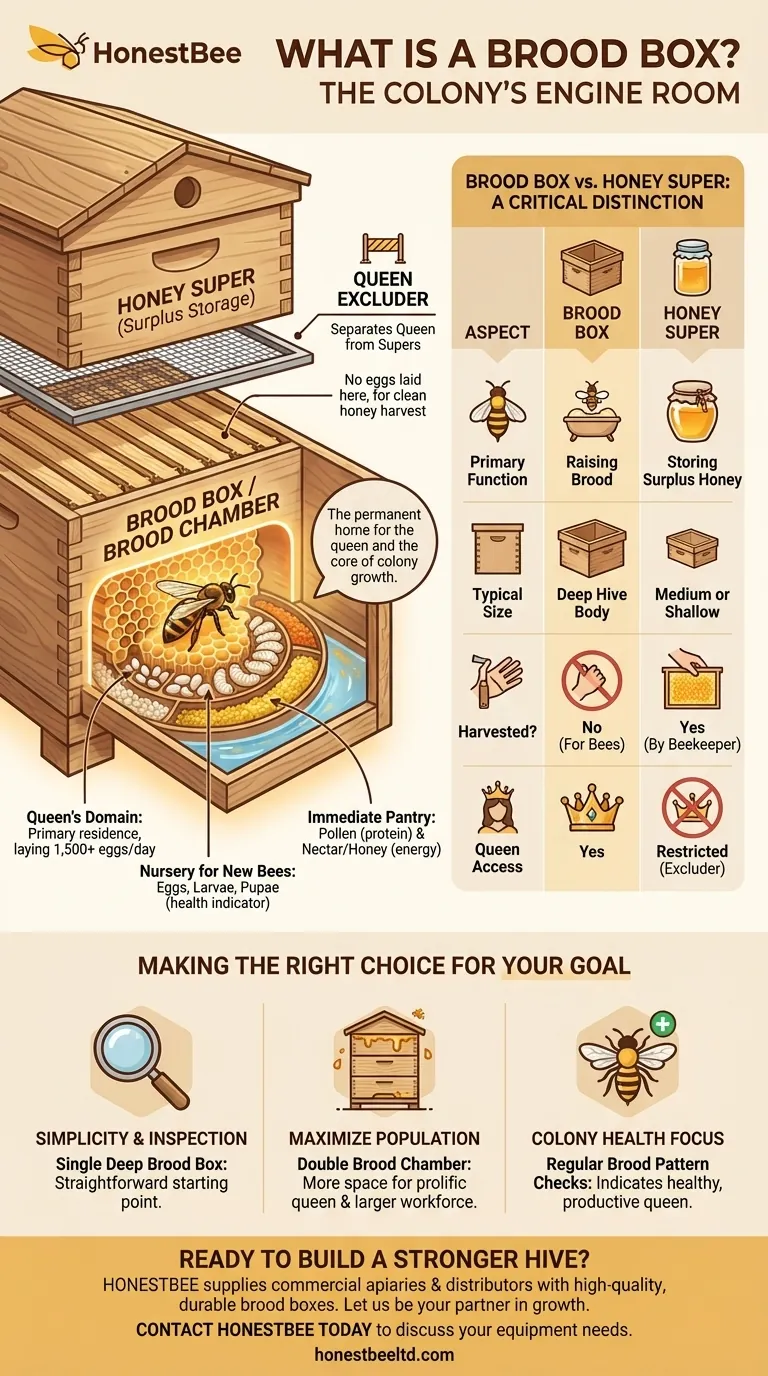
In beekeeping, a brood box (also called a brood chamber or hive body) is the central nursery and living quarters of the hive. This is the dedicated space where the queen bee lays her eggs and where the colony raises its brood—the next generation of bees. It serves as the permanent home for the queen and the core of the colony's population growth.
The brood box isn't just a piece of wooden equipment; it's the engine room of the colony. Understanding its function is the first step to understanding the health, growth, and survival of your bees.

The Core Function of the Brood Chamber
A hive is a system, and the brood chamber is its heart. Its purpose is to provide a protected, organized space for the most critical activities in the colony's life cycle.
The Queen's Domain
The brood box is the primary residence of the queen bee. Her biological imperative is to lay eggs, and this chamber provides the cellular infrastructure (the wax comb) for her to do so efficiently.
A healthy queen can lay over 1,500 eggs per day, and she moves systematically across the frames in the brood box to deposit them.
The Nursery for New Bees
This box is where you find the "brood" in all its stages of development. This includes eggs, tiny white specks at the bottom of a cell; larvae, the white, grub-like stage that follows; and pupae, the final stage where the larva is capped in its cell to transform into an adult bee.
The health and pattern of the brood are the most important indicators of a colony's overall well-being.
The Colony's Immediate Pantry
While honey is stored for the long term in upper boxes, the brood chamber contains the colony's immediate food supply. You will find rings of pollen (protein for feeding larvae) and nectar or honey (carbohydrates for energy) stored in cells directly surrounding the developing brood.
This ensures the nurse bees have immediate access to the resources needed to feed the thousands of developing young.
Brood Box vs. Honey Super: A Critical Distinction
To a new beekeeper, all the boxes of a hive can look the same. However, their function is fundamentally different, and the bees treat them as distinct zones.
Purpose Defines the Box
The name of the box describes its function. A brood box is used for raising bees. A honey super is any box placed above the brood chamber for the primary purpose of storing surplus honey.
Beekeepers harvest honey from the supers, not the brood box. The honey in the brood chamber is left for the bees to consume.
Common Physical Differences
Brood boxes are most often "deep" hive bodies. This larger size provides ample, uninterrupted space for the queen to establish a large and cohesive brood pattern.
Honey supers are often "medium" or "shallow" hive bodies. They are smaller and lighter, making them much easier for the beekeeper to lift when they are full of dense, heavy honey.
The Role of the Queen Excluder
To maintain this separation, many beekeepers place a queen excluder between the top brood box and the first honey super. This is a screen with gaps large enough for worker bees to pass through but too small for the larger queen.
This practice ensures that no eggs are laid in the honey supers, keeping them exclusively for clean honey storage and eventual harvest.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your management of the brood chamber directly impacts colony strength and potential honey yield. Your configuration will depend on your goals and local climate.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and ease of inspection: A single deep brood box configuration is the most straightforward starting point, as all brood is contained in one box.
- If your primary focus is maximizing colony population: A double brood chamber setup (e.g., two deeps) provides more space for a prolific queen, enabling a larger workforce for foraging.
- If your primary focus is colony health: Regularly check the brood pattern for a solid, contiguous patch of eggs and larvae, which indicates a healthy, productive queen.
Master the brood box, and you master the art of supporting a thriving, productive beehive.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Brood Box | Honey Super |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Raising brood (eggs, larvae, pupae) | Storing surplus honey |
| Typical Size | Deep hive body | Medium or shallow hive body |
| Harvested? | No, honey is for the bees | Yes, honey is harvested by the beekeeper |
| Queen Access | Yes, the queen's primary residence | Typically restricted by a queen excluder |
Ready to build a stronger, more productive hive?
Your brood chamber is the foundation of your colony's success. At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, durable brood boxes and hive components needed to support healthy, thriving bees.
Let us be your partner in growth. We offer wholesale-focused operations to meet the demands of your business.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your equipment needs and elevate your beekeeping operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Langstroth Honey Bee Box Hive Boxes for Different Depths
- Australian Langstroth Beehive Boxes for Beekeeping Wholesales
- In-Hive Dual Compartment Frame Bee Feeder for Targeted Colony Nutrition
- Portable Bee Mating Hive Boxes Mini Mating Nucs 8 Frames for Queen Rearing
- HONESTBEE Entrance Bee Feeder Professional Hive Nutrition Solution for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How does a hive box work? A Guide to the Langstroth Hive System for Beekeepers
- How deep is a medium bee box? Unlock the Key to a Versatile and Manageable Hive
- What are the sizes available for Langstroth boxes? A Guide to 8-Frame vs. 10-Frame & Depths
- How should hive boxes be aligned after reassembly? Ensure a Perfect Seal for Hive Health
- How is checking honey supers in a Langstroth hive different from inspecting Honey Flow supers? A Guide to Disruptive vs. Non-Invasive Methods



















