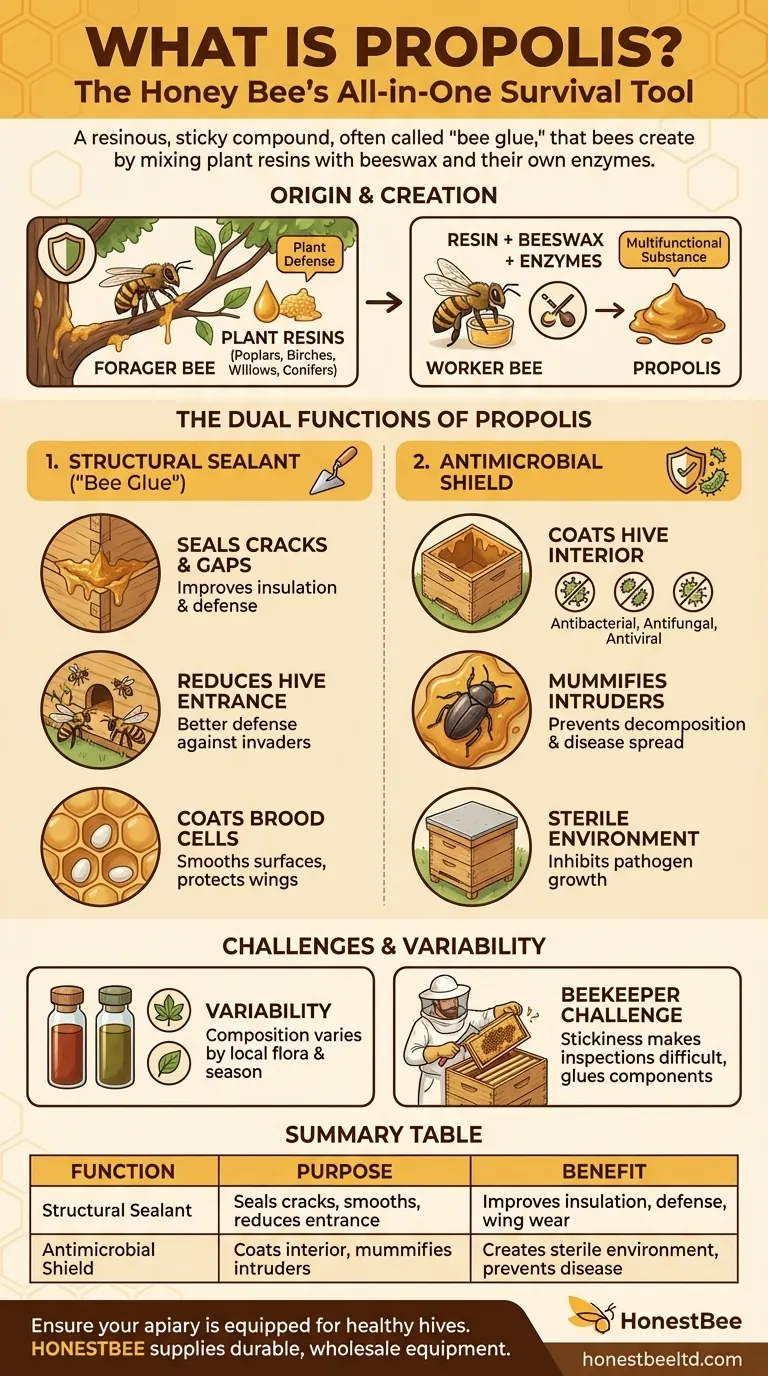
Propolis is the honey bee's all-in-one survival tool. It is a resinous, sticky compound, often called "bee glue," that bees create by mixing plant resins with beeswax and their own enzymes. Honey bees use this remarkable substance for two primary purposes: as a structural sealant to build and repair their hive, and as a powerful antimicrobial agent to keep the colony sterile and disease-free.
More than just a simple glue, propolis functions as the hive's combined immune system and construction material. It demonstrates the bee's sophisticated ability to harness natural chemistry to build, defend, and sanitize its home.
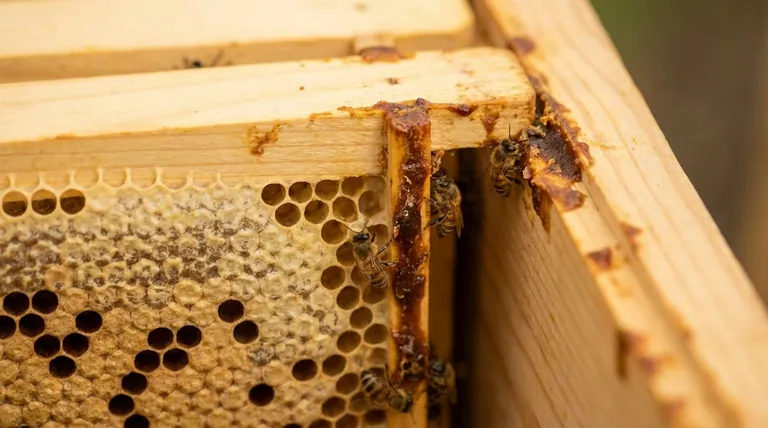

The Origin and Creation of Propolis
Propolis does not originate with the bee itself but is sourced from the surrounding environment. The process is a clear example of how bees adapt local resources for their specific needs.
From Plant Defense to Hive Resource
Forager bees collect sticky resins from the leaf buds, bark, and wounds of various trees and plants. Sources often include poplars, birches, willows, and conifers.
These plant resins are a natural defense mechanism, protecting the tree from fungal infections and insect attacks. Bees effectively borrow this protective chemistry for their own colony.
The Bee's Unique Formulation
After a forager bee gathers the resin on its hind legs, it is brought back to the hive. There, worker bees process it, blending the raw resin with beeswax and their own salivary secretions.
This combination transforms the plant resin into the final product—propolis—a multifunctional substance uniquely suited to the hive's needs.
The Dual Functions of Propolis in the Hive
Propolis serves two distinct yet equally critical roles that ensure the colony's survival. It is simultaneously a construction material and a disinfectant.
Function 1: The Structural Sealant ("Bee Glue")
Bees use propolis to seal small cracks and unwanted gaps in the hive, protecting it from the elements and potential invaders. This improves insulation and helps maintain a stable internal temperature.
They also use it to reduce the size of the hive entrance for better defense, coat the interior surfaces of brood cells before the queen lays eggs, and smooth rough surfaces to reduce wear on their delicate wings.
Function 2: The Antimicrobial Shield
The plant resins used to make propolis retain their potent antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties. This turns the substance into a powerful disinfectant.
By coating the interior of the hive, bees create a sterile environment that inhibits the growth of pathogens and protects the colony from disease.
The Undertaker's Tool: Embalming Intruders
If an intruder, such as a mouse or a large beetle, is killed inside the hive and is too large for the bees to remove, they use propolis to solve the problem.
The bees will completely encase the carcass in propolis. This "mummification" process prevents the body from decomposing and spreading disease throughout the hive.
Understanding the Challenges and Variability
While essential for the hive, propolis is not a uniform substance, and its stickiness presents challenges.
Not All Propolis is Created Equal
The exact chemical composition, color, and properties of propolis vary significantly based on the local flora available to the bees. Propolis from a coniferous forest will have a different makeup than propolis from a region rich in poplar trees.
This means its effectiveness as an antimicrobial agent and its physical characteristics can change depending on geography and season.
A Double-Edged Sword for Beekeepers
For bees, the stickiness of propolis is a feature, not a bug. It securely glues hive components together, providing structural integrity.
For beekeepers, however, this same stickiness can make hive inspections difficult. Propolis can seal frames to the hive body and glue boxes together, requiring a hive tool to pry them apart.
How to Appreciate Propolis in Context
Understanding the role of propolis shifts our perspective on the honey bee colony from a simple group of insects to a highly organized superorganism.
- If your primary focus is on bee biology: View propolis as a key evolutionary adaptation for colony health, allowing tens of thousands of individuals to live in close quarters without being overrun by disease.
- If your primary focus is on natural products: Recognize propolis as a potent bioactive compound whose properties are derived directly from the chemical defenses of the plant world.
- If your primary focus is practical beekeeping: Treat the presence of propolis as a vital sign of a healthy, productive hive, even when its stickiness makes your work more challenging.
Ultimately, propolis reveals the honey bee's remarkable ingenuity in creating a single substance to build, defend, and sanitize its entire world.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Benefit to the Colony |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Sealant | Seals cracks, smooths surfaces, reduces hive entrance. | Improves insulation, defense, and reduces wing wear. |
| Antimicrobial Shield | Coats hive interior and mummifies intruders. | Creates a sterile environment, preventing disease spread. |
Ensure your apiary or distribution business is equipped for healthy, productive hives. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, wholesale-focused supplies needed to manage hives effectively—including handling propolis-rich colonies. Contact our experts today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our equipment supports superior colony health.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Frame Preparation: The HONESTBEE Electric Wire Embedder
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Heavy-Duty Galvanized Steel W-Style Pallet Clip
- Versatile Ratchet Hive Strap with S-Hooks for Secure Fastening
- Endless Loop Ratchet Hive Strap
People Also Ask
- Why is multi-stage filtration necessary for propolis extracts? Ensure Purity for Precision Analytical Success
- How does high-precision filter paper affect propolis extract? Master Purity and Nutrient Uniformity
- What role do specialized propolis collection mats play? Unlock High-Purity Resin for Medical-Grade Apiculture
- What is the function of 80% concentration ethanol in propolis extraction? Maximize Bioactive Yield and Purity
- Is it possible to collect propolis without using a propolis trap? Easy Manual Harvesting Methods for Beekeepers
- Why is the use of standard grading sieves essential during the preparation of raw propolis? Boost Extraction Quality
- Why is it necessary to cool stingless bee propolis samples to -18 °C before crushing? Master Propolis Processing
- How do specialized consumables for collecting royal jelly and propolis help diversify apiary income? Boost Your Profits



















