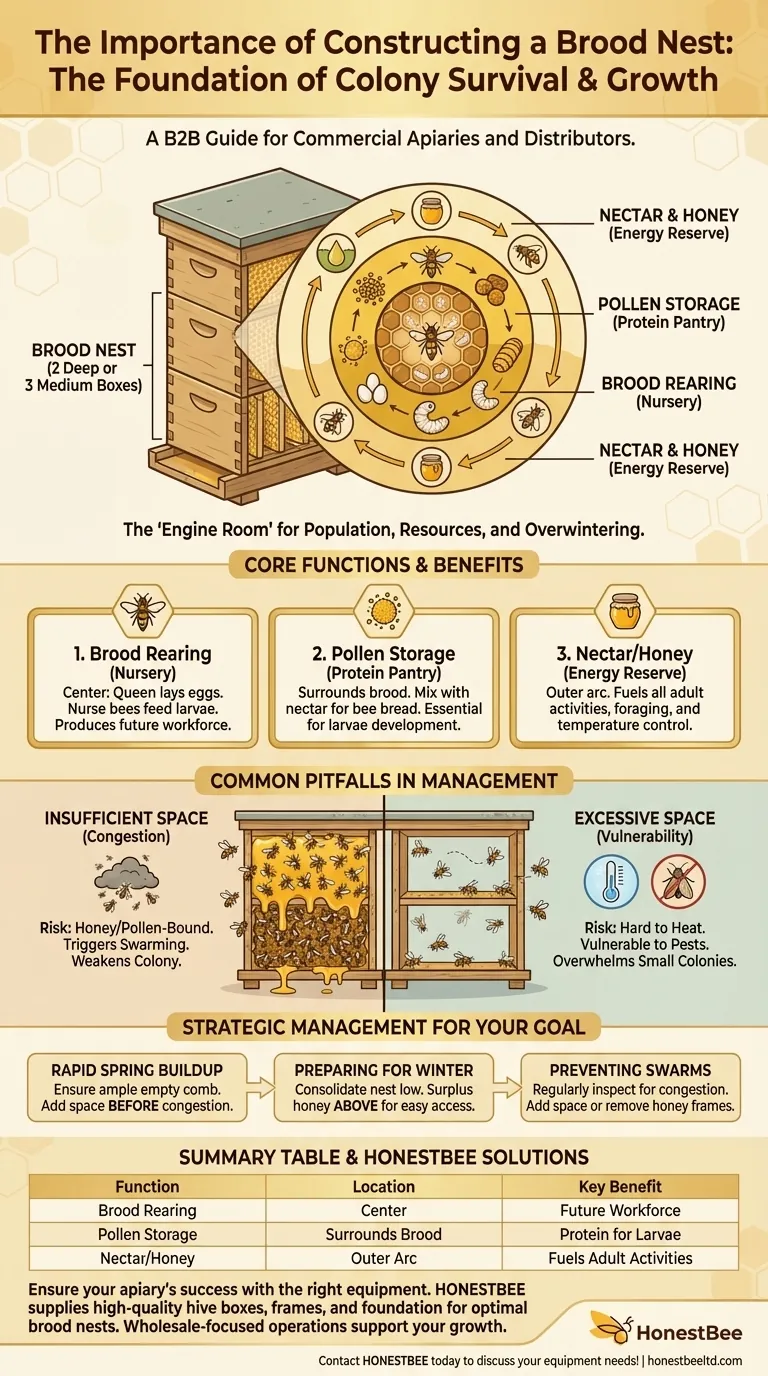
The brood nest is the absolute foundation of a bee colony's survival and growth. It is the dedicated area within the hive, typically composed of wax combs in two deep or three medium hive boxes, where the queen lays her eggs and the colony raises the next generation of bees. This area also serves as the immediate pantry for storing the pollen and nectar essential for feeding the young.
The brood nest is not simply a physical space; it is the highly organized nursery and engine room of the hive. Its proper construction and management directly determine the colony's ability to expand its population, gather resources, and survive the winter.

The Core Functions of the Brood Nest
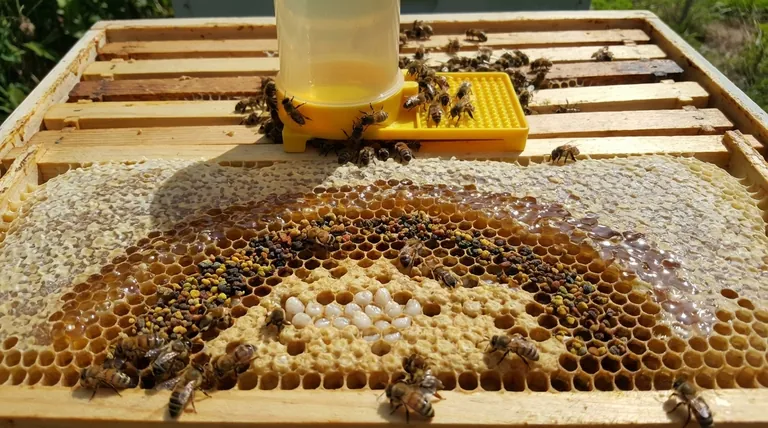
A healthy brood nest is a model of biological efficiency. The bees arrange their resources in a specific, concentric pattern to optimize the care of the developing brood.
Function 1: Brood Rearing (The Nursery)
At the very center of the nest, the queen lays her eggs in the wax cells. Worker bees, or "nurse bees," maintain this area at a constant temperature and humidity, feeding the larvae until they pupate and emerge as adult bees.
A strong, consistent pattern of eggs, larvae, and capped brood is the primary indicator of a healthy, productive queen and a thriving colony. This is the source of the future workforce.
Function 2: Pollen Storage (The Protein Pantry)
Immediately surrounding the central brood area, the bees pack cells with pollen. They mix this pollen with nectar to create "bee bread."
This protein-rich food is essential for the development of young bees. Placing it directly next to the brood ensures nurse bees can access it quickly and efficiently feed the thousands of growing larvae.
Function 3: Nectar and Honey (The Energy Reserve)
Forming an arc above and around the band of pollen, the bees store nectar and ripening honey. This carbohydrate-rich food is the primary energy source for the adult bees.
This stored energy fuels all colony activities, from foraging and wax production to defending the hive and maintaining the critical temperature of the brood nest itself.
Common Pitfalls in Brood Nest Management
A beekeeper's primary role is to ensure the brood nest has what it needs to function without constraint. Mismanaging this space can lead to significant problems.
The Risk of Insufficient Space
If the brood nest becomes congested with honey, pollen, or too many bees, the queen will run out of room to lay eggs. This is known as being "honey-bound" or "pollen-bound."
A lack of laying space is a primary trigger for swarming, where the old queen leaves with half the colony to find a new home. This dramatically weakens the original hive.
The Danger of Excessive Space
Giving a colony too much space, especially early in the spring, can also be detrimental. The bees may struggle to maintain the necessary temperature for the brood.
An overly large, undefended space also makes the colony more vulnerable to pests like wax moths and small hive beetles, which can quickly overwhelm a small or struggling colony.
How to Manage the Brood Nest for Your Goal
Your management strategy should adapt to the colony's needs throughout the season.
- If your primary focus is rapid spring buildup: Ensure the queen has ample empty comb to lay in, and consider adding a new box before the existing ones become completely full to prevent swarming.
- If your primary focus is preparing for winter: Ensure the colony has a consolidated brood nest in the lower boxes with a large surplus of honey stored directly above them for easy access during the cold months.
- If your primary focus is preventing swarms: Regularly inspect the brood nest for signs of congestion and be prepared to provide more space, either by adding another box or removing frames of honey to create room.
Ultimately, understanding the structure and function of the brood nest is central to effective and responsible beekeeping.
Summary Table:
| Function | Location in Nest | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Brood Rearing (Nursery) | Center | Produces the colony's future workforce. |
| Pollen Storage (Protein Pantry) | Surrounding brood | Provides essential protein for developing larvae. |
| Nectar/Honey (Energy Reserve) | Above and around pollen | Fuels all adult bee activities and temperature control. |
Ensure your apiary's success with the right equipment. A properly managed brood nest is the key to strong, productive colonies. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality hive boxes, frames, and foundation needed to build and maintain optimal brood nests. Let our wholesale-focused operations support your growth. Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your equipment needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Professional Entrance Bee Feeder Hive Nutrition Solution
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Classic Pry Bar Hive Tool with High Visibility Finish for Beekeeping
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Premium Wood Framed Metal Wire Queen Bee Excluder
People Also Ask
- How do you make an entrance feeder for bees? A Guide to Safe & Effective Hive Feeding
- What are the different types and applications of beehive feeders? Optimize Colony Nutrition with the Best Equipment
- How to make an entrance feeder for bees? A DIY Guide for Safe & Effective Feeding
- What are the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of entrance feeders? Essential Guide for Modern Apiaries
- What measures should be taken to prevent robbing when using an internal hive top feeder? Pro Bee Defense Tips



















