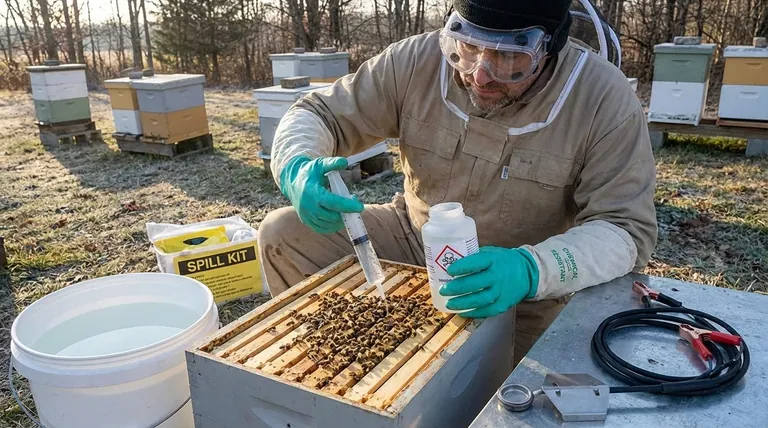
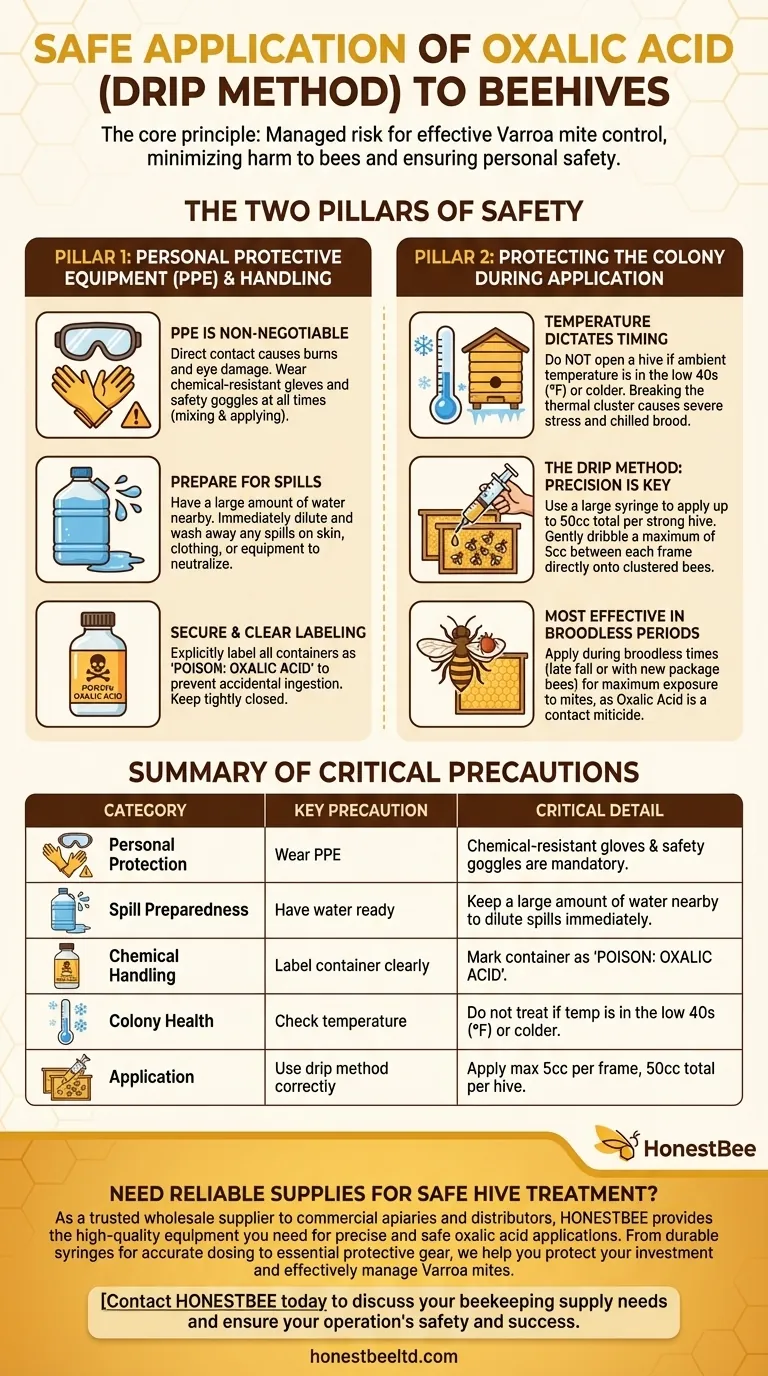
To safely apply an oxalic acid mixture to beehives, you must wear protective gear like gloves and goggles, avoid opening the hive in temperatures below the low 40s (°F), and keep a large amount of water nearby to dilute any spills immediately. The correct application involves using a syringe to dribble no more than 5cc of the solution over the bees between each frame, with a maximum total of 50cc per hive.
The core principle of using oxalic acid is managing a controlled risk. Your goal is to effectively kill Varroa mites with a substance that is toxic to them, while minimizing harm to your bees and ensuring your own personal safety through careful handling and precise application.

The Two Pillars of Oxalic Acid Safety
Safe handling procedures are divided into two critical areas: protecting yourself from the chemical and protecting the colony from harm during treatment.
H3: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Non-Negotiable
Oxalic acid is a corrosive organic compound. Direct contact can cause chemical burns to the skin and severe damage to the eyes.
Therefore, wearing chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles is the absolute minimum requirement. This protects you during both the mixing and application phases.
H3: Preparing for Spills and Accidents
Accidents can happen, and preparation is key. Always have a considerable amount of water on hand before you begin.
This water serves to quickly dilute and wash away any mixture that spills on your skin, clothing, or equipment, neutralizing its corrosive effect.
H3: Secure and Clear Labeling
When mixing your solution, it is crucial to label the container immediately and clearly.
The label must explicitly state 'POISON: OXALIC ACID'. This prevents catastrophic accidents where someone might mistake the sugar-based solution for something edible. Keep the container tightly closed until the moment of application.
Protecting the Colony During Application
Your application technique directly impacts the health of the hive. The goal is to be effective against mites while inflicting the least possible stress on the bees.
H3: Temperature Dictates Timing
Do not open a hive for treatment if the ambient temperature is in the low 40s (°F) or colder.
Opening the hive in cold weather breaks the colony's warm thermal cluster. This causes severe stress and can lead to a chilled brood, jeopardizing the hive's survival.
H3: The Drip Method: Precision is Key
The most common method described is the "drip" or "dribble" application. This requires careful measurement.
Draw up to 50cc of the oxalic acid solution into a large syringe. This is the maximum dose for one strong, fully populated hive.
Gently apply a maximum of 5cc of the solution in the space between each frame, directly onto the bees clustered there. Continue this process until you have treated all bee-covered frames or have used the full 50cc.
Understanding the Broader Context
While the drip method is common, it's important to understand its place among other treatments and its limitations.
H3: Different Methods, Different Rules
Oxalic acid can also be applied through vaporization (sublimation). This method turns the acid crystals into a gas that fills the hive.
The safety precautions and application rules for vaporization are different and require specialized equipment, including a respirator. The instructions here are specific to the sugar-solution drip method.
H3: Why This Works
Oxalic acid is a contact miticide. It is most effective when the mites are exposed on the bodies of adult bees.
This is why treatment is often performed during broodless periods, such as late fall or when installing a new package of bees. When there is no sealed brood, nearly all the mites in the hive are exposed and vulnerable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your primary objective will determine which precautions you emphasize most heavily, though all are important.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Prioritize wearing your PPE at all times and ensuring your mixture is clearly labeled as poison.
- If your primary focus is colony health: Pay strict attention to the weather and never exceed the recommended dosage of 5cc per frame or 50cc total per hive.
- If your primary focus is maximum mite control: Apply the treatment when the colony has little to no sealed brood, ensuring the acid contacts the highest possible number of mites.
Following these established protocols allows you to manage mite populations effectively and confidently.
Summary Table:
| Safety Category | Key Precaution | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Protection | Wear PPE | Chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles are mandatory. |
| Spill Preparedness | Have water ready | Keep a large amount of water nearby to dilute spills immediately. |
| Chemical Handling | Label container clearly | Mark container as 'POISON: OXALIC ACID' to prevent accidents. |
| Colony Health | Check temperature | Do not treat if temperature is in the low 40s (°F) or colder. |
| Application | Use drip method correctly | Apply a maximum of 5cc per frame, 50cc total per hive. |
Need Reliable Supplies for Safe Hive Treatment?
As a trusted wholesale supplier to commercial apiaries and distributors, HONESTBEE provides the high-quality equipment you need for precise and safe oxalic acid applications. From durable syringes for accurate dosing to essential protective gear, we help you protect your investment and effectively manage Varroa mites.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your beekeeping supply needs and ensure your operation's safety and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Heavy Duty 12V Oxalic Acid Evaporator Vaporizer for Bee Varroa Mite Treatment Beekeeping Fumigator Atomizer
- Durable 12V Oxalic Acid Vaporizer for Varroa Mite Treatment Beehive Beekeeping Tool
- Oxalic Acid Vaporizer 12V for Bee Varroa Mite Treatment
- 12V Bee Mite Removal Evaporator Oxalic Acid Vaporizer for Bee Fumigation Treatment 180W Atomization
- Professional Hive Front Entrance Bee Feeder
People Also Ask
- What safety precautions should beekeepers take when using oxalic acid? Essential PPE for Varroa Mite Control
- Why are stainless steel screen bottom boards required when performing Varroa mite treatments with Oxalic Acid? IPM Guide
- What is the role of oxalic acid in plants? A Key to Plant Defense and Internal Regulation
- What safety precautions should be taken when using oxalic acid for vaporization? Protect Yourself and Your Bees
- How do oxalic acid-based products contribute to honeybee colony health management? Essential Varroa Control Strategies



















